AI-Generated Misinformation Threatens Democratic Integrity Following Bondi Beach Terror Attack
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI bots can swing elections with fake content that has very real consequences
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
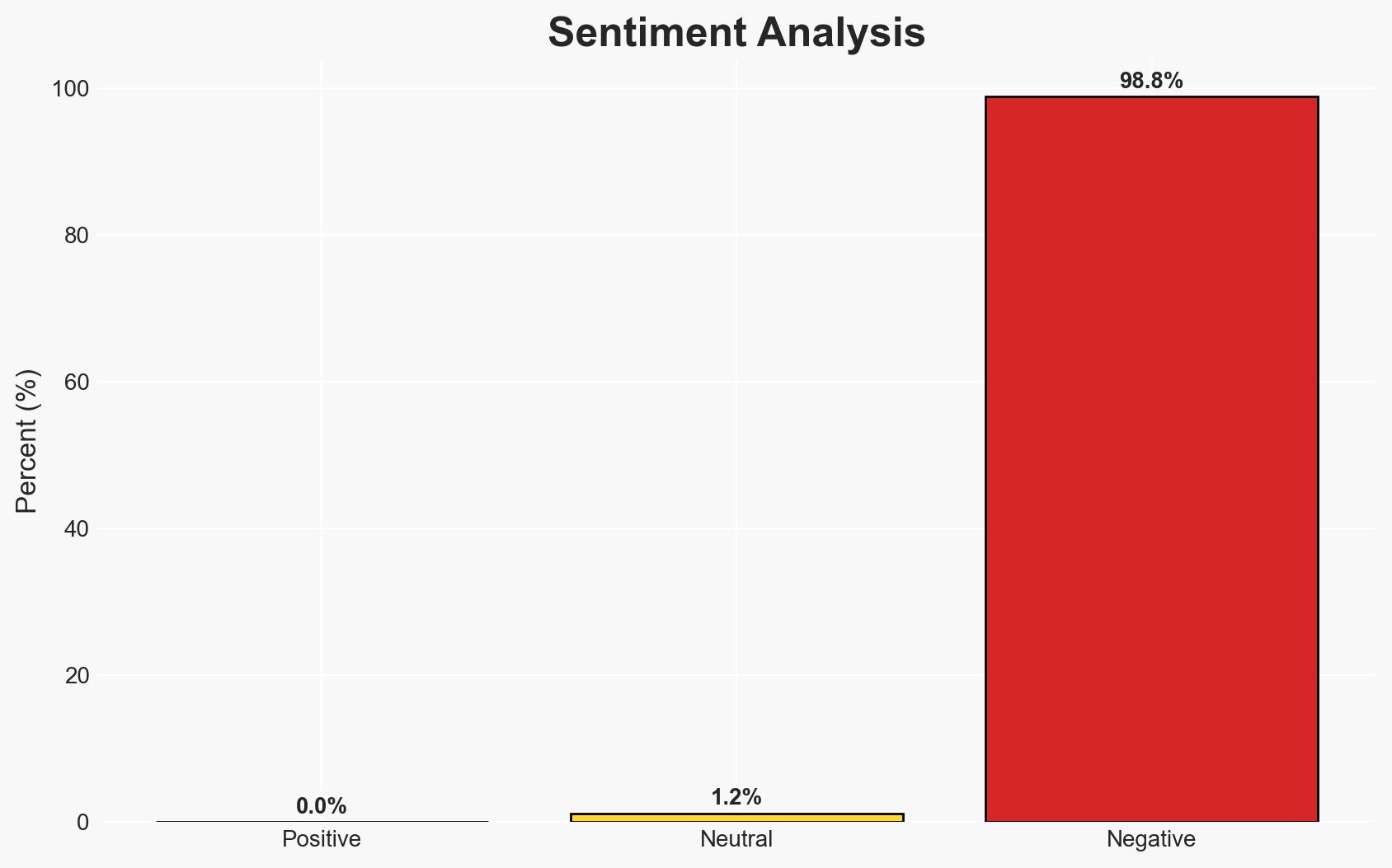
The use of generative AI to create and disseminate misinformation poses a significant threat to democratic processes and public trust. The most likely hypothesis is that AI-driven misinformation campaigns can effectively influence public perception and electoral outcomes, with moderate confidence. This affects political stability, security, and social cohesion.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI-driven misinformation campaigns can significantly influence election outcomes by creating false narratives and manipulating public opinion. Evidence includes the rapid spread of AI-generated misinformation following the Bondi Beach attack and the results of the “Capture the Narrative” wargame. Key uncertainties include the scalability of such operations and the effectiveness of countermeasures.
- Hypothesis B: While AI-driven misinformation is prevalent, its actual impact on election outcomes is limited due to public skepticism and existing countermeasures. Evidence against significant impact includes potential overestimation of AI capabilities and underestimation of public resilience. However, the increasing sophistication of AI bots challenges this view.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the demonstrated ability of AI to create convincing fake content and influence perceptions, as evidenced by the wargame. Indicators that could shift this judgment include advancements in AI detection technologies and increased public awareness and skepticism.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to advance in sophistication; public trust in digital content remains vulnerable; existing countermeasures are insufficient to fully mitigate AI-driven misinformation.
- Information Gaps: The full extent of AI’s influence on real-world election outcomes; effectiveness of current and emerging countermeasures; detailed understanding of public perception dynamics.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive biases include confirmation bias and overreliance on AI-generated data; source bias may arise from entities with vested interests in downplaying AI threats; indicators of manipulation include coordinated bot activity and deepfake proliferation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-driven misinformation could exacerbate political polarization, undermine electoral integrity, and erode public trust in democratic institutions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political instability and influence operations by state and non-state actors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment due to misinformation-fueled radicalization and recruitment.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber operations targeting misinformation detection and mitigation; increased demand for AI literacy and digital resilience.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from destabilized markets and social unrest; erosion of social cohesion due to fractured public discourse.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-driven misinformation; initiate public awareness campaigns on digital literacy; strengthen partnerships with tech companies for rapid response capabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop and deploy advanced AI detection tools; invest in cross-sector collaborations to bolster resilience; promote international norms and regulations on AI use in information operations.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures and public education reduce AI misinformation impact.
- Worst: AI-driven misinformation leads to significant electoral disruptions and societal unrest.
- Most-Likely: Continued challenges in balancing AI innovation with misinformation mitigation, with gradual improvements in public resilience.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Chris Minns, Premier of New South Wales
- Arsen Ostrovsky, Human Rights Lawyer
- Edward Crabtree, Fictional Hero Defender
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, AI misinformation, election interference, cyber operations, public trust, digital literacy, information warfare, social media manipulation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us