AI Tools Exploited for Covert Malware Command and Control Communications
Published on: 2026-02-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI platforms can be abused for stealthy malware communication
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
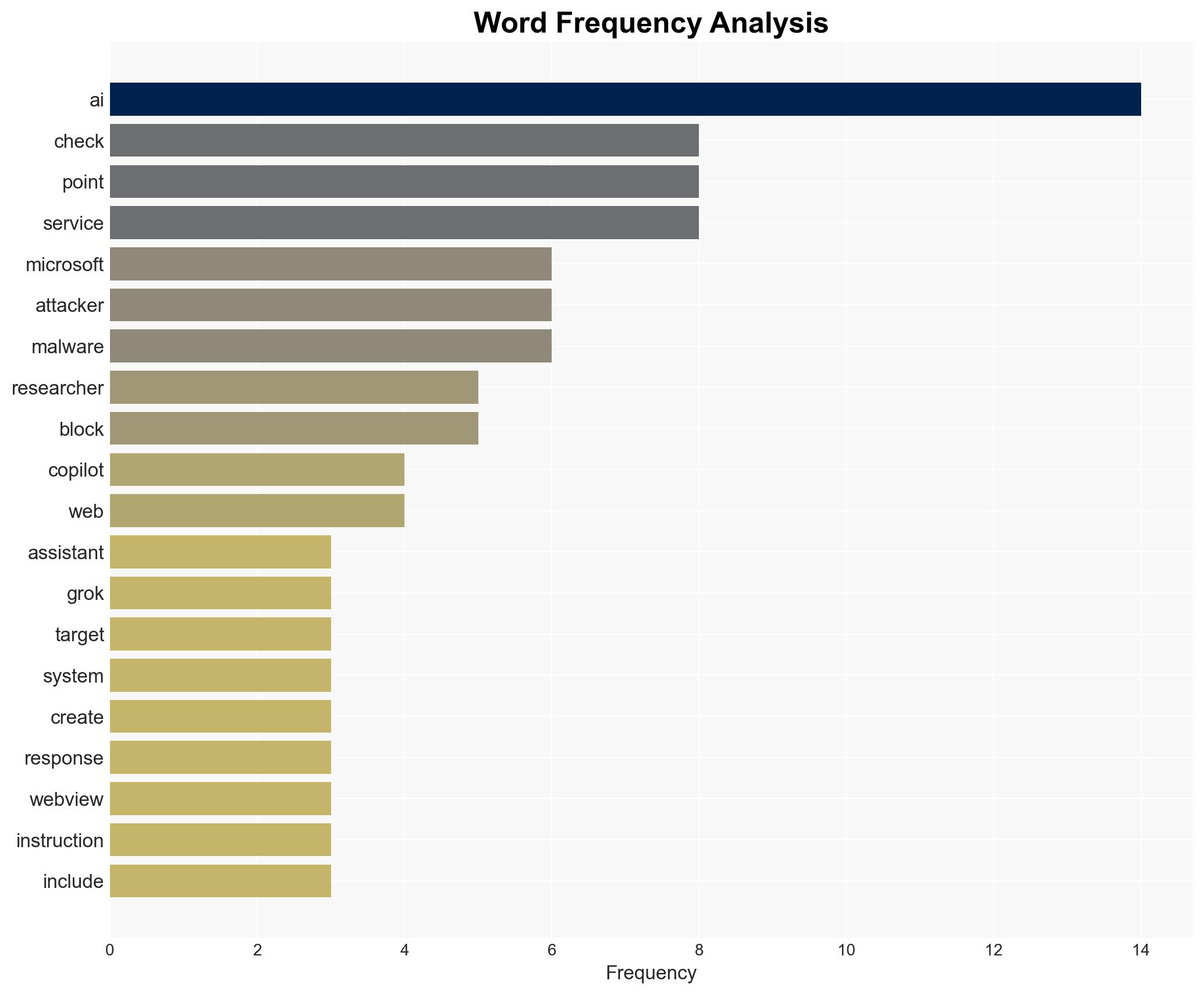
AI platforms with web browsing capabilities, such as Grok and Microsoft Copilot, can be exploited for stealthy command-and-control (C2) communications by threat actors. This method circumvents traditional security measures, posing significant risks to cybersecurity. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors will increasingly adopt this technique due to its low traceability. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors will increasingly use AI platforms for C2 communications due to their ability to bypass traditional security measures. Supporting evidence includes the proof-of-concept by Check Point and the low traceability of such methods. However, uncertainties exist regarding the scalability and detection of these methods by AI service providers.
- Hypothesis B: The use of AI platforms for C2 communications will remain limited due to potential countermeasures by AI service providers and the inherent complexity of the method. While AI platforms can be exploited, service providers may enhance detection and prevention mechanisms, reducing the feasibility of this approach.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the demonstrated feasibility and low traceability of using AI platforms for C2 communications. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include enhanced security measures by AI service providers and increased detection of such activities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI platforms will continue to allow anonymous interactions; threat actors have the technical capability to exploit AI services; AI service providers will not immediately implement effective countermeasures.
- Information Gaps: The extent of current threat actor adoption of AI-based C2 methods; specific countermeasures being developed by AI service providers.
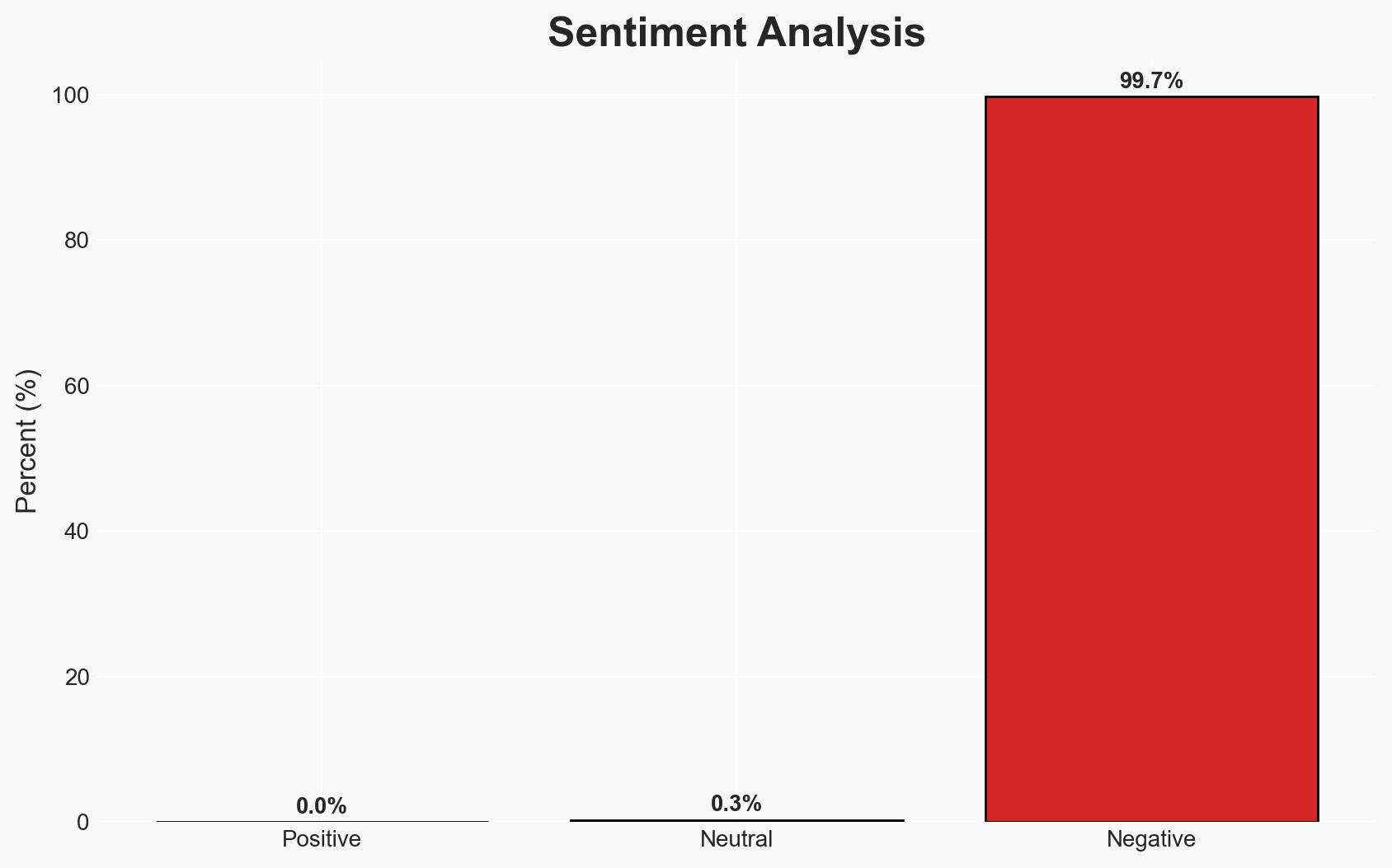
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Check Point’s findings due to commercial interests; possible deception by threat actors in demonstrating capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of AI platforms for C2 communications could significantly alter the cybersecurity landscape, with potential impacts across multiple domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cybersecurity breaches attributed to state-sponsored actors using AI platforms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced operational capabilities for threat actors, complicating detection and response efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread adoption of AI-based C2 methods, challenging existing cybersecurity frameworks.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for organizations to enhance cybersecurity measures, potentially impacting economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor AI platform usage for anomalous activity; engage with AI service providers to discuss potential countermeasures.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI companies for threat intelligence sharing; invest in AI and machine learning capabilities for enhanced threat detection.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: AI service providers implement effective countermeasures, reducing the feasibility of AI-based C2 methods.
- Worst: Widespread adoption of AI-based C2 methods leads to a significant increase in successful cyberattacks.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI-based C2 usage with intermittent detection and mitigation by service providers.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Check Point (Cybersecurity Company)
- Microsoft (AI Platform Provider)
- xAI (AI Platform Provider)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI exploitation, command-and-control, threat actors, cyber defense, AI platforms, malware communication
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us