AI Voice Cloning Exploits: A Case Study in Social Engineering Vulnerabilities
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Real-world AI voice cloning attack A red teaming case study
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
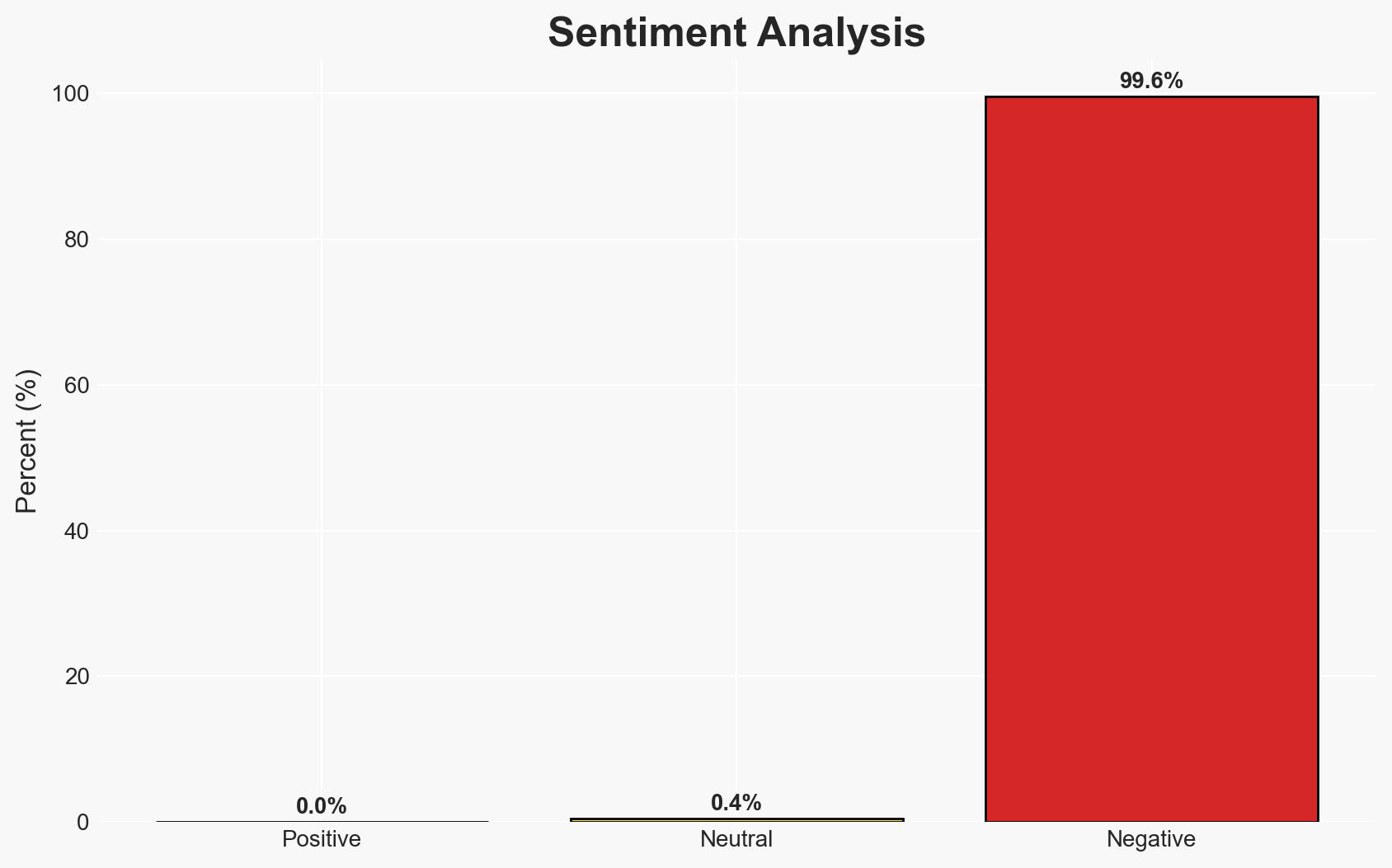
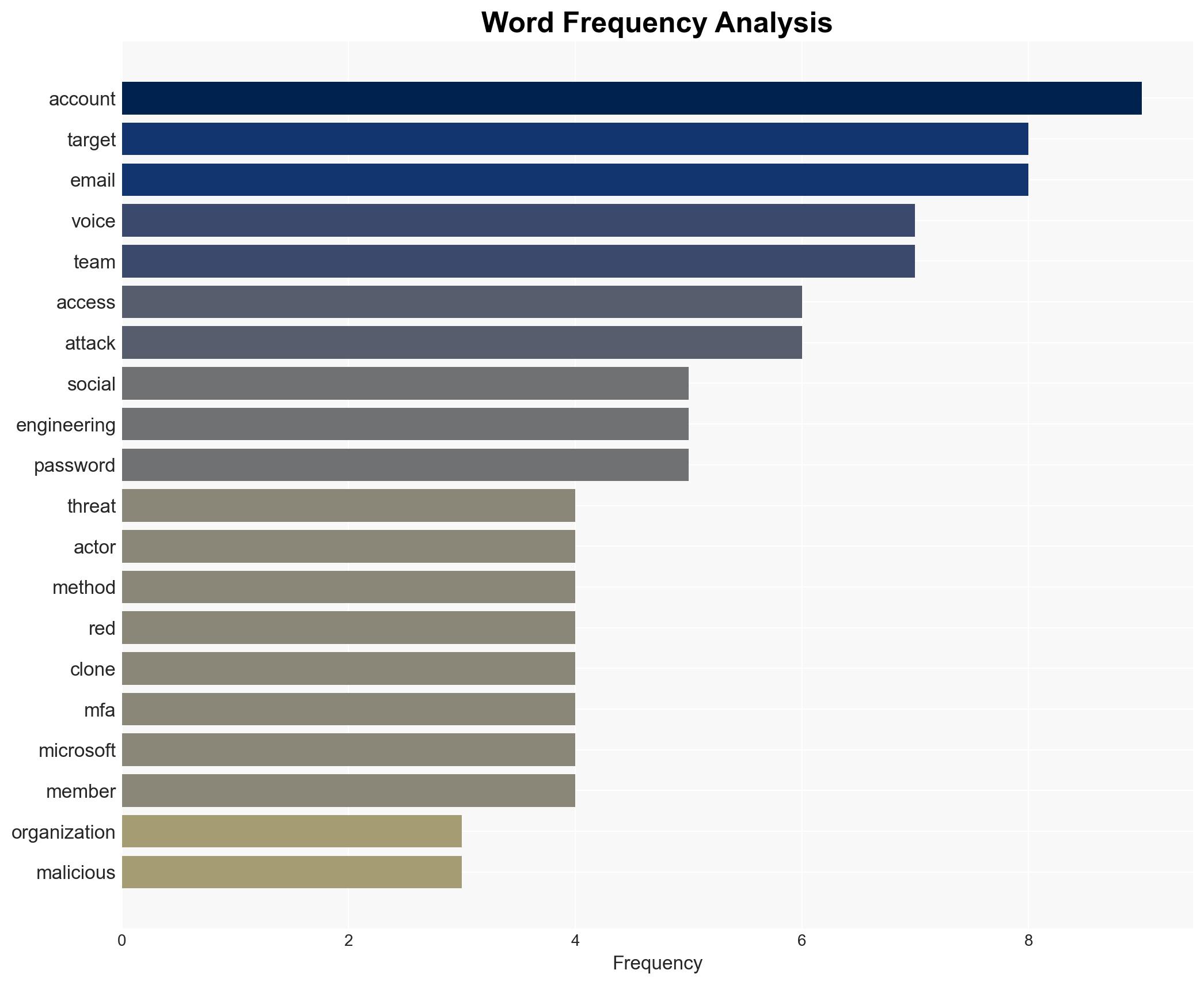
The use of AI-enabled voice cloning in social engineering attacks represents a significant and evolving threat to organizational cybersecurity, with moderate confidence. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors will increasingly leverage these technologies to bypass traditional security measures, affecting enterprises with publicly available employee data. This development necessitates enhanced security protocols and employee training.
2. Competing Hypotheses
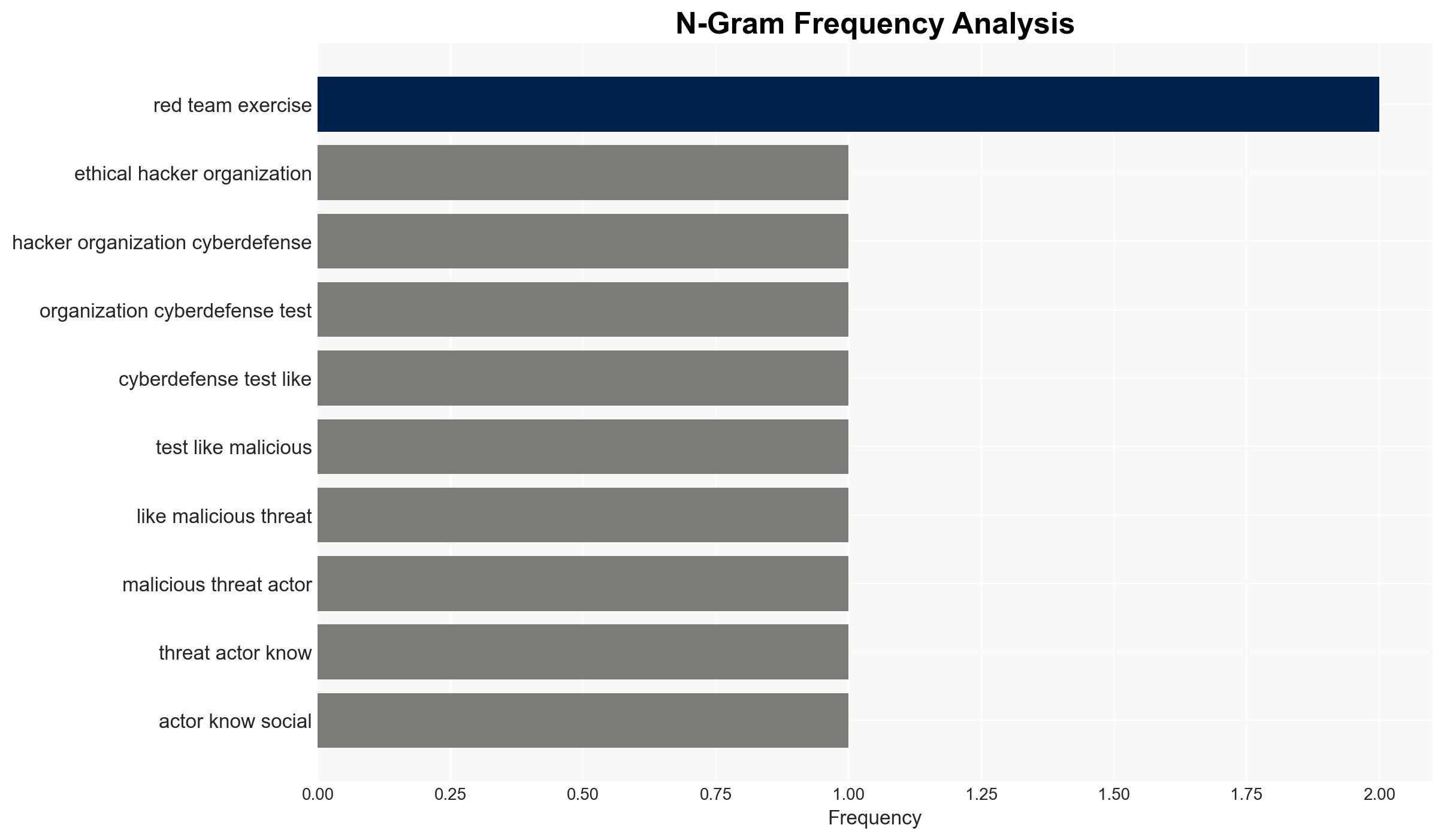
- Hypothesis A: The increase in AI voice cloning attacks is primarily driven by advances in technology making such attacks more accessible and effective. Supporting evidence includes the availability of tools like ElevenLabs and the successful use of voice cloning in red teaming exercises. Key uncertainties include the extent of adoption by threat actors and the speed of technological advancement.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in these attacks is more a result of poor cybersecurity practices, such as password reuse and inadequate employee training, rather than technological advances alone. Contradicting evidence includes the sophisticated nature of recent attacks that bypass even well-implemented security measures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the demonstrated effectiveness of AI voice cloning in bypassing security protocols. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of widespread adoption of improved cybersecurity practices or significant technological setbacks in voice cloning capabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will continue to have publicly available employee data; AI voice cloning technology will remain accessible and improve in quality; social engineering will remain a preferred method for attackers.
- Information Gaps: The extent of current adoption of AI voice cloning by malicious actors and the effectiveness of current mitigation strategies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the speed of technological advancement or overestimating the effectiveness of current security measures; possible deception in publicly available information about the capabilities of voice cloning tools.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI voice cloning attacks could lead to more sophisticated and targeted cyber threats, challenging existing security frameworks and requiring adaptive responses.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased state-sponsored cyber operations utilizing voice cloning to conduct espionage or influence operations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with potential for increased breaches and data theft, impacting national security and critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased complexity in cyber defense strategies, necessitating advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from breaches, including financial losses and reputational damage; increased public concern over data privacy and security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Implement comprehensive employee training on recognizing and responding to social engineering attacks; audit and update security protocols, particularly around MFA.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms specializing in AI threat mitigation; invest in AI-driven security solutions to detect and counter voice cloning attacks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Organizations adapt quickly, reducing the effectiveness of voice cloning attacks through robust security measures.
- Worst Case: Widespread adoption of voice cloning by threat actors leads to significant breaches and loss of sensitive data.
- Most Likely: Gradual increase in voice cloning attacks with varying degrees of success, prompting ongoing adjustments in security strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Scattered Spider hacking group
- Caesars Entertainment
- MGM Resorts
- Marks and Spencer
- ElevenLabs (voice cloning tool)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, social engineering, AI voice cloning, threat actors, information security, cyber defense, organizational resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us