Analysis of Drone Warfare Tactics Employed by Mexican Drug Cartels and Their Impact on U.S. Security
Published on: 2026-02-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Mapping Weaponized Drone Attacks Attributed to Mexican Drug Cartels
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
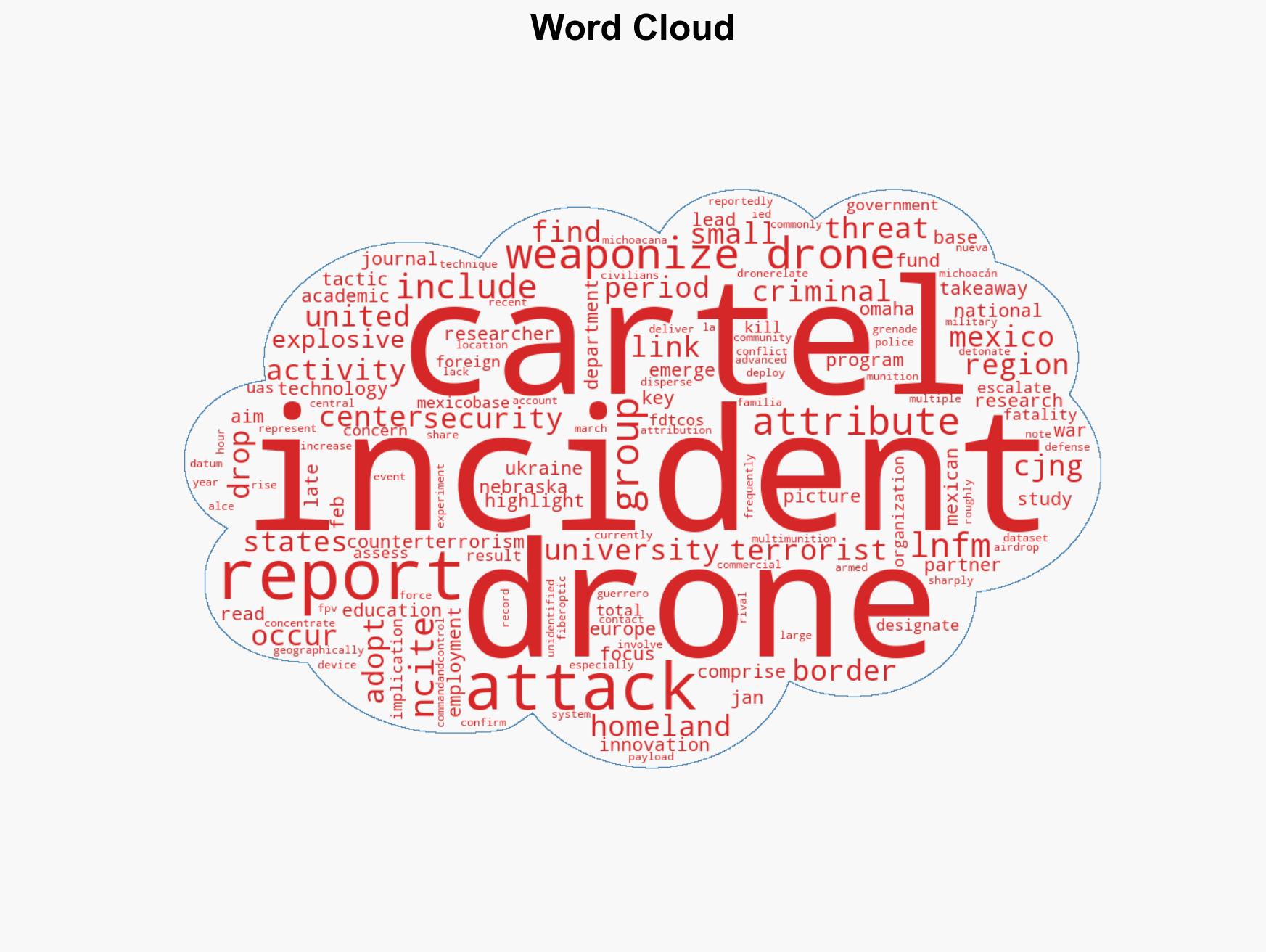
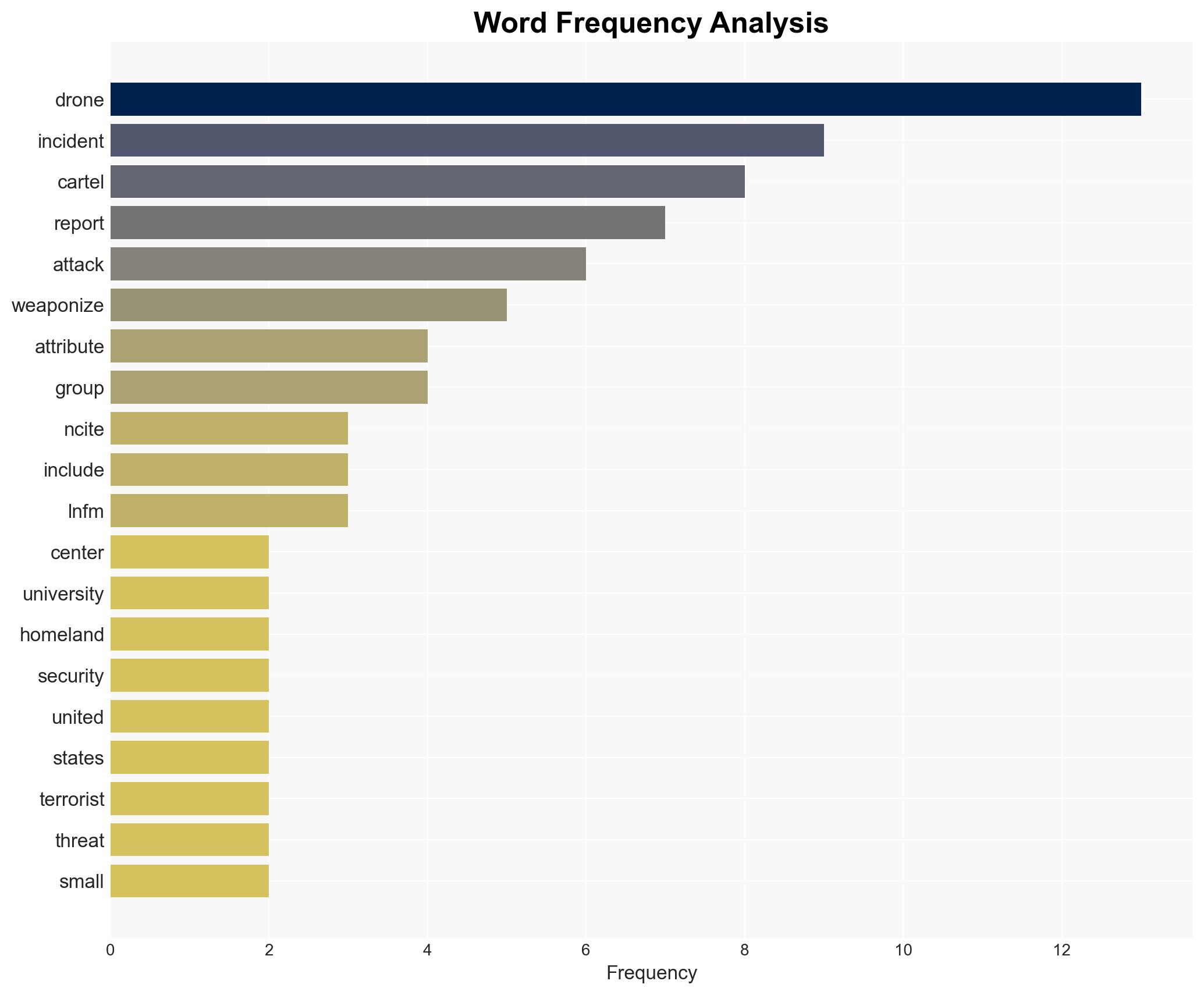
The use of weaponized drones by Mexican drug cartels, notably CJNG and LNFM, represents an escalating threat to regional stability and U.S. homeland security. The trend of increasing sophistication and frequency of attacks suggests a growing capability and intent to use drones in targeted violence. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to significant attribution challenges and data gaps.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Mexican cartels are independently advancing their drone capabilities to enhance operational effectiveness and territorial control. This is supported by the observed increase in attack frequency and sophistication, particularly by CJNG. However, the lack of confirmed attribution for many incidents introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: External actors or state sponsors are providing technological support to Mexican cartels, facilitating the rapid advancement of drone capabilities. While plausible given the sophistication of some attacks, there is currently insufficient direct evidence to support this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in cartel-driven drone activities and the lack of clear evidence of external support. Indicators such as discovery of foreign technology or communications could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cartels have the technical capacity to develop and deploy weaponized drones; cartels are motivated to use drones for strategic advantage; U.S. intelligence has accurately assessed the scale of the threat.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of drone incidents to specific cartels; technical sources of drone technology; motivations behind the choice of targets.
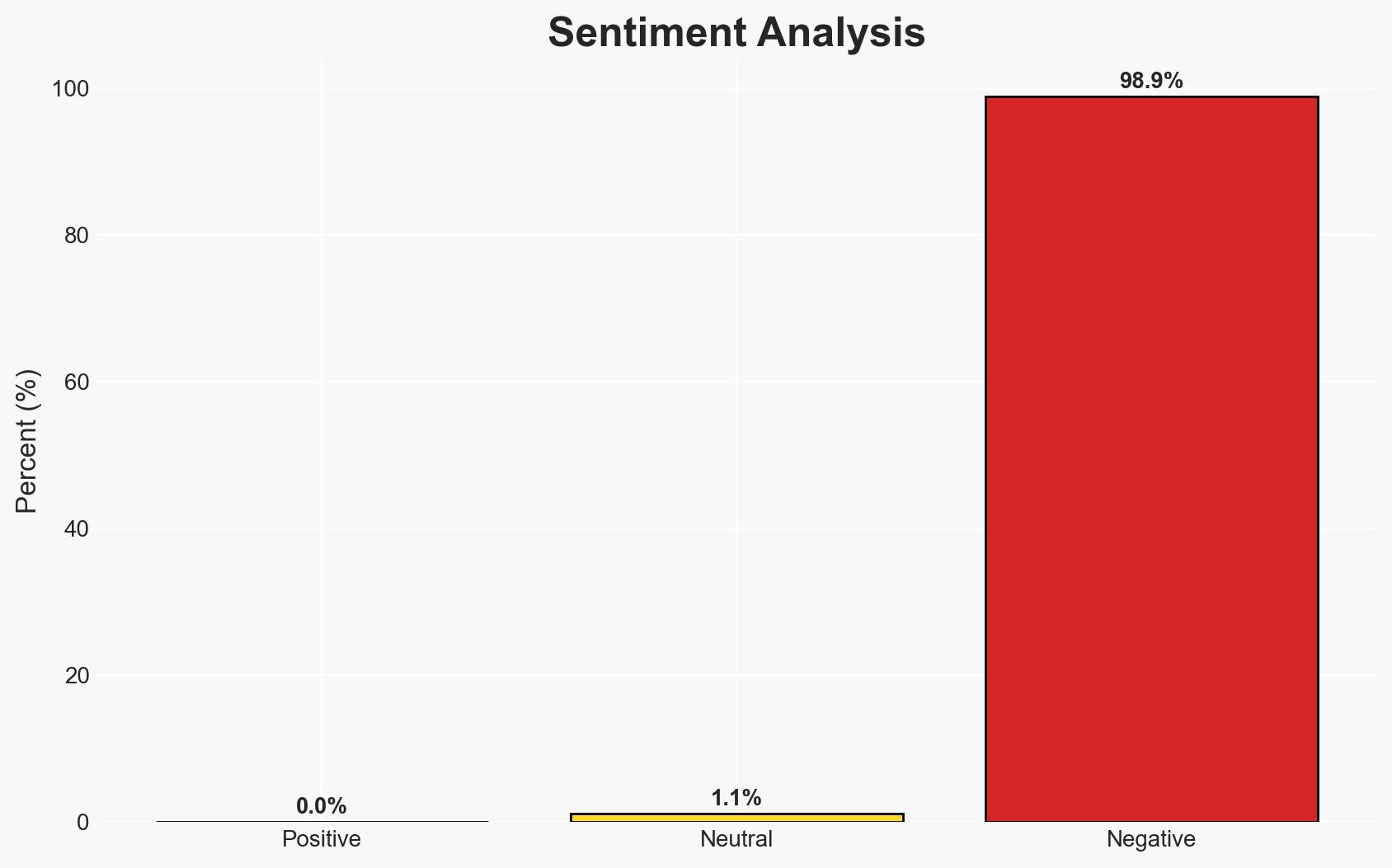
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on open-source data; confirmation bias in attributing incidents to known cartels; possible misinformation from cartel sources.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of cartel drone capabilities could destabilize regional security and complicate U.S. border security efforts. The potential for these tactics to be adopted by other non-state actors poses a broader counter-terrorism challenge.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased pressure on U.S.-Mexico relations; potential for international intervention or sanctions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat to law enforcement and military operations; possible spillover into U.S. territory.
- Cyber / Information Space: Risk of cyber-attacks on drone control systems; potential for propaganda use by cartels.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of local economies; increased civilian casualties leading to social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance border surveillance for drone detection; increase intelligence sharing with Mexican authorities; deploy counter-drone technologies in high-risk areas.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop joint U.S.-Mexico task forces for drone threat mitigation; invest in research on counter-drone technologies; strengthen community resilience programs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Successful interdiction of drone supply chains; reduction in drone attacks.
- Worst Case: Expansion of drone tactics to U.S. soil; increased civilian casualties.
- Most Likely: Continued use of drones by cartels with gradual increase in sophistication and geographic reach.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, drone warfare, Mexican cartels, homeland security, cross-border threats, organized crime, UAS technology
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us