Android Trojans leverage machine learning to evade script-based ad click detection methods
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Machine learningpowered Android Trojans bypass script-based Ad Click detection
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
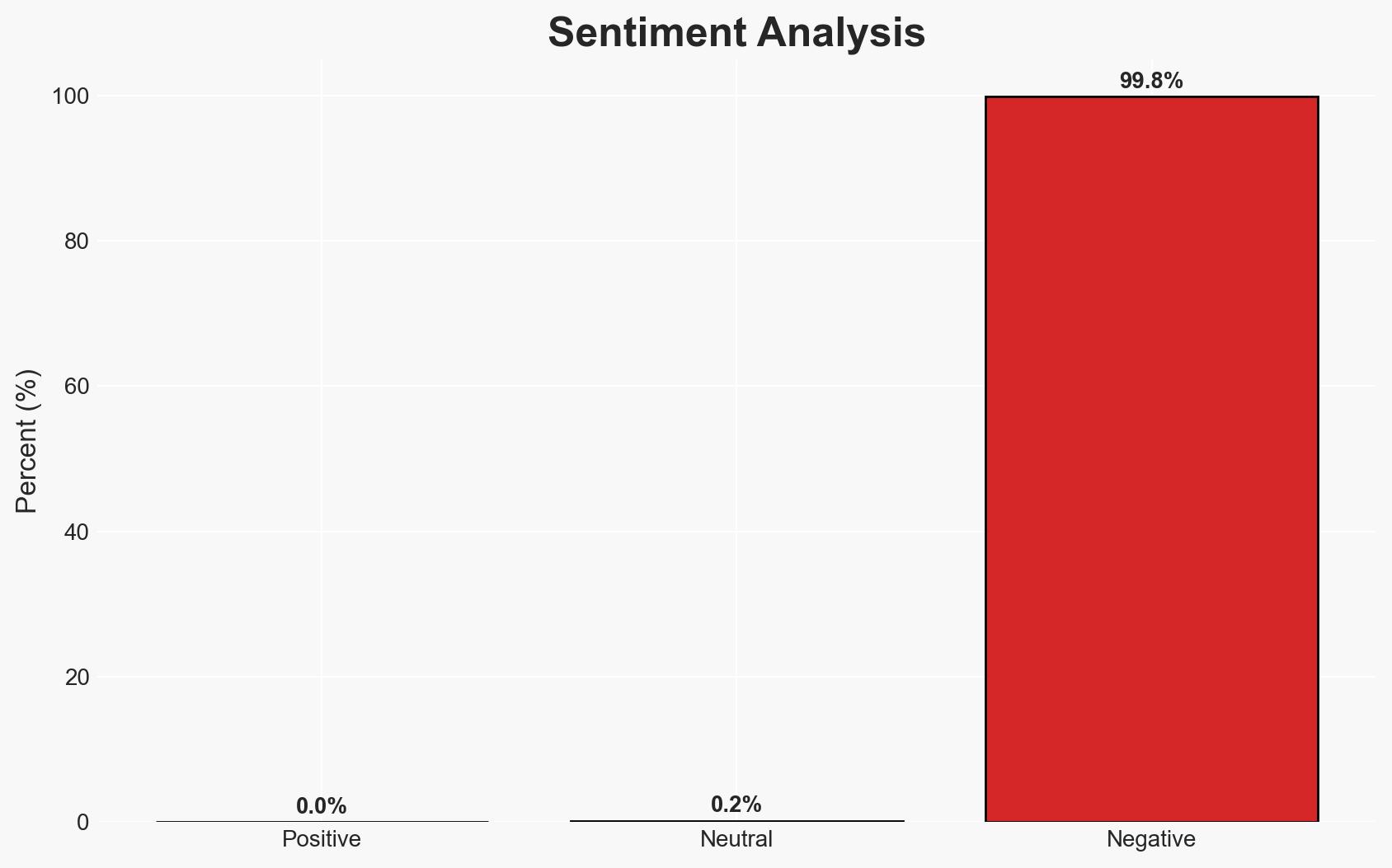
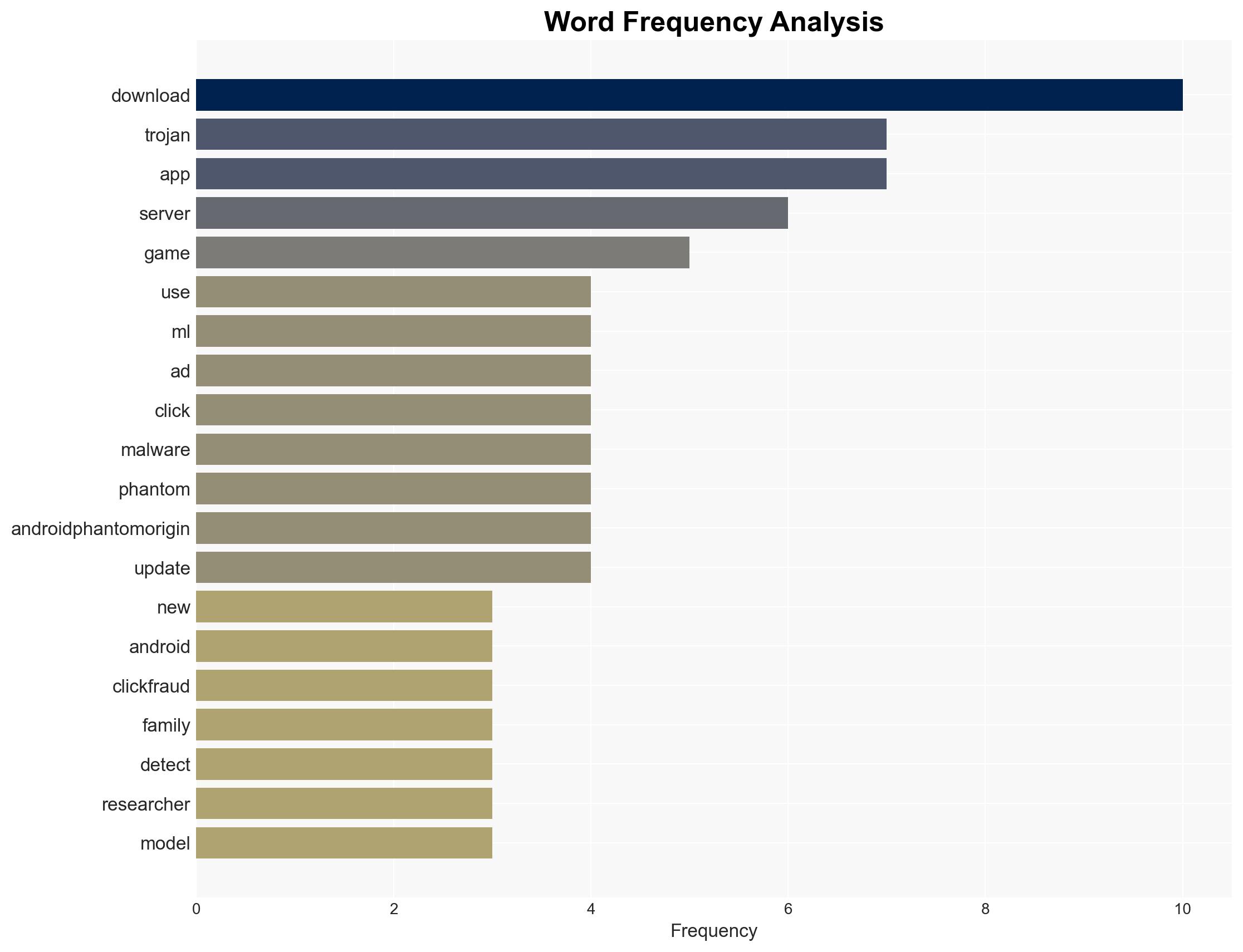
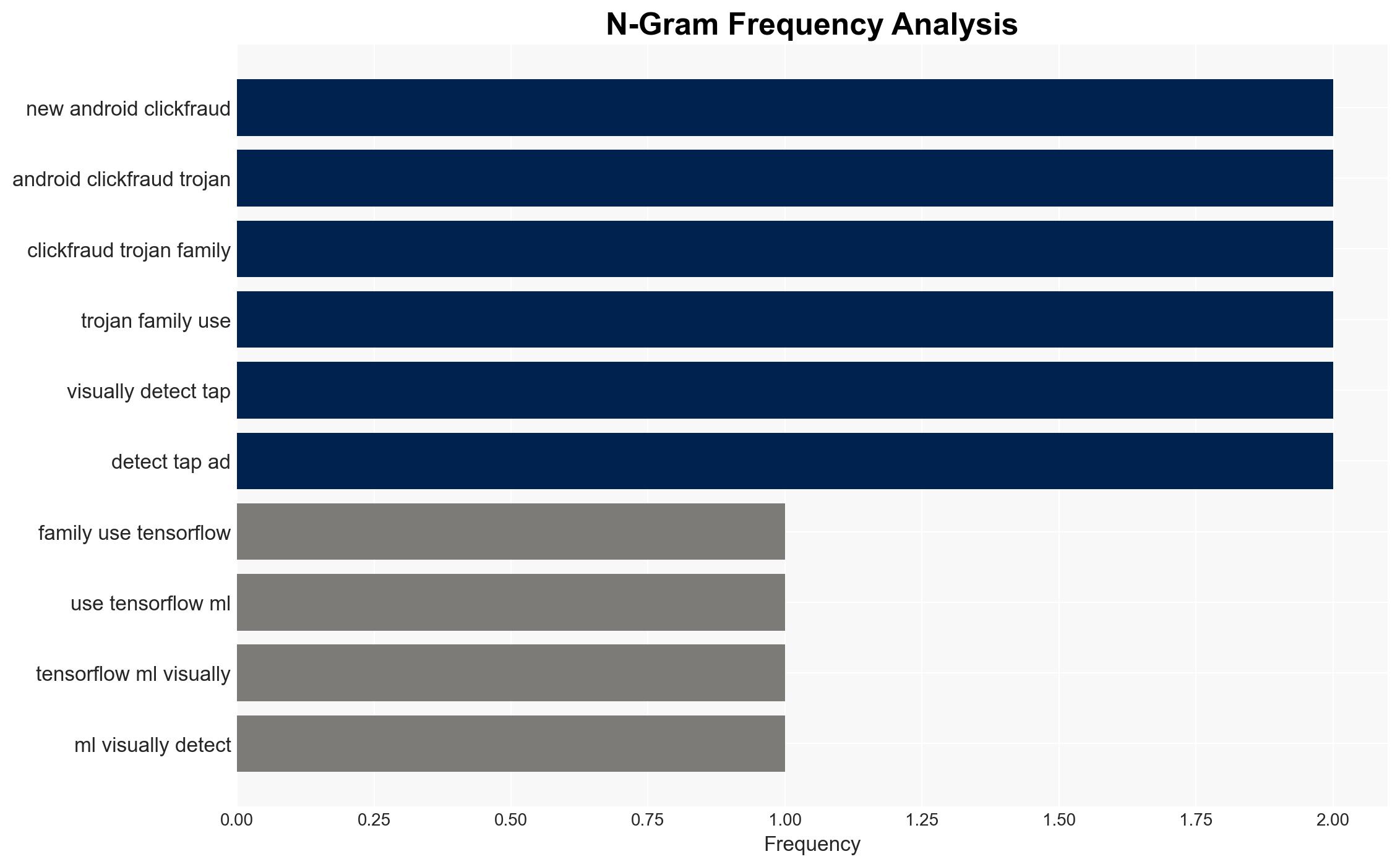
The discovery of a new Android click-fraud trojan family utilizing TensorFlow ML models to bypass traditional detection methods represents a significant evolution in mobile malware sophistication. The malware, distributed via popular apps and third-party APK sites, poses a threat to user privacy and security. The most likely hypothesis is that the trojan’s deployment is part of a coordinated effort to exploit ad revenue streams. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to information gaps regarding the malware’s full operational scope and control infrastructure.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The trojan family is primarily designed for financial gain through ad fraud, leveraging advanced ML techniques to increase click-through rates. This is supported by the malware’s focus on ad interaction and its distribution through popular apps. However, uncertainties remain about the potential for other malicious uses.
- Hypothesis B: The trojan may serve as a multipurpose tool for broader cyber-espionage or data exfiltration, with ad fraud as a cover. This is less supported by current evidence, which predominantly highlights ad-related activities, but cannot be entirely ruled out given the malware’s capabilities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the malware’s specific targeting of ad interactions and the lack of evidence for broader espionage activities. Indicators such as changes in command-and-control patterns or new malware functionalities could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The malware’s primary objective is financial gain through ad fraud; the ML models are optimized for ad detection; the distribution is coordinated by a single entity.
- Information Gaps: Detailed understanding of the command-and-control infrastructure; the full extent of the malware’s distribution network; potential links to broader cybercriminal operations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in focusing on financial motives without considering espionage; possible deception in malware capabilities as reported by sources.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of Android malware using ML techniques could signal a broader trend towards more sophisticated cyber threats, impacting various domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cybercrime origins and responses, particularly if state actors are suspected.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape requiring updated detection and response strategies for mobile platforms.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for similar techniques to be adapted for other malicious purposes, increasing the complexity of cyber defense.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for advertisers and app developers; erosion of user trust in mobile applications.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of app stores and APK sites for malware distribution; enhance detection capabilities for ML-based threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies for threat intelligence sharing; invest in research for ML-based threat detection and mitigation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures reduce the malware’s impact, leading to improved security standards.
- Worst: Malware evolves to evade new defenses, leading to widespread financial and data losses.
- Most-Likely: Continued adaptation by both attackers and defenders, with periodic disruptions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- SHENZHEN RUIREN NETWORK CO., LTD.
- Dr.Web (cybersecurity firm)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, mobile malware, machine learning, ad fraud, Android, cybercrime, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us