Apple addresses critical zero-day vulnerability exploited in targeted attacks across multiple devices.
Published on: 2026-02-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Apple patches zero-day flaw that could let attackers take control of devices
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
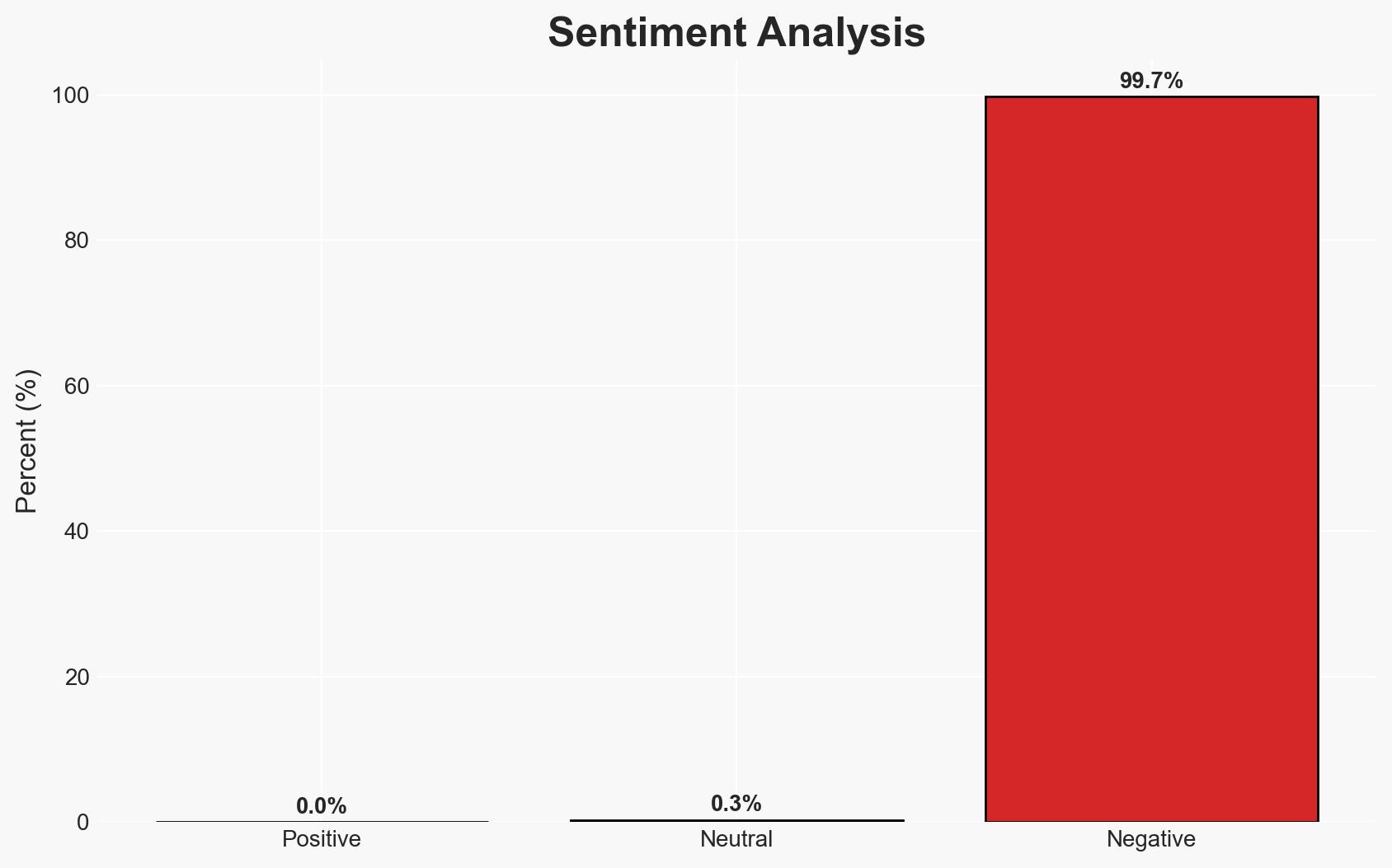
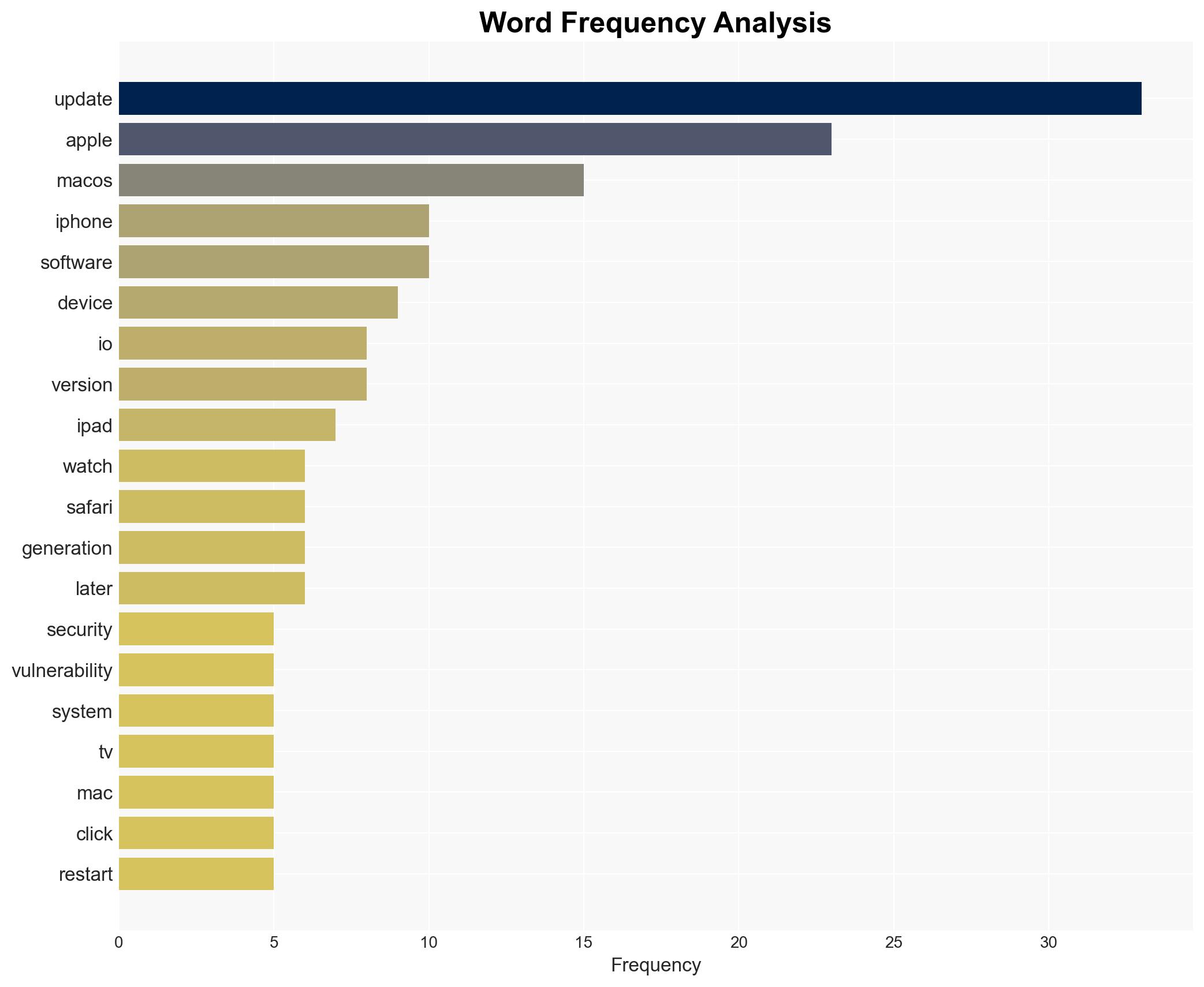
Apple has addressed a critical zero-day vulnerability affecting multiple devices, which was actively exploited in targeted attacks. This vulnerability allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code, posing significant security risks. The most likely hypothesis is that the exploitation was part of a sophisticated cyber operation targeting specific entities. The affected devices include iPhones, iPads, Macs, Apple Watches, Apple TVs, and Safari browsers. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the attackers and their objectives.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The zero-day vulnerability was exploited by a state-sponsored actor as part of a targeted cyber-espionage campaign. This is supported by the sophistication of the attack and the combination of multiple vulnerabilities in an infection chain. However, there is uncertainty regarding the specific state actor involved.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation was conducted by cybercriminals aiming for financial gain through the installation of spyware or ransomware. While possible, this is less supported due to the complexity of the attack and the lack of immediate financial indicators.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the advanced nature of the attack and the use of multiple vulnerabilities, which is characteristic of state-sponsored operations. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of financial transactions linked to the exploit or identification of a specific state actor.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers have advanced capabilities; the vulnerabilities were unknown to Apple prior to exploitation; the patch effectively mitigates the risk.
- Information Gaps: Identity of the attackers, specific targets of the exploitation, and the full scope of the impact on affected devices.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the attack to state-sponsored actors without concrete evidence; risk of underestimating the capabilities of non-state actors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development highlights the persistent threat of zero-day vulnerabilities and the need for robust cybersecurity measures. The exploitation could lead to increased tensions if linked to state actors, and it underscores the vulnerability of widely used technology platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if a state actor is identified; increased scrutiny on cybersecurity policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for entities using Apple devices; possible increase in cyber-espionage activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased awareness and urgency in patch management and cybersecurity practices; potential for copycat attacks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on Apple due to trust issues; increased demand for cybersecurity solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Ensure all Apple devices are updated with the latest patches; monitor for any signs of exploitation or unusual activity.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; enhance internal capabilities to detect and respond to zero-day exploits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further exploitation occurs, and the patch is effective in preventing future attacks.
- Worst: Additional vulnerabilities are discovered, leading to widespread exploitation and significant data breaches.
- Most-Likely: Sporadic attempts to exploit the vulnerability continue, but are largely mitigated by the patch and increased vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerability, state-sponsored attacks, Apple devices, cyber-espionage, software patching, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us