Apple Faces Cybersecurity Crisis as Supply Chain Partner Suffers Major Data Breach
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Apple Got Hacked – Massive Cyberattack May Have Leaked Sensitive Data from iPhone Maker
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
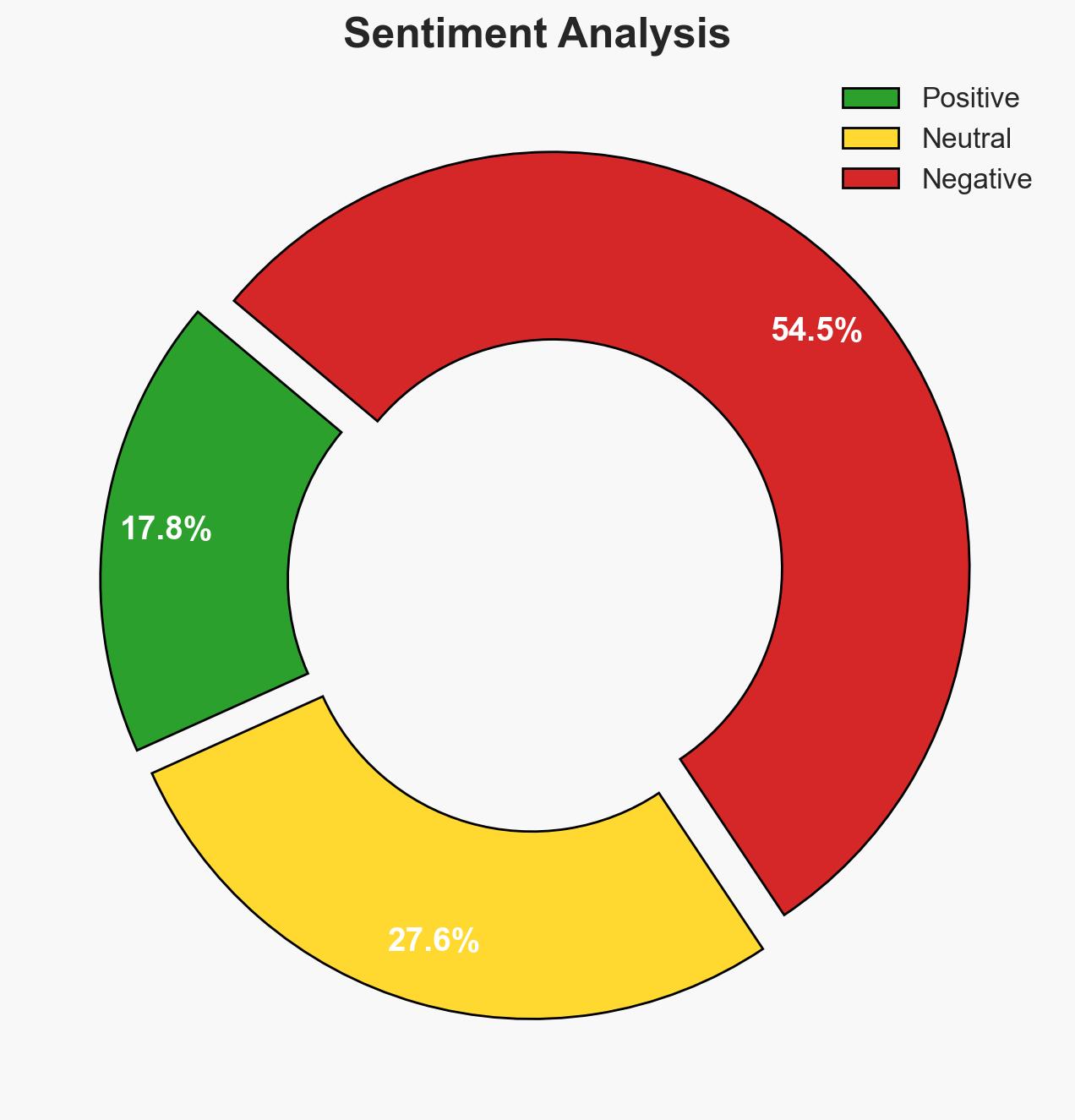
The reported cyberattack on an Apple supply chain partner in China potentially exposed sensitive production data, highlighting vulnerabilities in Apple’s logistical network. The incident underscores the risks associated with supply chain security, even for technologically advanced companies. The most likely hypothesis is that the attack aimed to gather competitive intelligence. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete information on the attack’s scope and impact.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The cyberattack was conducted by a state-sponsored group seeking to gather competitive intelligence on Apple’s manufacturing processes. This is supported by the strategic value of the data and the sophistication required to breach a major supply chain partner. However, the lack of attribution and specific details about the attackers introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was perpetrated by cybercriminals aiming to sell proprietary information to competitors or on the black market. This is plausible given the economic incentives and the potential market for such data. Contradicting this is the absence of evidence that the data has been monetized or leaked publicly.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic nature of the targeted data and the potential geopolitical implications. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of data sale or public leaks, which would support Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was limited to a single supply chain partner; the attackers sought manufacturing data rather than consumer data; Apple’s internal systems were not directly compromised.
- Information Gaps: The identity of the supply chain partner and the attackers; the exact data compromised; Apple’s internal assessment results.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential source bias from industry reports; confirmation bias in attributing state sponsorship without concrete evidence; possible deception by attackers to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny on supply chain security and influence global cybersecurity policies. It may also prompt other tech companies to reassess their supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between China and Western countries over cybersecurity practices and intellectual property protection.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness of supply chain vulnerabilities could lead to improved security measures, but also increased targeting by sophisticated actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely to trigger discussions on enhancing cybersecurity frameworks and collaboration between tech companies and governments.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on Apple’s operations and reputation; broader implications for global supply chain resilience.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough forensic analysis of the breach; enhance monitoring of supply chain partners; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop stronger cybersecurity protocols for supply chain partners; foster international cooperation on cybersecurity standards; invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened cybersecurity measures prevent future breaches, and no significant data is leaked.
- Worst: Data is leaked, causing reputational damage and operational disruptions for Apple.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in supply chain security with no immediate public data leaks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
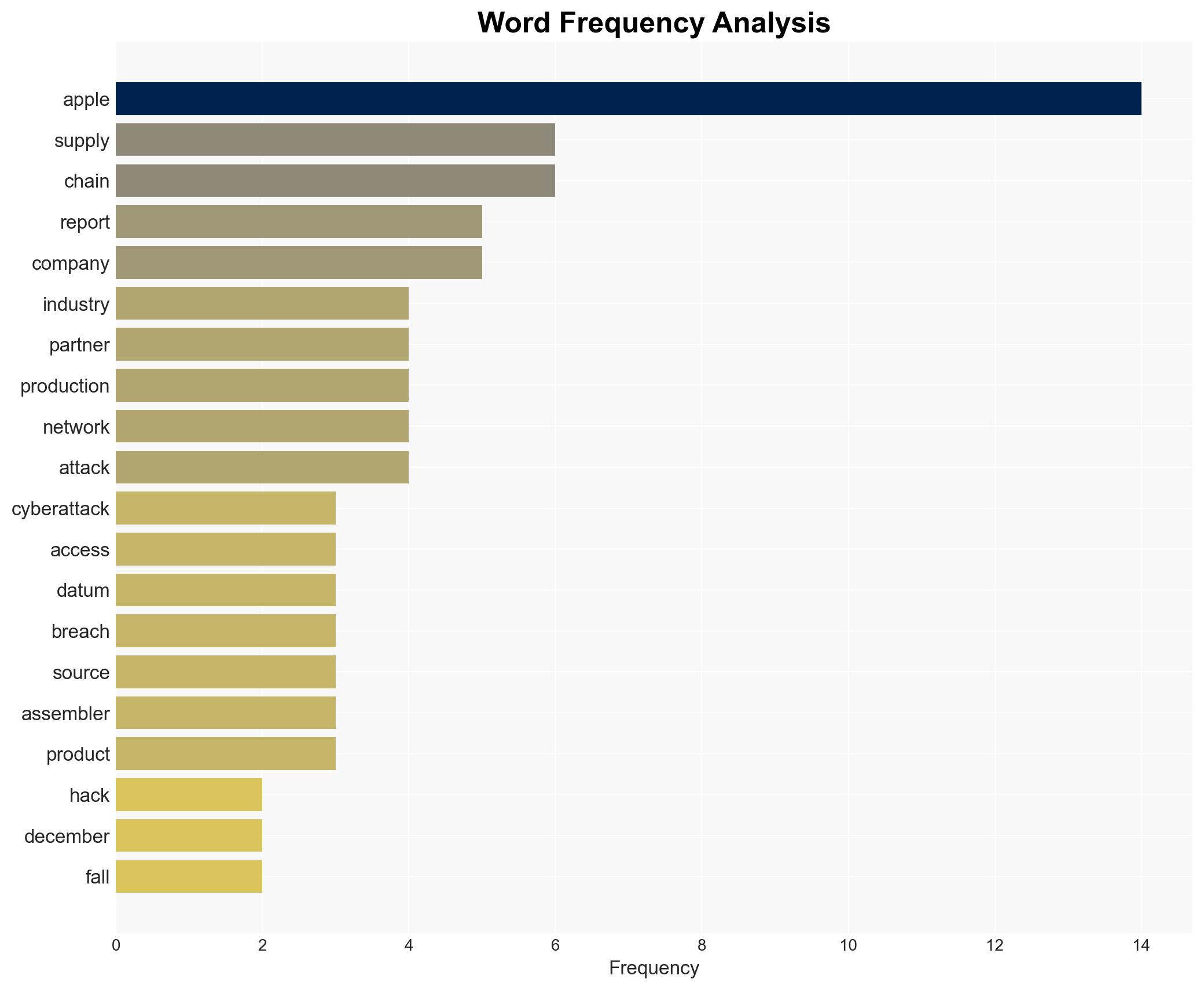
cybersecurity, supply chain, cyber-espionage, data breach, technology, geopolitical tensions, Apple
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us