Archaeologists Discover Site of Ancient Alexandria Amid Ongoing Conflict in Southern Iraq
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Researchers Unveil Ancient Conquerors Forgotten City In War-Torn Desert
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
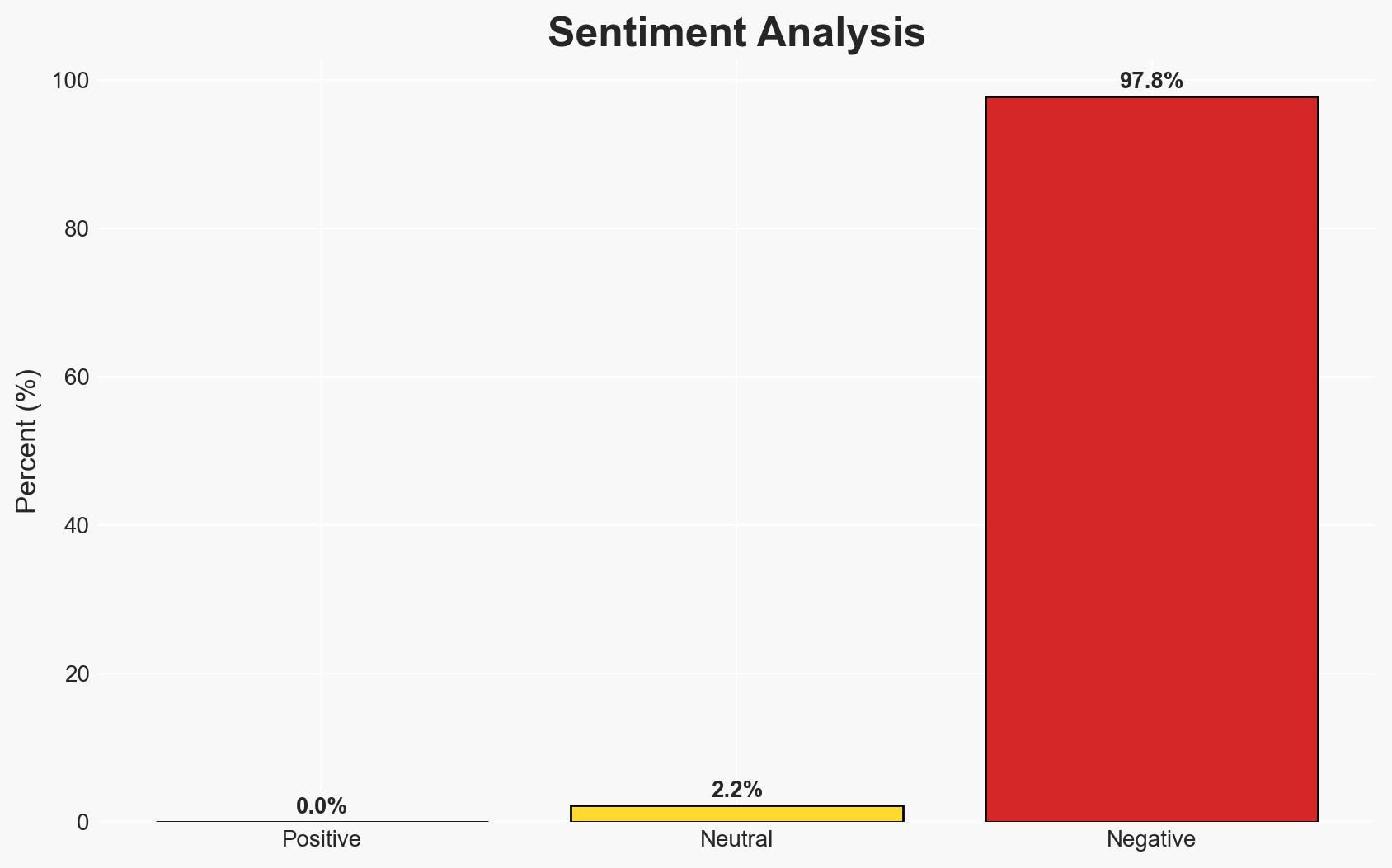
The discovery of an ancient city founded by Alexander the Great in Southern Iraq, near the Tigris River, highlights significant historical and archaeological value. The site’s rediscovery as a major trading hub suggests potential for increased academic interest and geopolitical attention. The ongoing security concerns in the region, primarily due to past ISIS activities, pose challenges to further exploration. Overall confidence in the assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The site of ancient Alexandria was a significant trading hub that connected Mesopotamia with broader trade networks, as evidenced by surface mapping and historical records. However, the extent of its influence remains uncertain due to incomplete archaeological data.
- Hypothesis B: The site was a minor outpost with limited regional influence, and its perceived significance is overstated due to the romanticization of Alexander the Great’s legacy. This hypothesis is less supported due to the scale of infrastructure identified.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported by the evidence of extensive infrastructure and historical records indicating a major trading hub. Future archaeological findings could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The archaeological data collected is accurate and representative; historical records are reliable; current security conditions will not deteriorate further.
- Information Gaps: Detailed excavation data; comprehensive security assessment of the region; full historical context of the city’s operational period.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in historical records; romanticization of Alexander the Great’s legacy; security reports may understate risks due to political pressures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The rediscovery of the ancient city could lead to increased geopolitical interest in the region, potentially affecting local and international relations. The site’s historical significance may attract academic and cultural investments, but security concerns could hinder progress.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic engagement or tension over cultural heritage claims.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Risk of site becoming a target for extremist groups seeking to exploit its symbolic value.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible use of digital platforms to promote the site’s significance or to spread misinformation.
- Economic / Social: Opportunities for local economic development through tourism, but contingent on improved security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance security measures around the site; initiate diplomatic discussions for international archaeological collaboration.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with academic institutions for research; invest in local infrastructure to support potential tourism.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Site becomes a center for cultural tourism and research. Worst: Security deteriorates, halting further exploration. Most-Likely: Gradual increase in academic interest with ongoing security challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, archaeology, historical sites, security, trade networks, Alexander the Great
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us