Arctic Wolf Reports Rise in Automated Attacks Targeting Fortinet FortiGate Firewall Configurations
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Arctic Wolf detects surge in automated Fortinet FortiGate firewall configuration attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
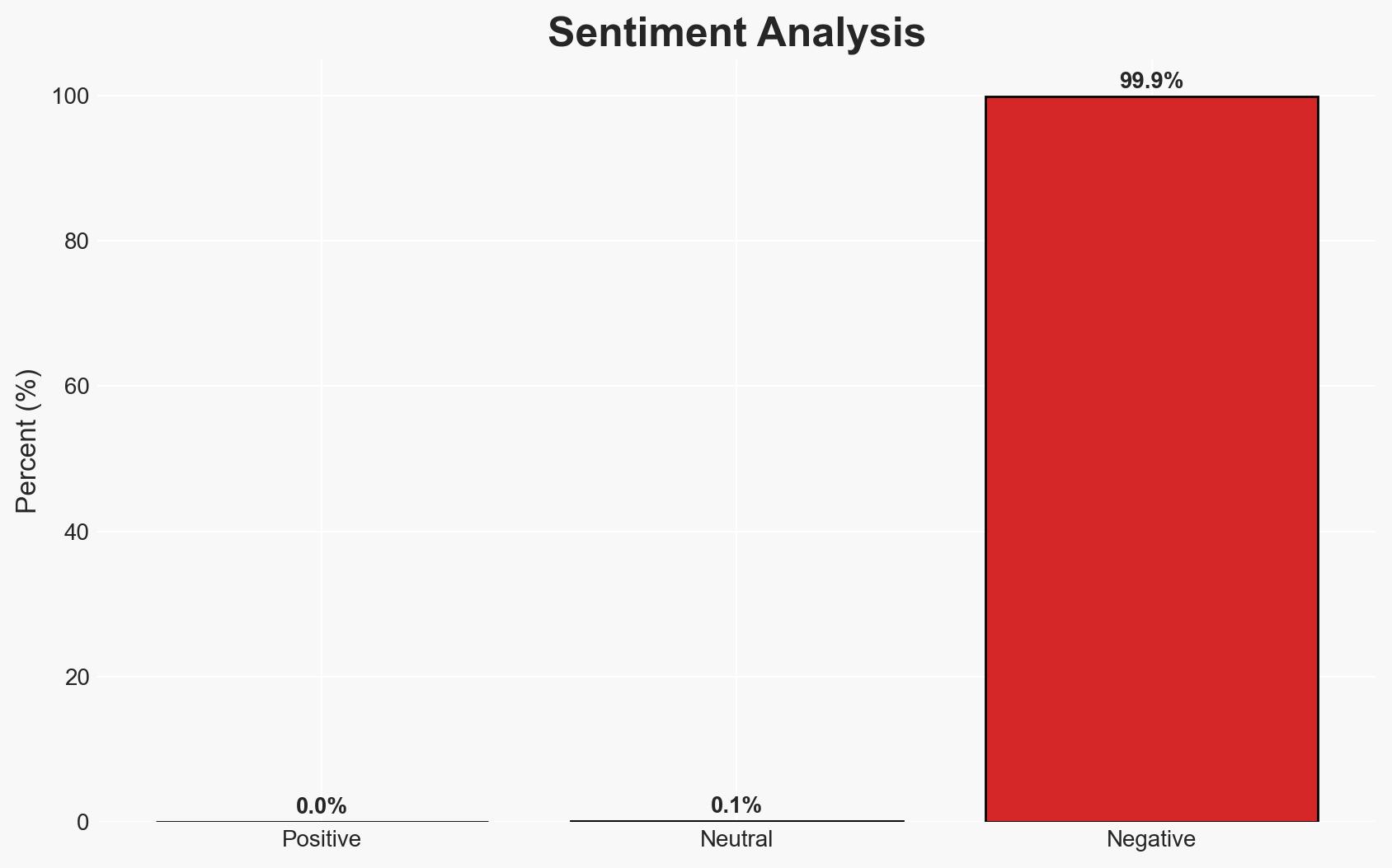
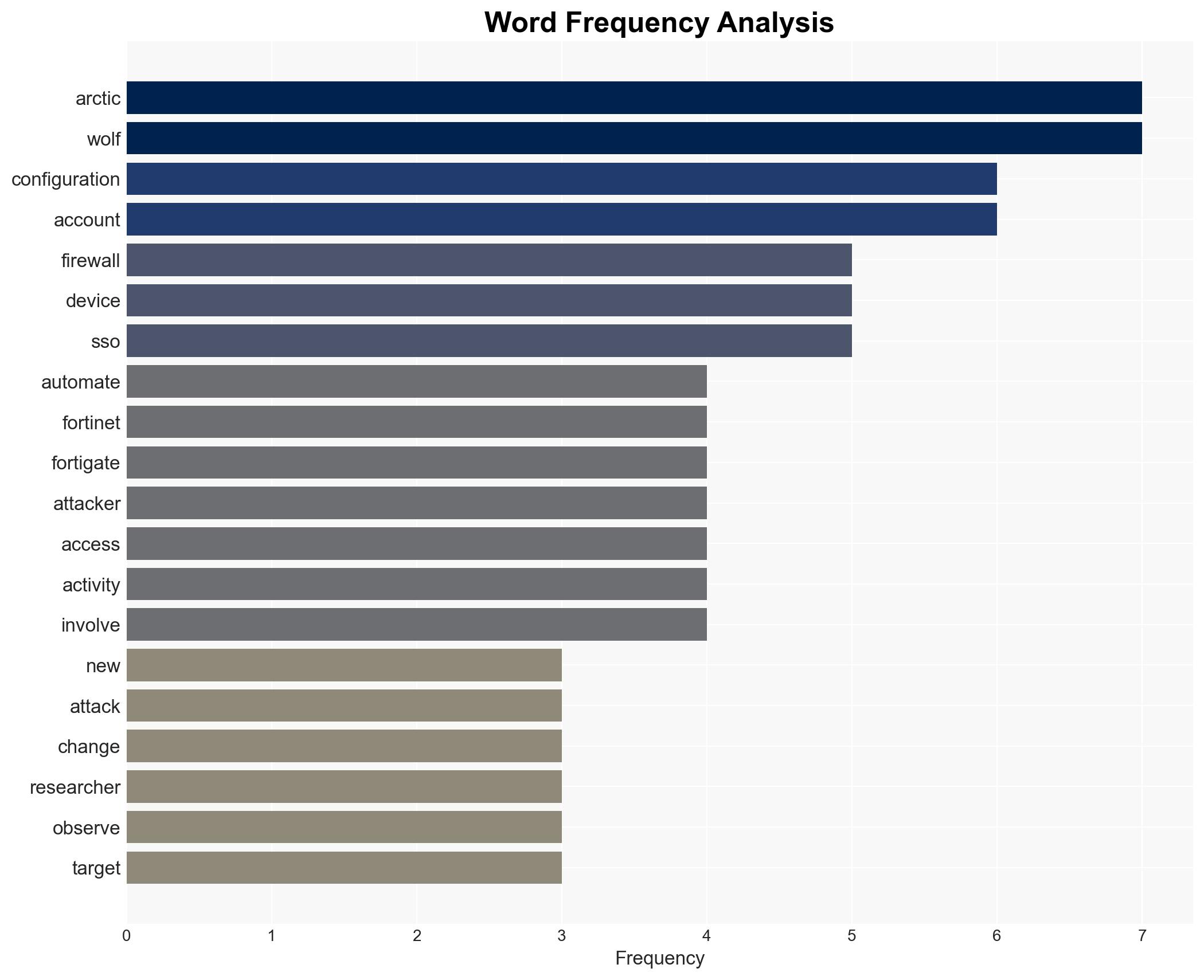
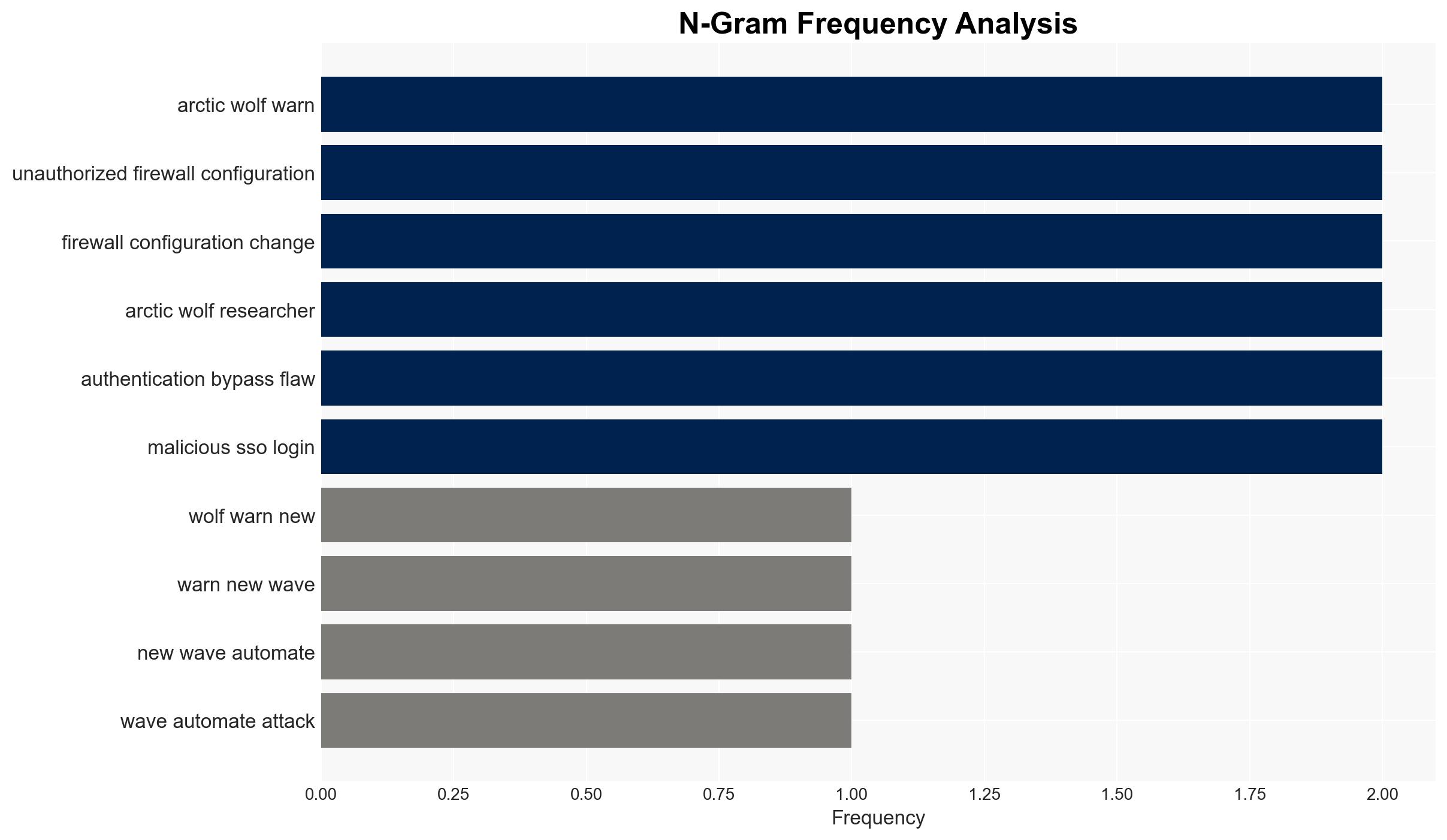
Arctic Wolf has identified a surge in automated attacks on Fortinet FortiGate devices, exploiting recent vulnerabilities to alter configurations and exfiltrate data. The attacks, which began in January 2026, are highly automated and persistent, posing a significant threat to network security. This activity primarily affects organizations using FortiGate devices, with moderate confidence in the assessment due to the evolving nature of the threat and limited visibility into attacker motivations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attacks are part of a coordinated campaign by a state-sponsored actor aiming to gather intelligence and establish persistent access to critical infrastructure. This is supported by the sophisticated nature of the attacks and the rapid exploitation of vulnerabilities. However, the exact attribution remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are conducted by financially motivated cybercriminals seeking to sell access or data on the black market. This is plausible given the creation of generic accounts and data exfiltration, but lacks direct evidence of financial transactions or ransom demands.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the complexity and automation of the attacks, which suggest resources and capabilities typical of state-sponsored operations. Indicators such as targeting patterns and further technical analysis could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Attackers have access to advanced tools and resources; Fortinet vulnerabilities are the primary entry point; affected organizations have not fully implemented patches.
- Information Gaps: Lack of detailed attribution to specific actors; limited insight into the full scope of affected entities; unclear long-term objectives of the attackers.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias towards state-sponsored attribution; reliance on Arctic Wolf’s data may introduce source bias; possibility of false flag operations by attackers.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing attacks on Fortinet FortiGate devices could lead to widespread network compromises, affecting both public and private sectors. The situation may escalate if attackers leverage access for disruptive operations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored attribution is confirmed, especially if critical infrastructure is targeted.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for organizations using FortiGate devices; potential for similar tactics against other network devices.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased scrutiny on Fortinet’s security practices; potential for further exploitation of similar vulnerabilities in other products.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact from data breaches and service disruptions; erosion of trust in cybersecurity measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently apply all available patches to FortiGate devices; enhance monitoring for Indicators of Compromise (IoCs); conduct security audits on network configurations.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced threat detection capabilities; conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patching and mitigation efforts prevent further breaches. Worst: Attackers leverage access for disruptive operations, causing significant damage. Most-Likely: Continued attempts to exploit vulnerabilities with varying success, requiring ongoing vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, state-sponsored threats, Fortinet vulnerabilities, network security, automated attacks, threat intelligence, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us