Are Financial Institutions Ready to Tackle Emerging Cybersecurity Challenges?
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Is Your Bank Prepared for the Next Big Cybersecurity Threat
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
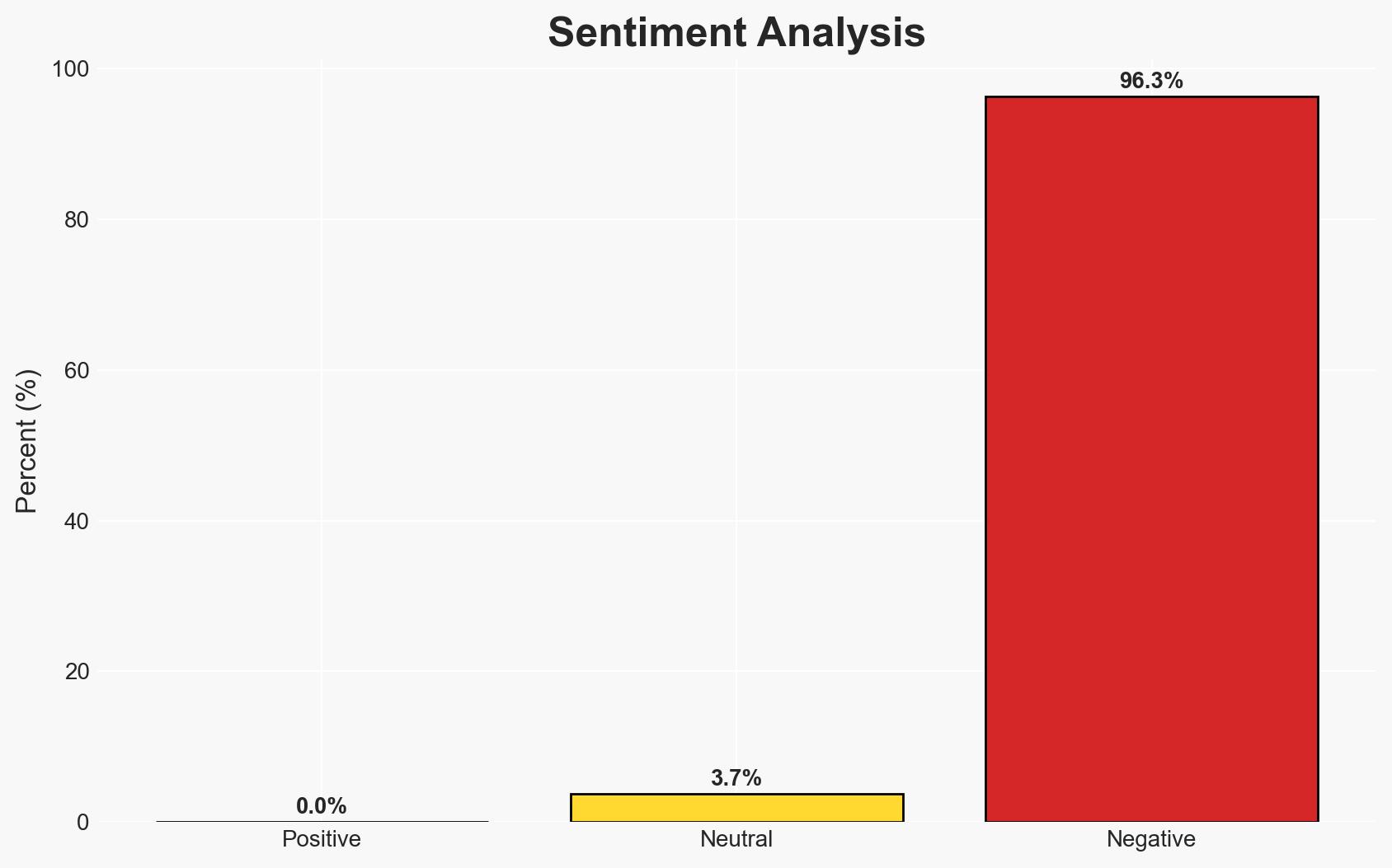
The cybersecurity threat landscape for financial institutions is evolving rapidly, with sophisticated tactics such as ransomware and spear-phishing posing significant risks. The most likely hypothesis is that banks will increasingly adopt proactive cybersecurity measures, including AI and ML technologies, to mitigate these threats. This affects financial institutions globally, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to the dynamic nature of cyber threats and evolving defensive technologies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Financial institutions will successfully adapt to emerging cyber threats by adopting advanced technologies and proactive security measures. This is supported by the increasing reliance on managed IT services and AI/ML tools. However, the effectiveness of these measures is uncertain due to the rapid evolution of cyber threats and potential resource constraints.
- Hypothesis B: Financial institutions will struggle to keep pace with the sophistication of cyber threats, leading to increased breaches and financial losses. This is supported by the complexity of modern attacks and the inherent vulnerabilities in human elements of cybersecurity. Contradicting evidence includes the proactive steps some banks are already taking.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to observable trends in technology adoption and proactive security strategies. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant increase in successful breaches or evidence of widespread inefficacy in current security measures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Financial institutions have the resources to invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies; AI/ML tools will be effective against evolving threats; employee training programs will reduce human vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of current AI/ML implementations in preventing breaches; comprehensive statistics on the frequency and impact of recent cyber attacks on banks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on technology solutions without addressing human factors; source bias from cybersecurity vendors promoting their solutions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of cyber threats against financial institutions could lead to significant changes in security strategies and regulatory frameworks. Over time, this may influence broader financial stability and consumer trust in digital banking.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber threats could lead to heightened regulatory scrutiny and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced cybersecurity measures may reduce the risk of financial systems being exploited for terrorism financing.
- Cyber / Information Space: The adoption of AI/ML in cybersecurity could set new benchmarks for digital defense strategies across sectors.
- Economic / Social: Successful mitigation of cyber threats could bolster consumer confidence in digital banking, while failures could lead to economic disruptions and loss of trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct comprehensive audits of current cybersecurity measures; implement regular simulated phishing exercises for employees; enhance monitoring capabilities using AI/ML tools.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in continuous employee training programs; review and update incident response plans.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Banks effectively mitigate threats, leading to enhanced security and consumer trust.
- Worst: Significant breaches occur, causing financial losses and regulatory backlash.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security posture with occasional breaches prompting further enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
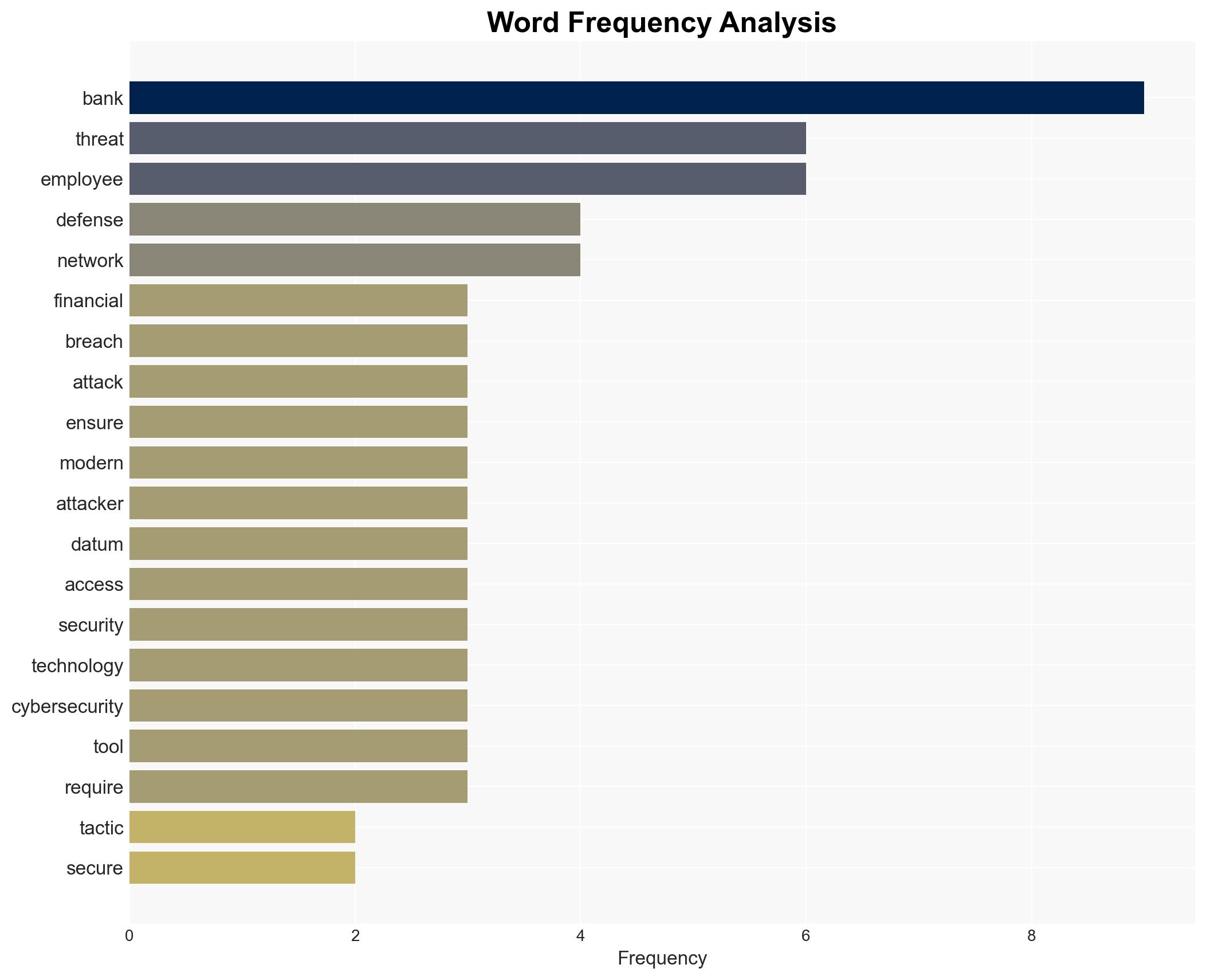
cybersecurity, financial institutions, ransomware, AI/ML, spear-phishing, digital banking, threat mitigation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us