Army Antidrone Laser Disrupts Flights at El Paso International Airport Amid Border Drone Threat
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why an Army antidrone laser grounded flights at El Paso International Airport
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
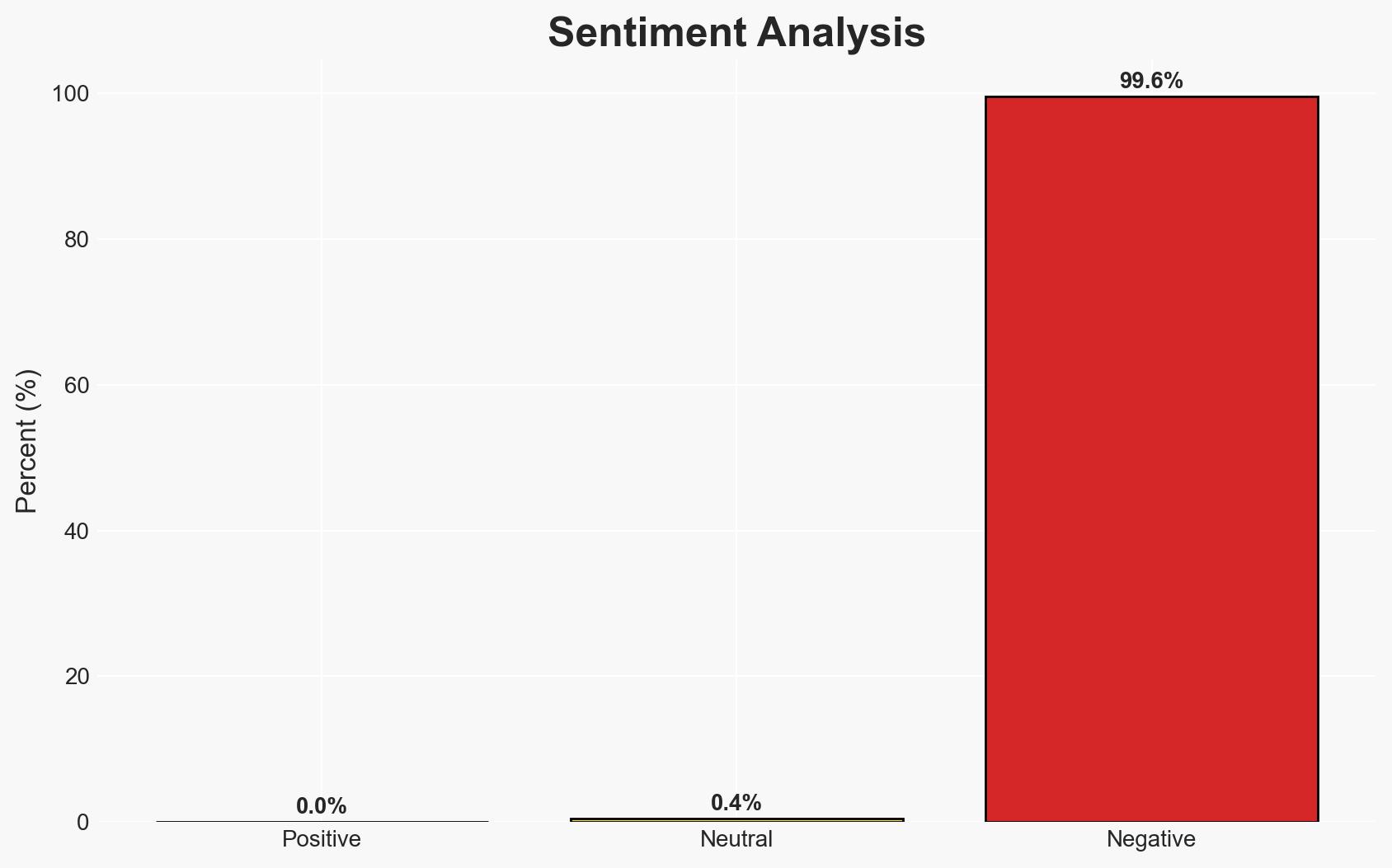
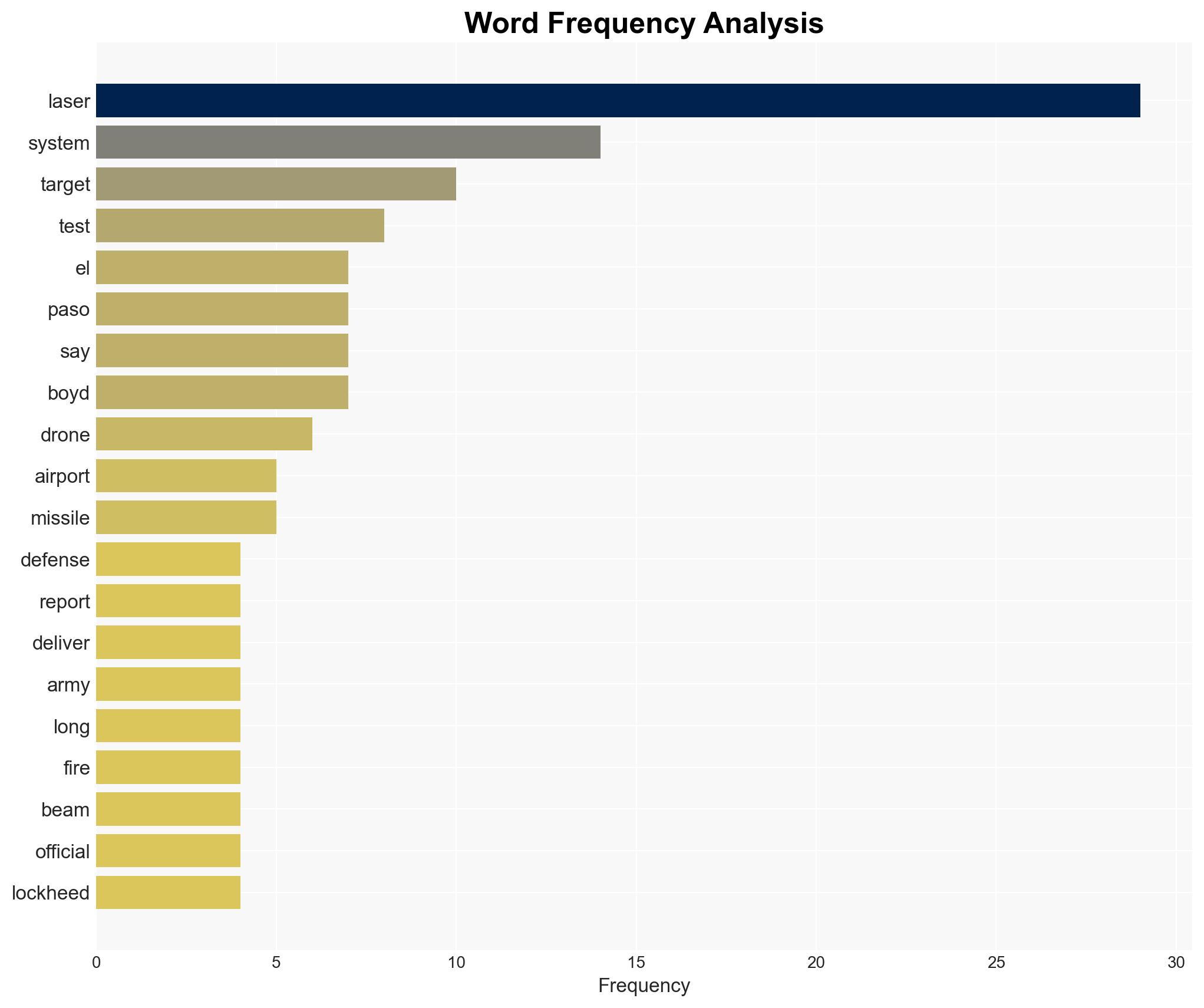
The temporary closure of El Paso International Airport’s airspace was due to a reported “cartel drone incursion” along the border, prompting the use of a military-grade antidrone laser system. This incident highlights the complexities and risks associated with deploying advanced counter-drone technologies near civilian infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that the laser system was used to neutralize a perceived threat, but misidentification or operational errors may have occurred. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The antidrone laser system was deployed in response to a genuine threat from a cartel-operated drone, necessitating the temporary closure of airspace to ensure safety. Supporting evidence includes the official statement regarding a “cartel drone incursion” and the deployment of a military-grade system. Contradicting evidence includes reports suggesting the target may have been a misidentified object, such as a party balloon.
- Hypothesis B: The closure and laser deployment were due to a misidentification or operational error, potentially involving a non-threatening object like a party balloon. Supporting evidence includes media reports suggesting the target was a benign object and the lack of detailed official explanation. Contradicting evidence is the official narrative of a cartel threat.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the official statements and the seriousness of deploying military assets. However, the lack of transparency and conflicting reports leave room for reevaluation if further evidence emerges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The laser system was operational and correctly targeted; the threat was significant enough to warrant airspace closure; official statements are accurate and complete.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the nature of the threat, the exact target, and the criteria for deploying the laser system.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in official narratives to justify military actions; media reports may be influenced by sensationalism or incomplete information.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident underscores the potential for misidentification and collateral risks when deploying advanced military technologies in civilian areas. It may influence future policy on drone threat responses and airspace management.
- Political / Geopolitical: Could escalate tensions along the border and prompt diplomatic discussions on cross-border drone threats.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Highlights the evolving threat landscape and the need for robust counter-drone strategies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation or disinformation campaigns exploiting the incident.
- Economic / Social: Temporary disruptions to air travel could affect local economies and public perception of safety.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough investigation to clarify the incident details; enhance communication protocols for similar future events.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop guidelines for the use of military technologies in civilian areas; strengthen cross-agency coordination and training.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved counter-drone measures with minimal impact on civilian operations.
- Worst: Increased incidents leading to public safety concerns and economic disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual policy adjustments and enhanced inter-agency collaboration.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Secretary of Transportation Sean Duffy
- Senator Ted Cruz
- Customs and Border Protection
- Department of Defense
- AeroVironment
- BlueHalo
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, counter-drone technology, airspace security, military-civilian coordination, border security, misinformation risks, operational safety
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us