Attackers turn trusted OAuth apps into cloud backdoors – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-10-22
Intelligence Report: Attackers turn trusted OAuth apps into cloud backdoors – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
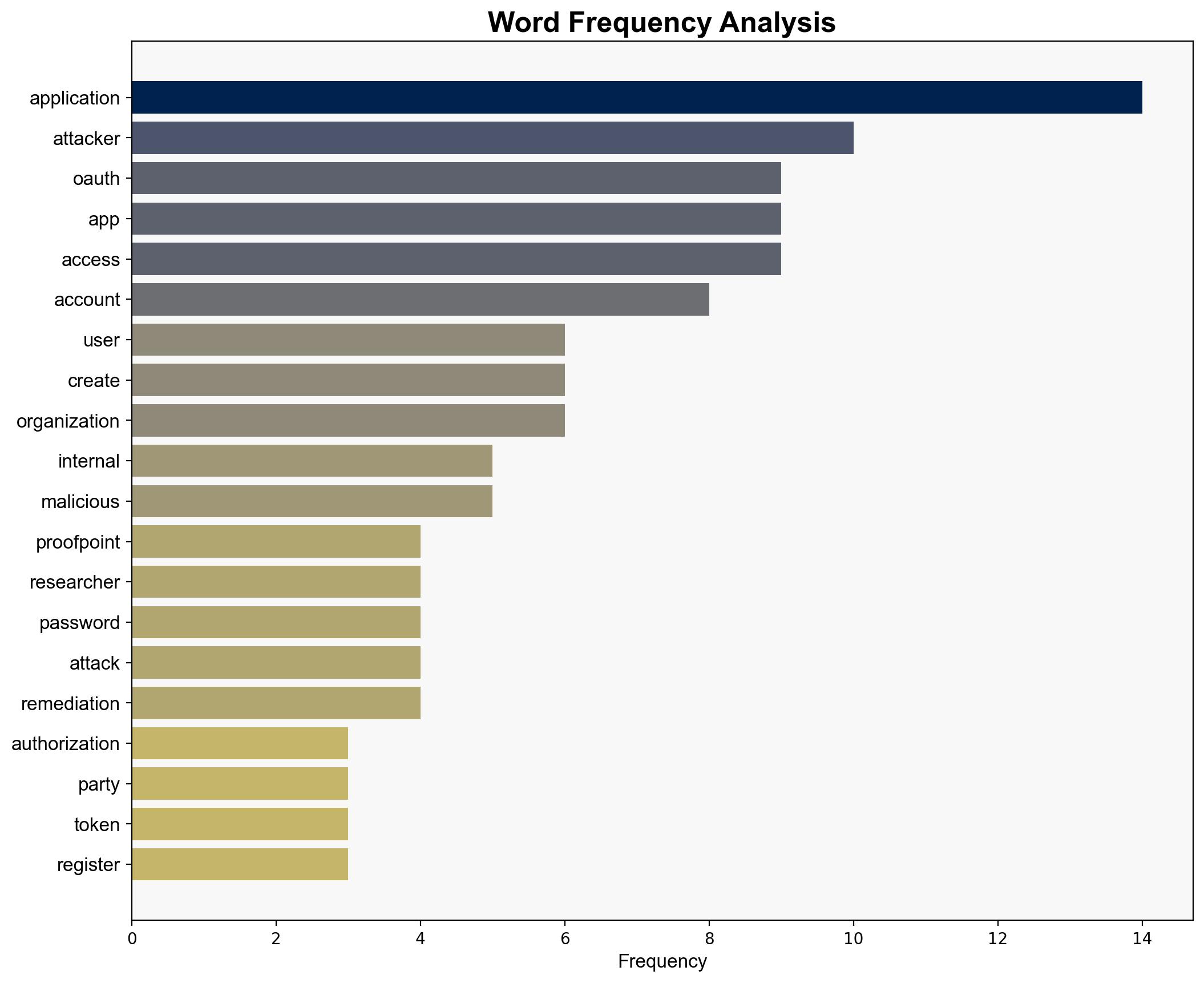
Attackers are exploiting OAuth applications to gain persistent access to cloud environments, posing a significant cybersecurity threat. The most supported hypothesis is that attackers are leveraging OAuth apps to bypass traditional security measures, such as MFA, by exploiting inherent trust within organizations. Confidence level: High. Recommended action: Implement stricter monitoring and control measures for OAuth app permissions and user training to recognize suspicious activities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Attackers exploit OAuth apps primarily to bypass MFA and maintain persistent access to cloud environments.
– **Supporting Evidence**: Attackers use OAuth to gain access without needing passwords, even after password changes.
– **SAT Applied**: Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH 2.0) indicates strong alignment with observed attacker behavior and proof of concept tools.
2. **Hypothesis B**: Attackers use OAuth apps as a secondary method, focusing primarily on phishing and credential theft.
– **Supporting Evidence**: While OAuth exploitation is noted, traditional phishing remains prevalent.
– **SAT Applied**: Bayesian Scenario Modeling suggests lower probability due to the increasing sophistication of OAuth-based attacks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Organizations inherently trust internally registered OAuth apps, leading to potential blind spots in security protocols.
– **Red Flags**: The seamless integration of malicious apps into legitimate business environments suggests potential insider threats or inadequate internal controls.
– **Blind Spots**: Lack of visibility into OAuth app permissions and user consent processes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Cybersecurity Risks**: Persistent access via OAuth apps can lead to data breaches, intellectual property theft, and disruption of services.
– **Economic Risks**: Potential financial losses from data breaches and reputational damage.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Exploitation by state-sponsored actors could lead to increased tensions and cyber warfare.
– **Psychological Risks**: Erosion of trust in cloud services and internal IT systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement stricter OAuth app monitoring and permission controls.
- Conduct regular user training to recognize and report suspicious app requests.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Enhanced security measures prevent future OAuth-based attacks.
- **Worst Case**: Attackers refine techniques, leading to widespread breaches.
- **Most Likely**: Continued OAuth exploitation with gradual improvements in detection and response.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are named in the source text. Entities involved include Proofpoint researchers and Microsoft Entra.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus