Big Tech’s Complicity with China Poses a Significant Threat to U.S. National Security
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: BILL FLAIG Big Techs China Problem Is Americas National Security Problem
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
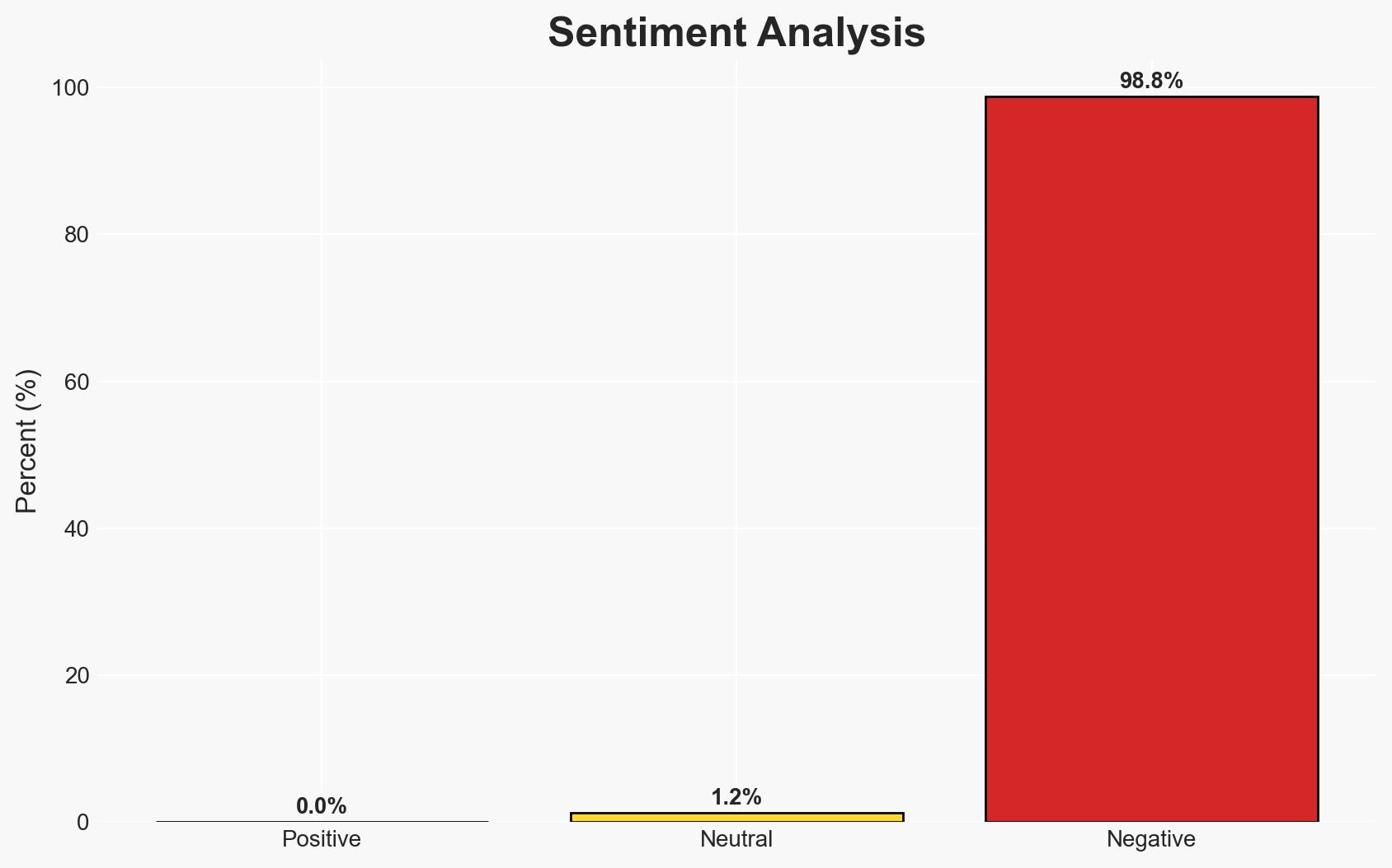
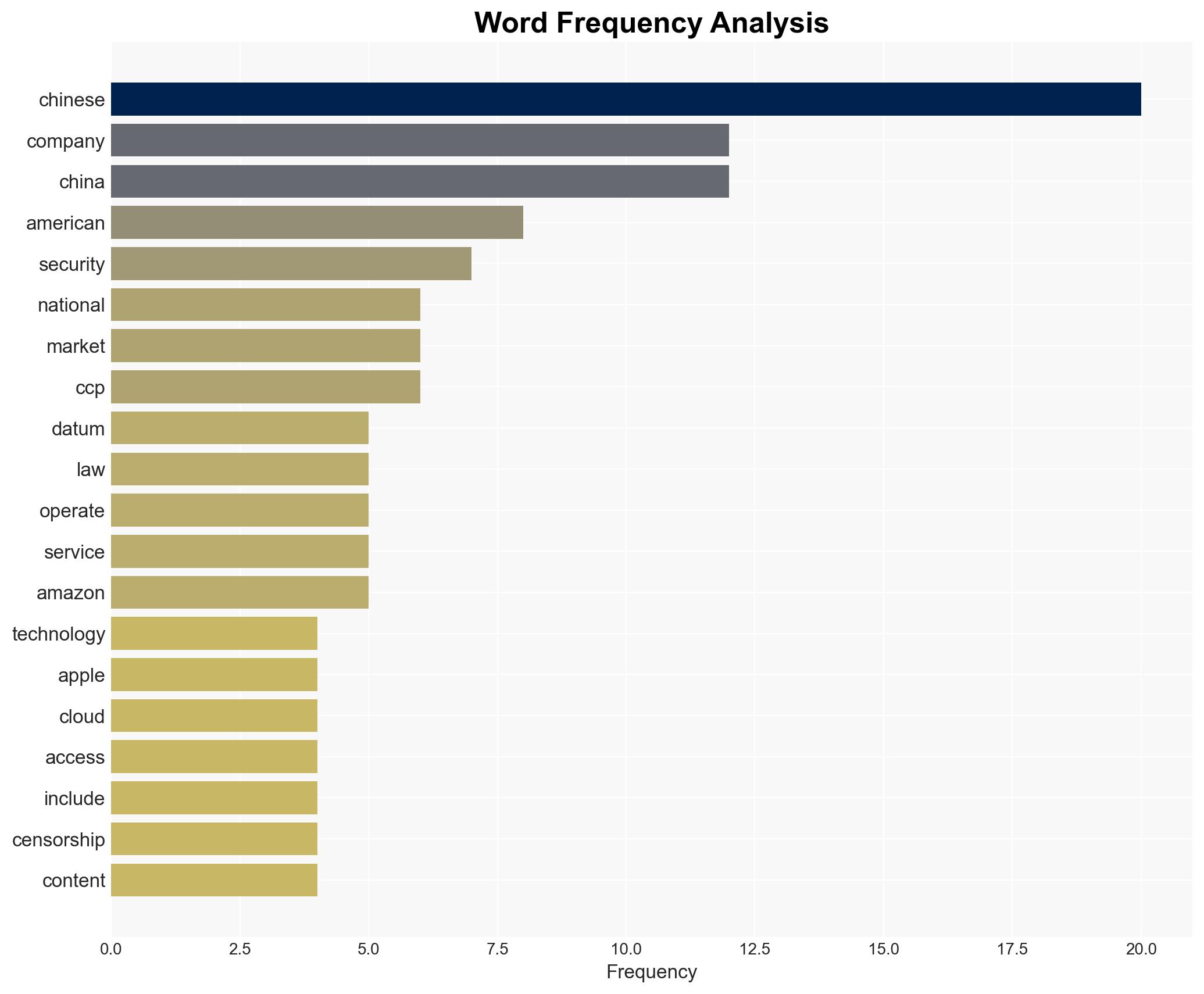
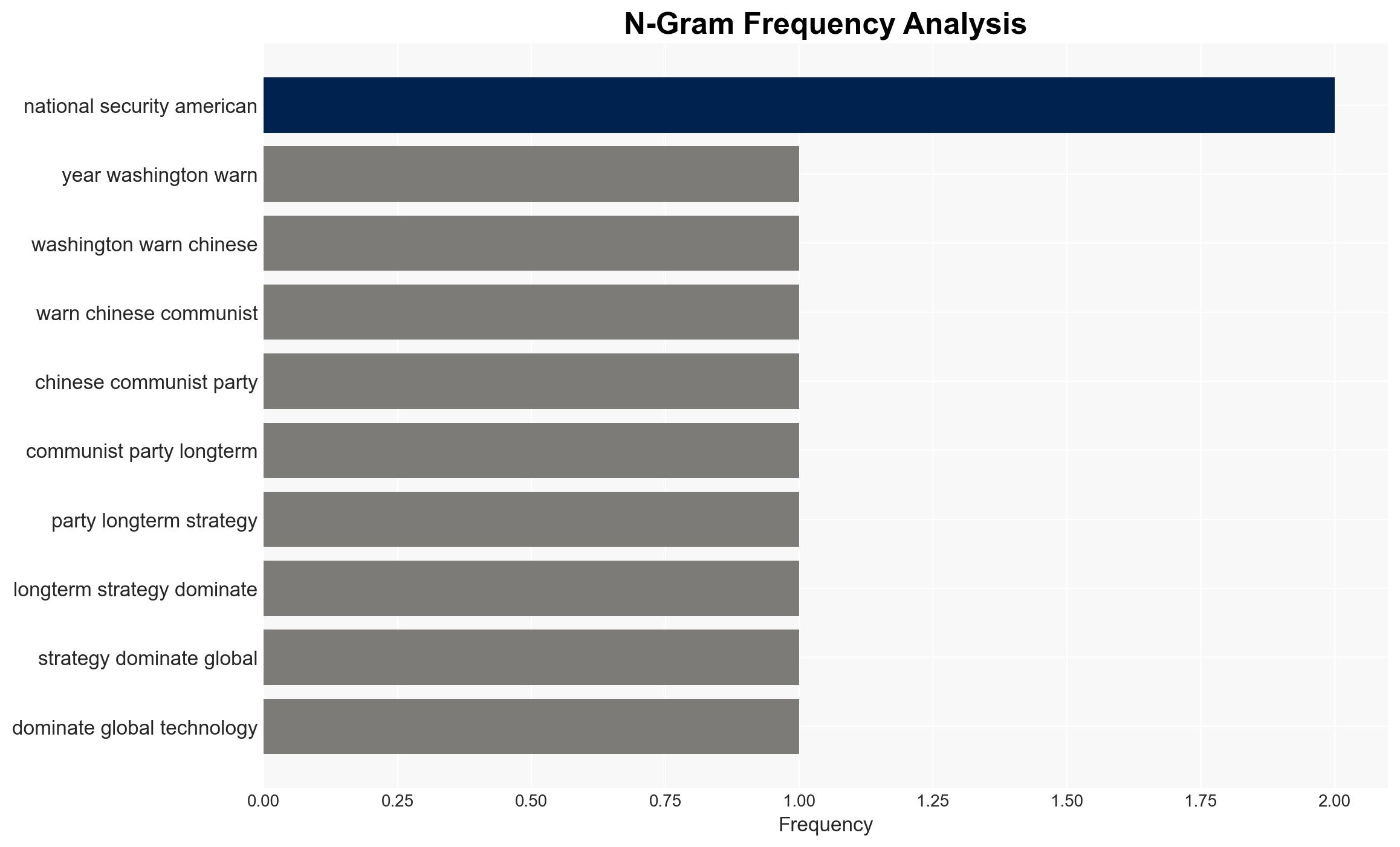
Major American technology companies are increasingly accommodating Chinese government demands, potentially compromising U.S. national security and values. This behavior is driven by market access ambitions and is supported by both large and small American investors. The most likely hypothesis is that economic incentives are outweighing national security concerns, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to documented corporate behaviors but incomplete data on internal decision-making processes.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: American tech companies are prioritizing market access in China over U.S. national security and ethical standards. This is supported by documented actions such as data storage compliance and content censorship. However, the internal motivations and strategic calculations remain partially opaque.
- Hypothesis B: These companies are attempting to balance compliance with Chinese regulations while maintaining core values, with compromises being strategic rather than indicative of a broader shift in priorities. This is contradicted by the extent of compliance and lack of transparency in decision-making.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the clear pattern of behavior aligning with Chinese government demands, though shifts in corporate governance or policy changes could alter this assessment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Companies act primarily in pursuit of profit; Chinese market access is a critical driver; U.S. regulatory frameworks are insufficient to deter compliance with foreign demands.
- Information Gaps: Detailed internal decision-making processes and strategic discussions within these companies; specific U.S. government responses or policy plans.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for corporate narratives to downplay security risks; reliance on public reporting may omit classified or proprietary information.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased U.S. regulatory scrutiny and potential legislative action against tech companies. It may also exacerbate geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China, impacting global technology standards and data governance.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased U.S.-China tensions and legislative actions targeting tech companies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and espionage facilitated by compliance with Chinese regulations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for enhanced Chinese influence over global information flows and technology standards.
- Economic / Social: Possible impacts on U.S. tech sector competitiveness and public trust in tech companies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of tech company compliance with foreign regulations; engage with corporate leaders to assess strategic priorities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures and partnerships to mitigate data security risks; consider legislative frameworks to address foreign compliance issues.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Companies realign priorities with national security interests. Worst: Continued compliance leads to significant data breaches. Most-Likely: Incremental policy adjustments with ongoing tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Apple
- Meta
- Amazon
- Guizhou Cloud Big Data
- Chinese Communist Party (CCP)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, national security, tech compliance, U.S.-China relations, data governance, corporate ethics, market access, regulatory scrutiny
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us