Black Cat Cybercrime Group Launches SEO Poisoning Attack to Distribute Data-Stealing Malware via Fake Softwar…
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Black Cat Behind SEO Poisoning Malware Campaign Targeting Popular Software Searches
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
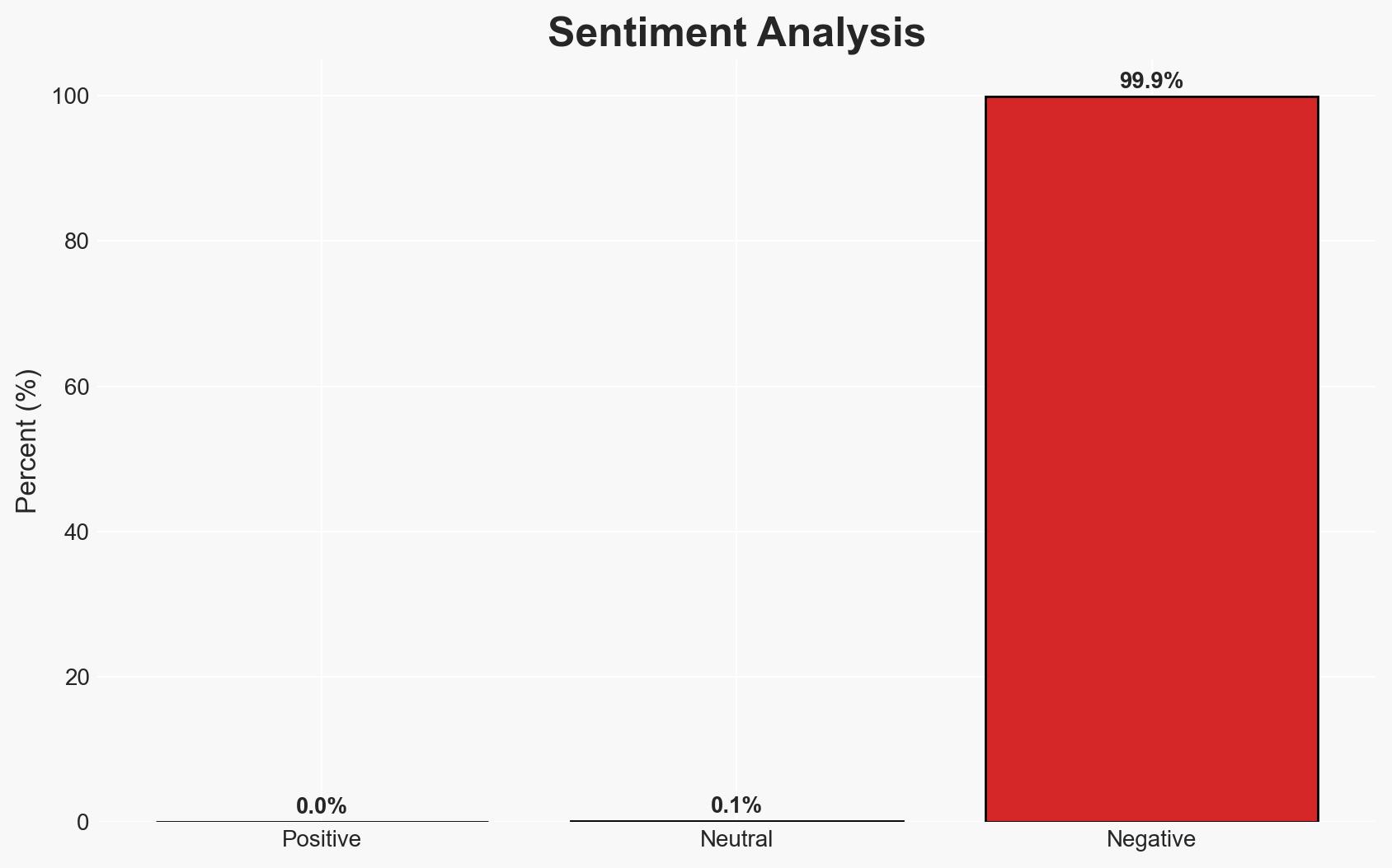
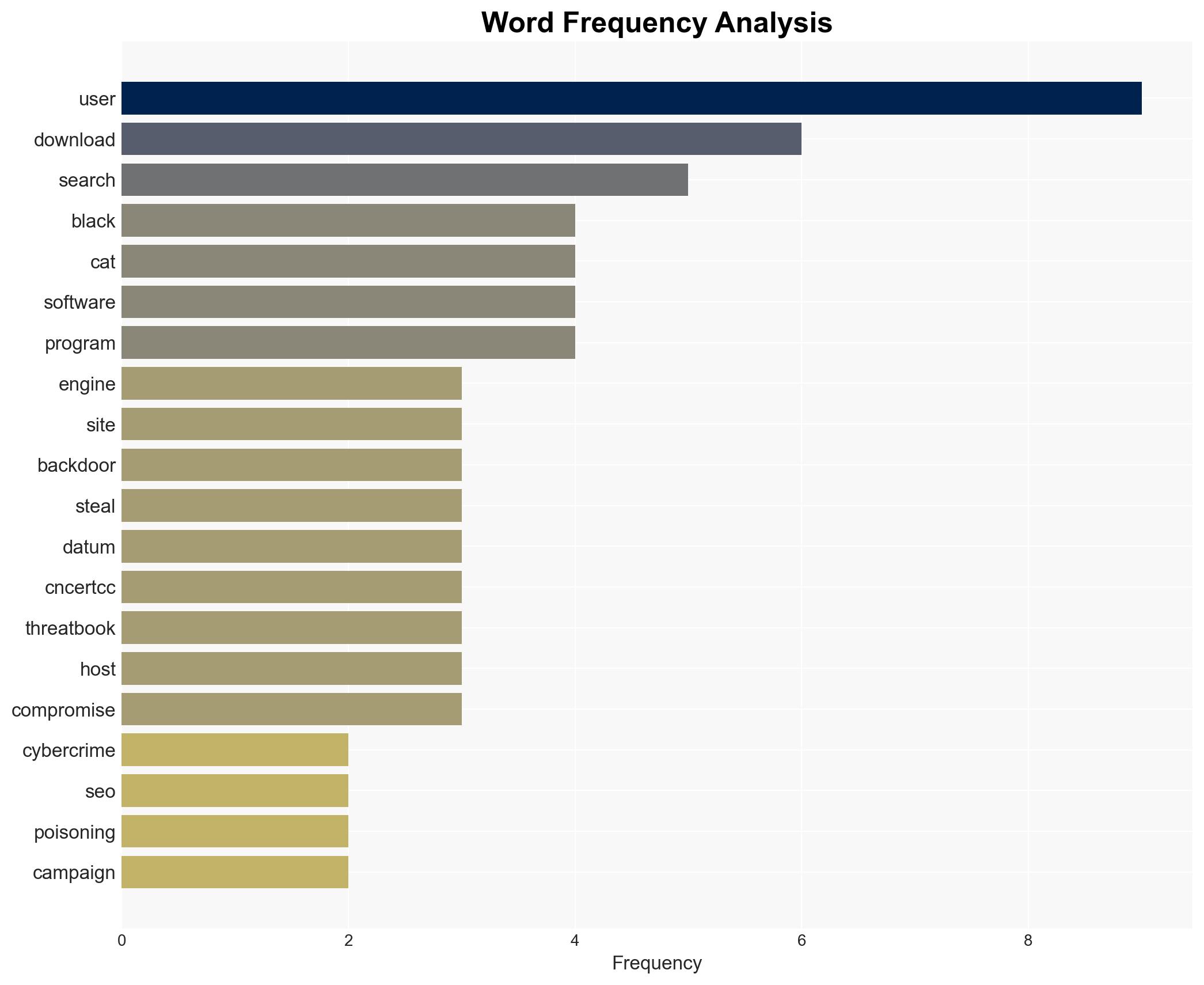
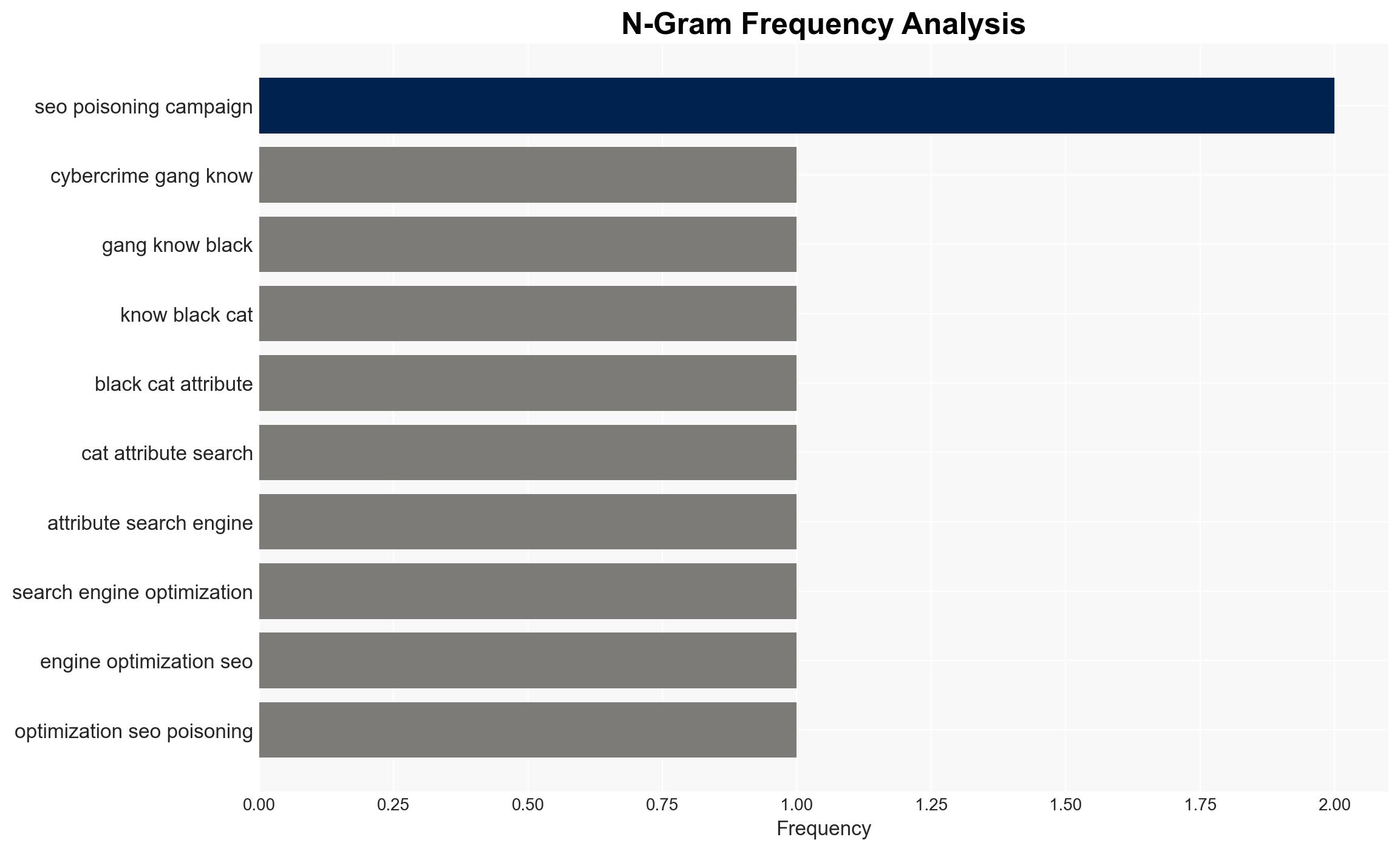
The Black Cat cybercrime group is conducting an SEO poisoning campaign targeting users searching for popular software, leading to data theft via a backdoor Trojan. This activity primarily affects Chinese users and poses significant cybersecurity risks. The most likely hypothesis is that Black Cat is leveraging these tactics for financial gain and data collection. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Black Cat is conducting the SEO poisoning campaign primarily for financial gain, as evidenced by their history of stealing cryptocurrency and targeting popular software searches to maximize victim numbers. However, the extent of their financial motivation remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign is part of a broader cyber-espionage effort, aiming to collect sensitive data from a wide range of users, potentially for state-sponsored purposes. Contradicting this is the lack of direct evidence linking Black Cat to state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the group’s previous financial theft activities and the nature of the targeted software searches. Indicators such as a shift in targets or evidence of state sponsorship could alter this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Black Cat is primarily financially motivated; the campaign targets Chinese users due to language and domain indicators; the malware’s primary function is data theft.
- Information Gaps: The identity and exact motivations of Black Cat; the full scope of compromised data; potential links to other cybercrime or espionage groups.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing motivations without direct evidence; risk of deception in malware attribution and intent due to sophisticated obfuscation tactics.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased cybersecurity threats and data breaches, affecting both individuals and organizations. The campaign’s evolution could influence broader cybercrime trends and international cybersecurity policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on international relations if state sponsorship is suspected; increased pressure on China to address domestic cybercrime.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for digital infrastructure; potential for similar tactics to be adopted by other groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased awareness and adaptation of SEO poisoning tactics; potential for widespread misinformation and data manipulation.
- Economic / Social: Economic impact from data breaches and financial theft; potential erosion of trust in digital platforms and software downloads.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of SEO poisoning activities; conduct awareness campaigns on safe software downloading practices; collaborate with search engines to identify and remove fraudulent sites.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced detection and response capabilities; strengthen international cooperation on cybercrime.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of the campaign with minimal data loss, leading to improved cybersecurity measures.
- Worst: Escalation of attacks with significant financial and data losses, prompting international tensions.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with gradual improvements in detection and prevention, driven by increased awareness and collaboration.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Black Cat cybercrime group
- National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China (CNCERT/CC)
- Beijing Weibu Online (ThreatBook)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, SEO poisoning, data theft, malware, financial gain, China
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us