Botnet Exploits AWS Outage to Launch Attacks Across 28 Nations, Targeting Vulnerable IoT Devices
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
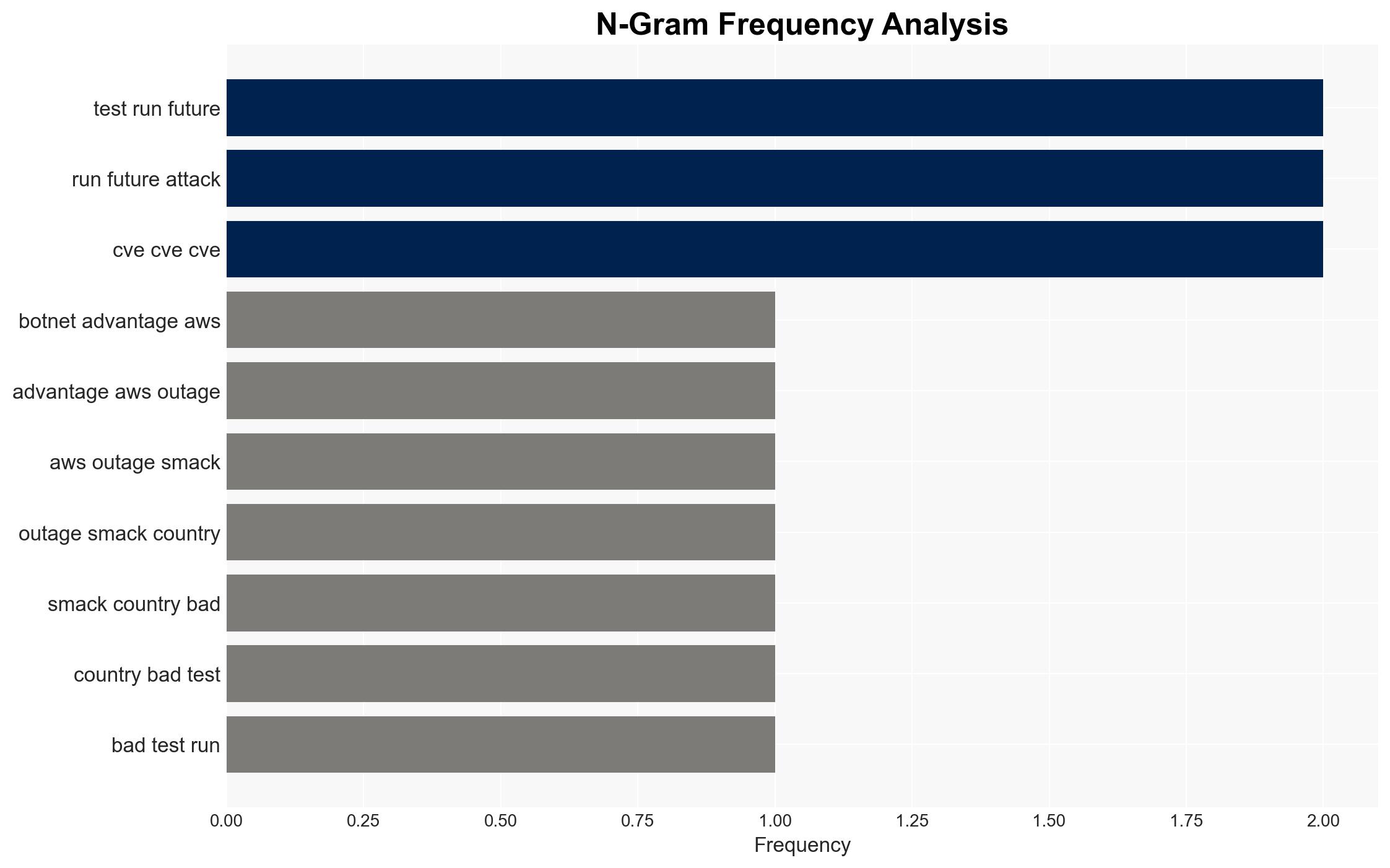
Intelligence Report: Botnet takes advantage of AWS outage to smack 28 countries
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
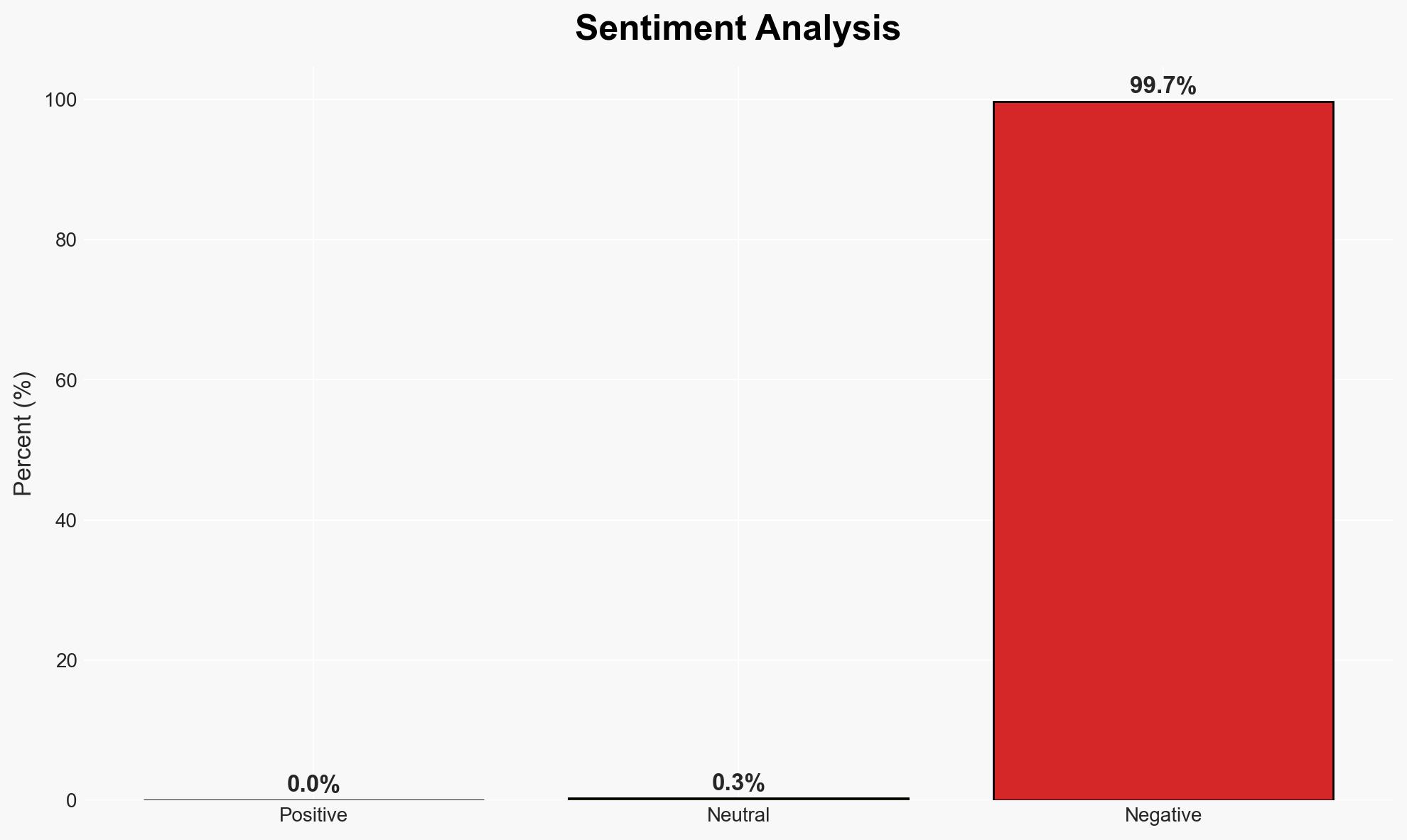
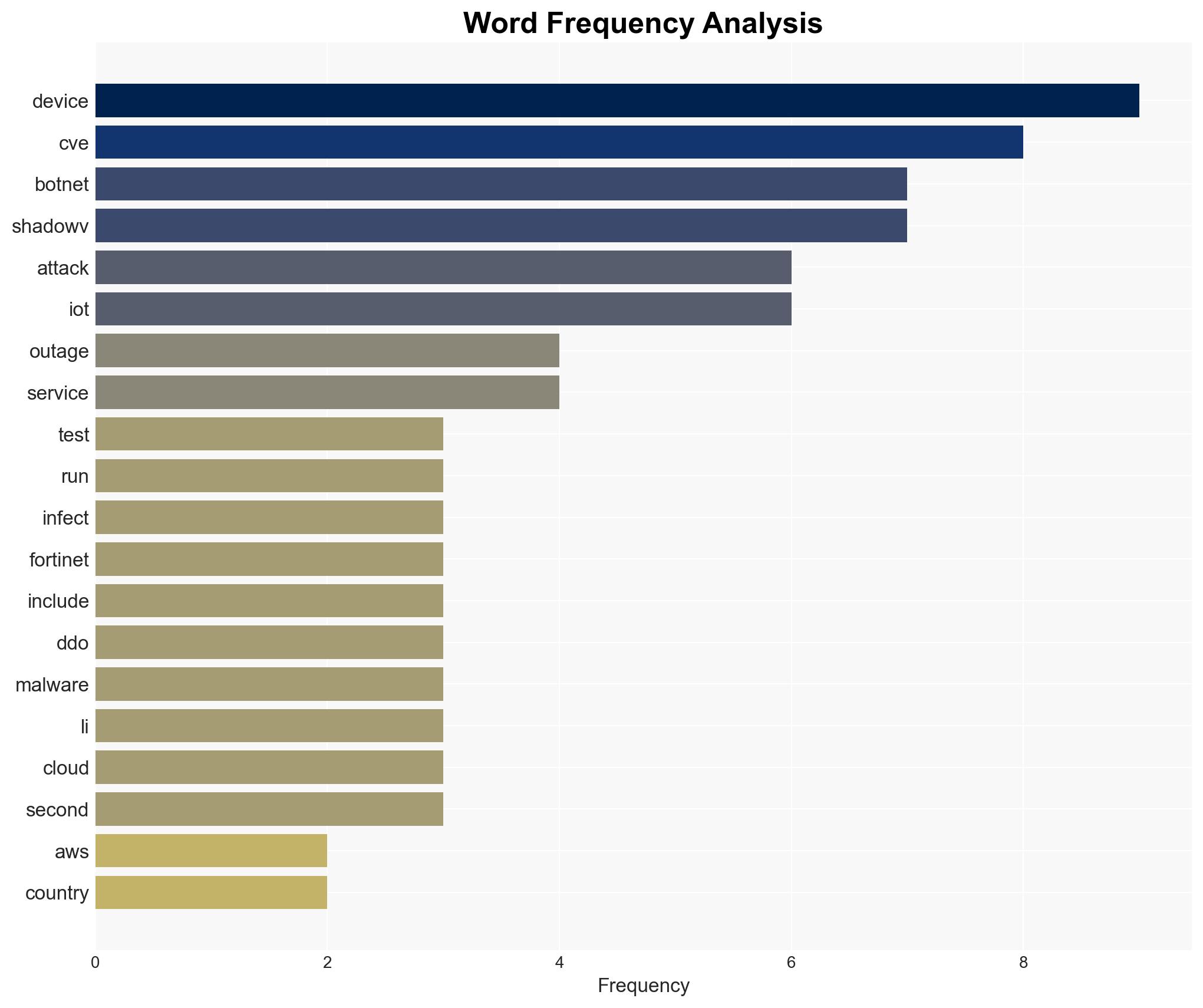
The ShadowV botnet exploited a recent AWS outage to infect IoT devices across 28 countries, potentially as a test run for future attacks. This incident highlights significant vulnerabilities in IoT security, with implications for multiple sectors including technology and government. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete data on the botnet’s full capabilities and intentions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The ShadowV botnet’s activity during the AWS outage was a deliberate test run for a larger, coordinated attack. This hypothesis is supported by the timing of the attack and the widespread infection across multiple sectors. However, the lack of concrete evidence on the botnet’s ultimate objectives introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The botnet’s actions were opportunistic, exploiting the AWS outage without a premeditated plan for future attacks. This is contradicted by the organized nature of the infection and the previous targeting of AWS EC2 instances, suggesting a strategic approach.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the systematic nature of the attack and its alignment with previous botnet activities. Indicators such as further coordinated attacks or increased sophistication in malware could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The botnet’s primary goal is to test vulnerabilities for future attacks; IoT devices remain a critical vulnerability; AWS outage provided a unique opportunity for exploitation.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the botnet’s command-and-control infrastructure; specific motivations and affiliations of the attackers; comprehensive impact assessment on all affected sectors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; risk of deception by attackers to mask true intentions or capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ShadowV botnet’s exploitation of an AWS outage could signal an evolving threat landscape where cloud service vulnerabilities are increasingly targeted. This development may prompt shifts in cybersecurity strategies and policies globally.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cybersecurity responsibilities and cloud service dependencies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alertness and resource allocation towards IoT and cloud security by national security agencies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting cloud infrastructure and IoT devices, necessitating enhanced defensive measures.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions in affected sectors could lead to economic losses and erode public trust in cloud services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough vulnerability assessments of IoT devices; enhance monitoring of cloud service outages; share threat intelligence across sectors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for improved IoT security standards; invest in cloud infrastructure resilience; implement regular security drills simulating similar attack scenarios.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enhanced security measures prevent further botnet exploitation, leading to decreased threat levels.
- Worst: Botnet evolves, launching more sophisticated attacks causing widespread disruption.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks exploiting similar vulnerabilities, prompting gradual improvements in security postures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet FortiGuard Labs
- Vincent Li (Antivirus Analyst)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us