Canopy Health Delays Notification of Cyber Attack Impacting Patient Data for Six Months
Published on: 2026-01-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Second health provider Canopy Health hit in major cyber attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
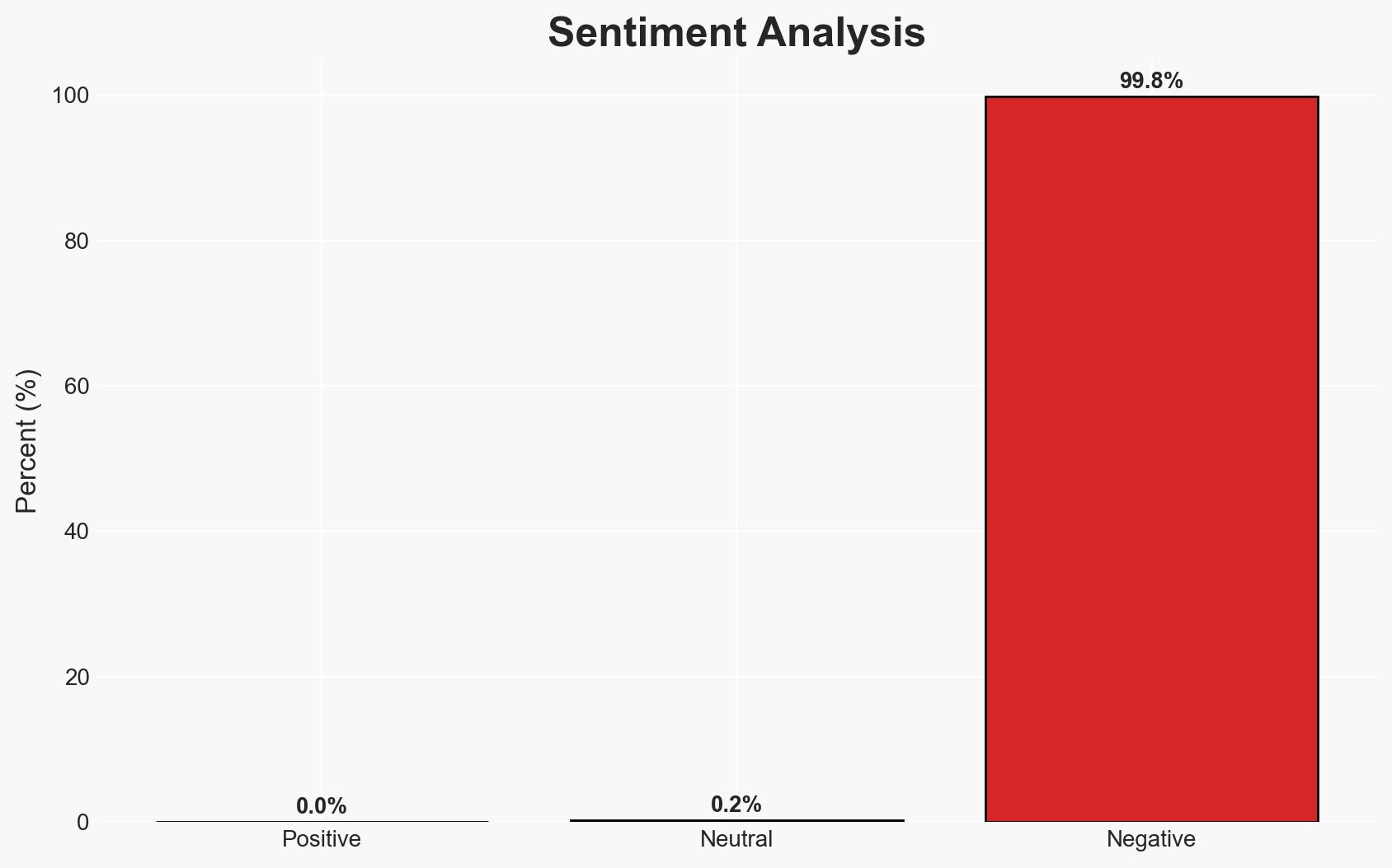
The Canopy Health cyber attack has exposed significant vulnerabilities in the healthcare sector’s data security practices, affecting patient trust and potentially compromising sensitive information. The delay in breach notification raises concerns about compliance and transparency. The most likely hypothesis is that the breach was opportunistic rather than targeted, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The cyber attack on Canopy Health was an opportunistic breach by cybercriminals seeking financial gain. Supporting evidence includes the lack of immediate high-value data theft and the general nature of the breach. Contradicting evidence includes the potential access to sensitive health data, which could indicate a more targeted approach.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was a targeted attack aimed at accessing sensitive health information for strategic purposes, such as identity theft or blackmail. Supporting evidence is the potential access to sensitive health data. Contradicting evidence includes the company’s statement that no critical financial data was compromised, suggesting a lack of focus on high-value targets.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the absence of evidence indicating a targeted attack. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of specific demands or the use of stolen data in targeted campaigns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was not state-sponsored; the attackers had limited access to high-value data; Canopy Health’s cybersecurity measures were below industry standards; the delay in notification was due to internal policy rather than intentional obfuscation.
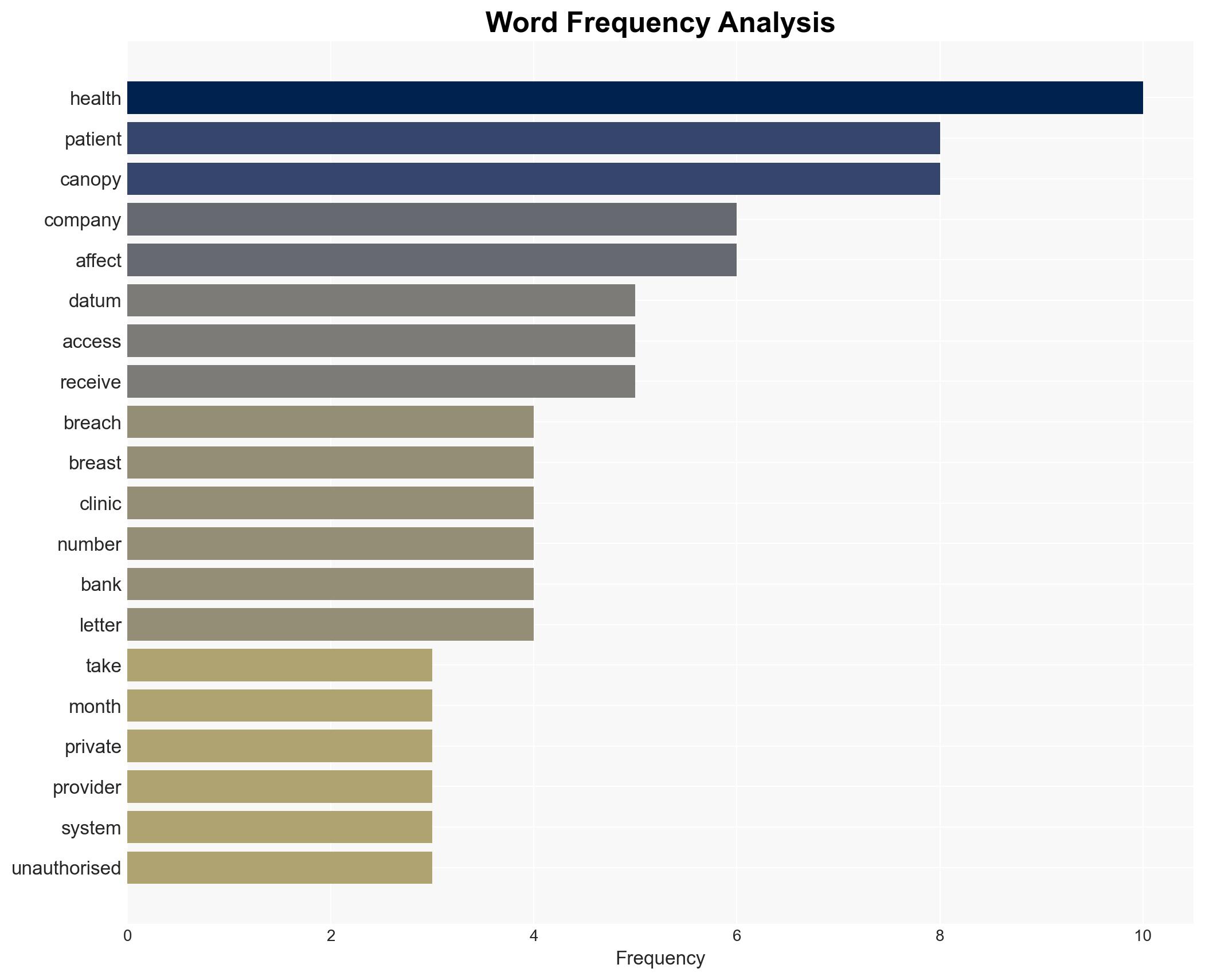
- Information Gaps: The identity and motives of the attackers; the full extent of data accessed; specific vulnerabilities exploited in the breach.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in company statements minimizing the breach impact; possible underreporting of the breach’s severity to protect reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of healthcare data security practices and regulatory changes. The breach may also erode public trust in healthcare providers and government-funded programs.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regulatory changes and increased government oversight in healthcare data security.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of similar attacks on healthcare providers, potentially affecting national security if sensitive data is compromised.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlighting vulnerabilities in healthcare cybersecurity could lead to increased cybercriminal activity targeting this sector.
- Economic / Social: Loss of patient trust could lead to reduced participation in healthcare programs and financial losses for affected providers.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit of healthcare providers; enhance breach notification protocols; engage with cybersecurity experts to mitigate immediate risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop sector-wide cybersecurity standards; foster public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity training for healthcare staff.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Strengthened cybersecurity and restored public trust. Worst: Continued breaches leading to significant data loss and regulatory penalties. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security with ongoing challenges in public trust.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
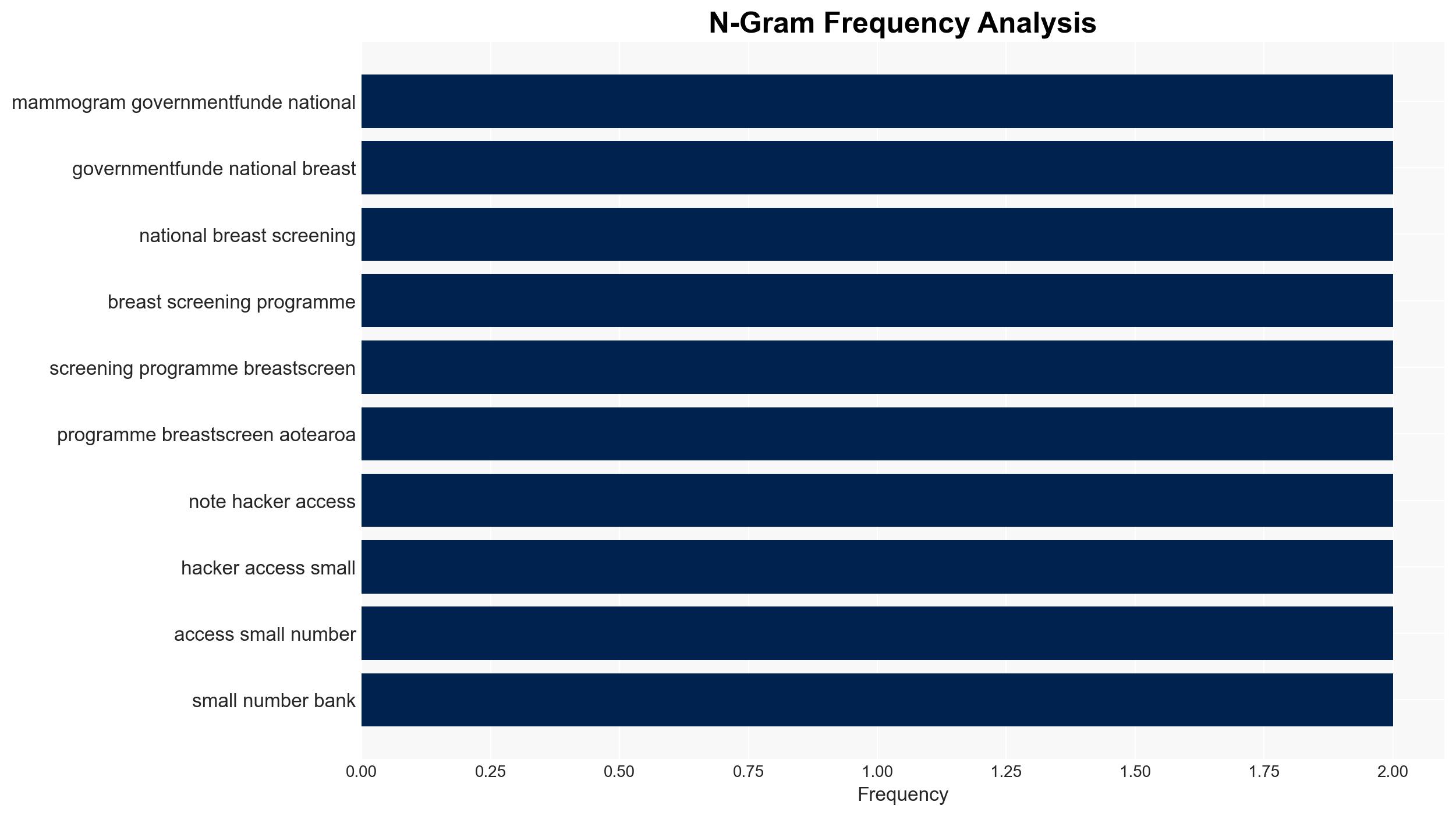
- Canopy Health
- BreastScreen Aotearoa
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, healthcare data breach, patient privacy, regulatory compliance, public trust, cybercrime, data protection
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us