Chad Faces Severe Challenges While Hosting Over 900,000 Sudanese Refugees Amid Ongoing Conflict
Published on: 2026-02-06
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chad Africa’s refugee haven struggles with its own stark challenges
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
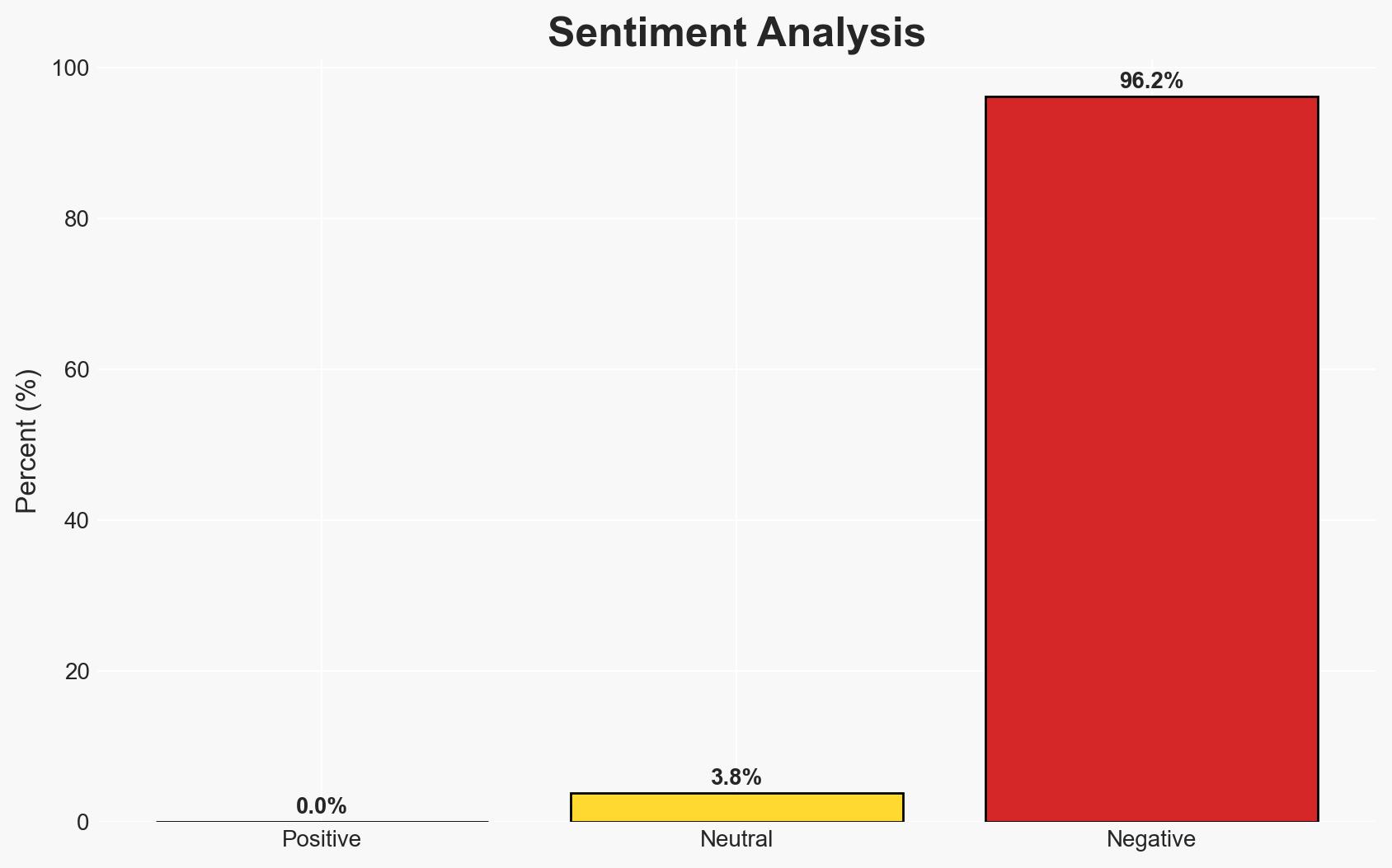
Chad is experiencing severe humanitarian and security challenges due to the influx of Sudanese refugees, compounded by internal vulnerabilities such as poverty, climate change impacts, and extremist threats. The most likely hypothesis is that Chad will continue to face increasing pressure on its resources and stability, with moderate confidence in this assessment. The situation affects regional stability and humanitarian conditions significantly.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Chad’s current challenges will exacerbate, leading to increased instability and humanitarian crises. Supporting evidence includes the high number of refugees, ongoing climate impacts, and existing poverty levels. Contradicting evidence is limited but could include potential international aid increases.
- Hypothesis B: Chad will stabilize through international support and effective management of refugee and internal challenges. Supporting evidence could include potential international interventions and aid. However, current evidence of effective management is limited.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the overwhelming evidence of resource strain and ongoing crises. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant increases in international aid or successful policy interventions by the Chadian government.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Chad will continue to receive refugees; international aid will not significantly increase; climate impacts will persist; extremist threats will remain active.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of current humanitarian interventions and the extent of international aid commitments.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from humanitarian agencies; risk of underreporting by local government to secure more aid.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing situation in Chad could lead to further destabilization in the region, affecting neighboring countries and potentially increasing refugee flows. This could exacerbate regional tensions and strain international humanitarian resources.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regional instability and international diplomatic pressure on Chad and its neighbors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of extremist activities exploiting the humanitarian crisis and resource scarcity.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited direct implications, but potential for misinformation campaigns targeting refugee and aid narratives.
- Economic / Social: Further economic strain on Chad, increased poverty, and social tensions due to resource competition.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of refugee movements and resource allocation; engage with international partners for immediate aid.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, enhance regional cooperation, and strengthen local governance and infrastructure.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Significant international aid stabilizes the situation.
- Worst: Resource depletion leads to widespread conflict and humanitarian disaster.
- Most-Likely: Continued strain with periodic international interventions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- UN High Commissioner for Refugees Barham Salih
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
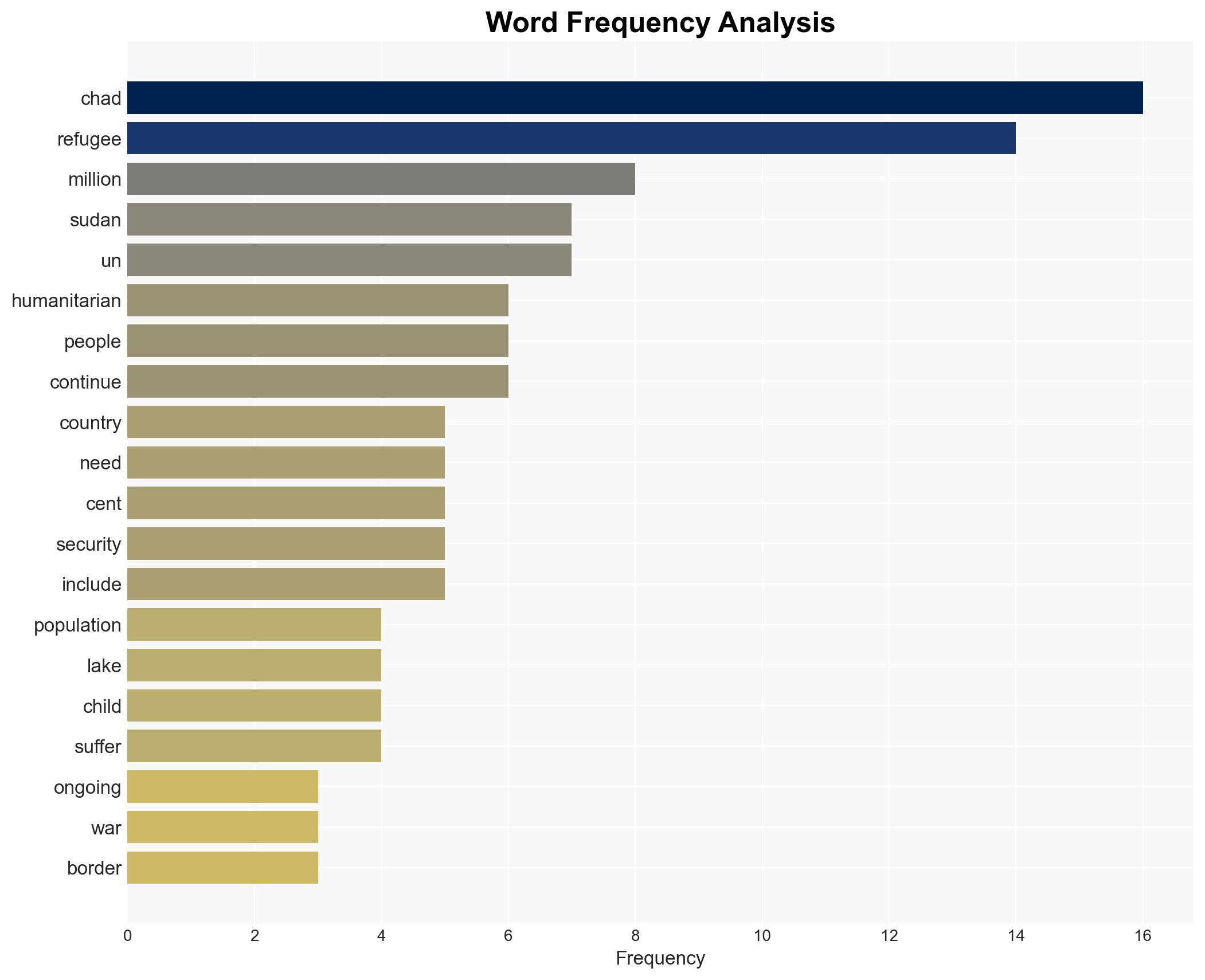
Counter-Terrorism, refugee crisis, humanitarian aid, regional stability, climate change, poverty, extremist threats, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us