Chat Control stumbles again as EU retreats from mandatory scanning – Cointelegraph
Published on: 2025-11-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
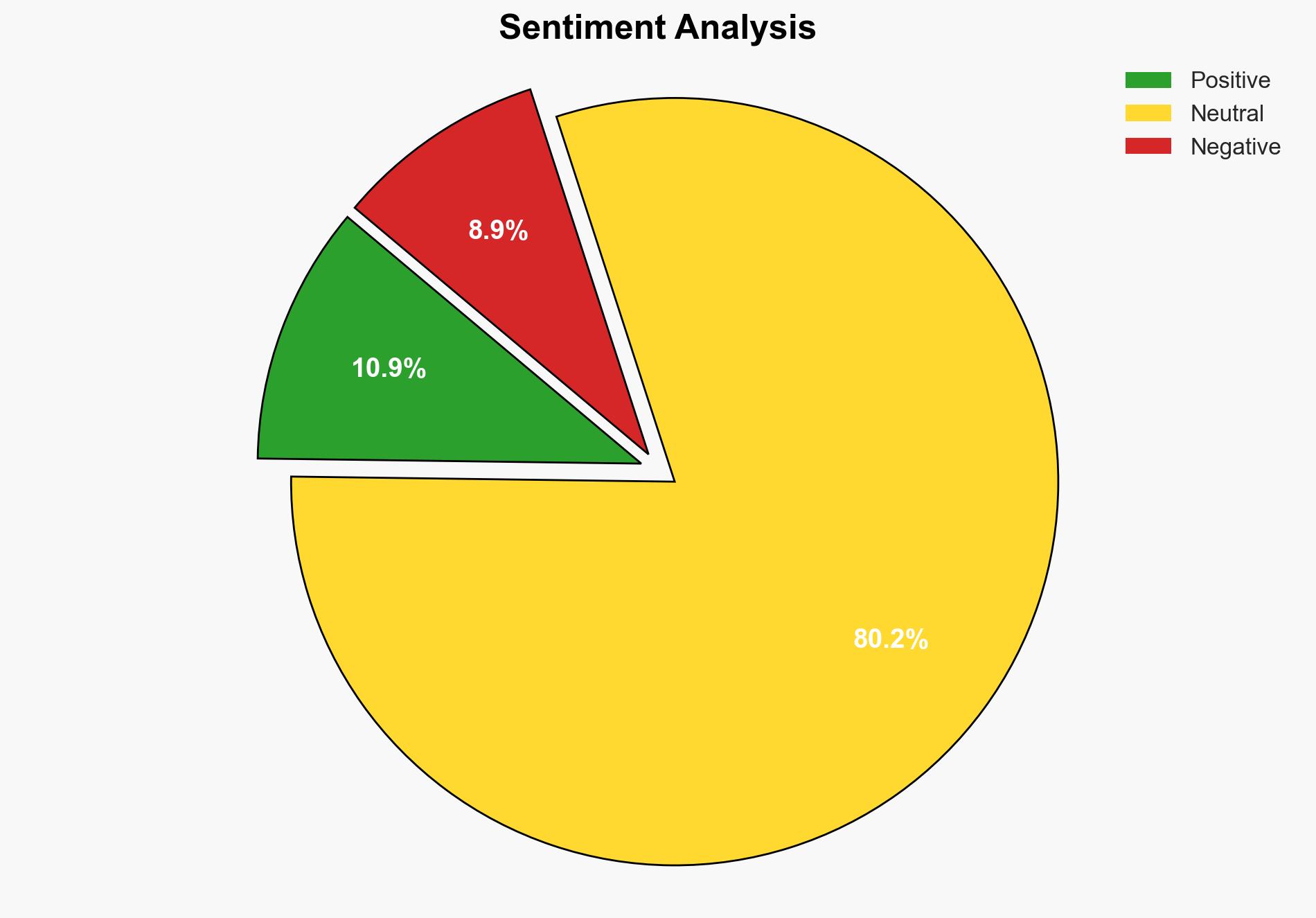
The European Union’s retreat from mandatory chat scanning reflects significant resistance from digital rights activists and member states, notably Germany. The most supported hypothesis is that the EU will continue to face challenges in implementing mandatory scanning due to privacy concerns and political opposition. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action: Monitor legislative developments and engage with stakeholders to balance privacy and security concerns.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The EU will eventually implement mandatory chat scanning with modifications to address privacy concerns. This hypothesis suggests that the EU might find a compromise that satisfies both security needs and privacy advocates.
Hypothesis 2: The EU will abandon mandatory chat scanning entirely due to sustained opposition and potential legal challenges. This hypothesis is supported by the current retreat and the strong stance of influential member states like Germany.
The second hypothesis is more likely given the current political climate and the EU’s history of valuing privacy rights. However, the possibility of a modified implementation cannot be entirely ruled out.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that privacy concerns will continue to outweigh security arguments in the EU. Another assumption is that member states will maintain their current positions.
Red Flags: Potential deception indicators include the EU’s use of vague language in draft regulations, which could be a tactic to reintroduce scanning measures later. The rapid shifts in legislative proposals may also indicate internal disagreements or external pressures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The EU’s struggle with chat control legislation could lead to increased fragmentation within the bloc, impacting its ability to present a unified front on cybersecurity issues. Politically, this may embolden digital rights groups and influence other privacy-related legislation. Economically, tech companies may face uncertainty, affecting their operations and compliance strategies. Informationally, the debate could fuel misinformation campaigns targeting EU policies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage with EU policymakers to advocate for balanced solutions that address both privacy and security concerns.
- Monitor the legislative process closely, particularly the positions of key member states like Germany and Denmark.
- Best-case scenario: The EU finds a compromise that enhances security without compromising privacy, strengthening its cybersecurity framework.
- Worst-case scenario: Continued legislative gridlock leads to a loss of trust in EU institutions and weakens its cybersecurity posture.
- Most-likely scenario: The EU will continue to face challenges in passing comprehensive chat control legislation, leading to a piecemeal approach.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Patrick Breyer, German Pirate Party politician, is a notable opponent of mandatory chat scanning. The European Commission, as the EU’s primary executive branch, plays a central role in legislative proposals.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Digital Rights, European Union, Privacy Legislation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·