China cautions Japan against nuclear armament, warning it could lead to global catastrophe amid regional tens…
Published on: 2026-01-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
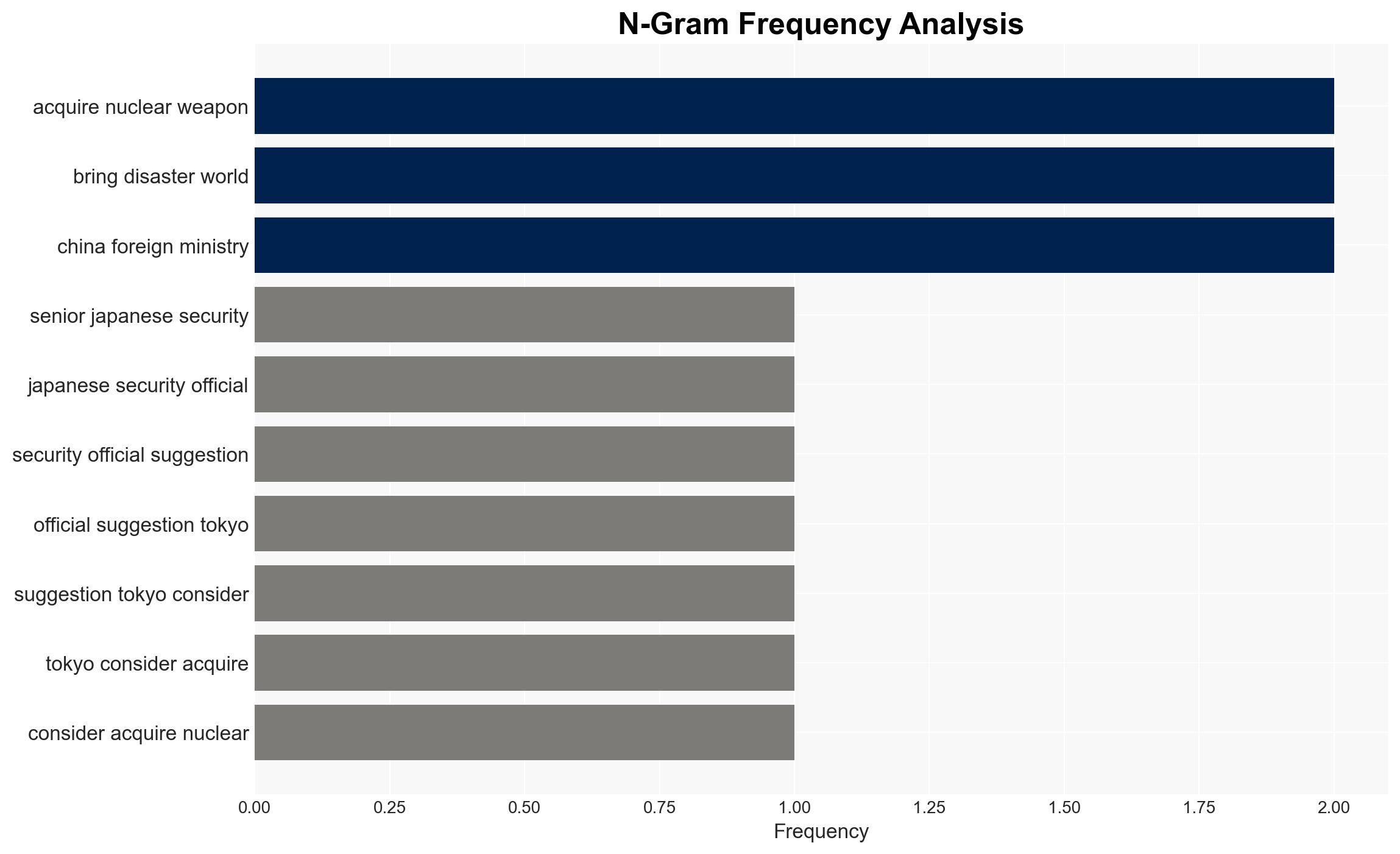
Intelligence Report: China warns Japan nuclear weapons pursuit would bring disaster to the world after official floats acquiring nukes
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The suggestion by a Japanese security official to consider nuclear armament has triggered significant regional backlash, particularly from China, and has highlighted underlying tensions regarding Japan’s security posture. The most likely hypothesis is that Japan will maintain its non-nuclear stance due to domestic and international pressures, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Japan will reconsider its non-nuclear principles and potentially pursue nuclear weapons to counter regional threats. Supporting evidence includes the official’s remarks on the unreliability of the U.S. nuclear umbrella and regional security threats. Contradicting evidence includes significant domestic opposition and legal hurdles.
- Hypothesis B: Japan will uphold its non-nuclear principles due to domestic opposition, international treaties, and diplomatic pressures. Supporting evidence includes reaffirmations by Japanese officials of their commitment to non-nuclear principles and strong regional and domestic backlash against the suggestion.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the immediate reaffirmation of non-nuclear principles by Japanese officials and the significant political, legal, and social barriers to nuclear armament. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in regional security dynamics or shifts in domestic public opinion.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Japan’s government will prioritize international diplomatic relations over unilateral security measures; domestic public opinion will continue to oppose nuclear armament; regional powers will maintain their current stance against Japanese nuclear armament.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into the internal Japanese government deliberations on nuclear policy; potential shifts in U.S. security commitments to Japan.
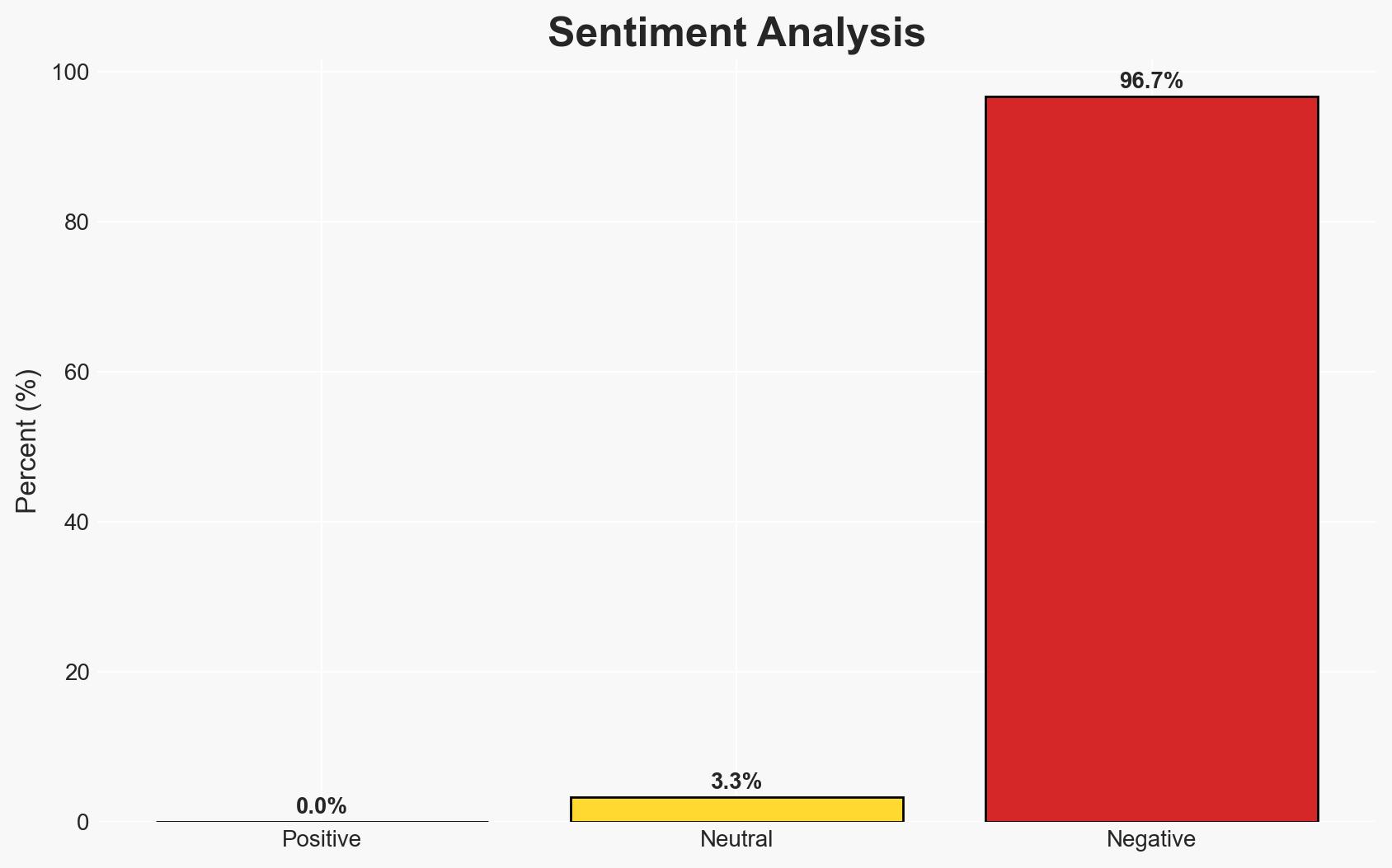
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in media reporting on the official’s remarks; risk of Chinese and North Korean statements being used as strategic messaging rather than genuine security assessments.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate regional tensions and influence Japan’s security policies. It may also impact Japan’s diplomatic relations and domestic political landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased diplomatic strain between Japan and neighboring countries, potential shifts in regional alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened regional security tensions, potential arms race in Northeast Asia.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting Japanese political and defense sectors to influence policy decisions.
- Economic / Social: Domestic unrest or political instability if public opinion shifts significantly; potential economic impacts from strained international relations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Japanese government statements and policy shifts; engage in diplomatic dialogue with regional partners to mitigate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances and security partnerships; invest in public diplomacy to reinforce Japan’s non-nuclear stance.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Japan reaffirms non-nuclear stance, regional tensions ease.
- Worst: Japan pursues nuclear capabilities, triggering regional arms race.
- Most-Likely: Japan maintains current policy, but regional tensions persist.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi (Adviser involved in remarks)
- Chief Cabinet Secretary Minoru Kihara (Reaffirmed non-nuclear stance)
- China’s Foreign Ministry (Issued warnings)
- Nihon Hidankyo (Atomic bomb survivors group)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
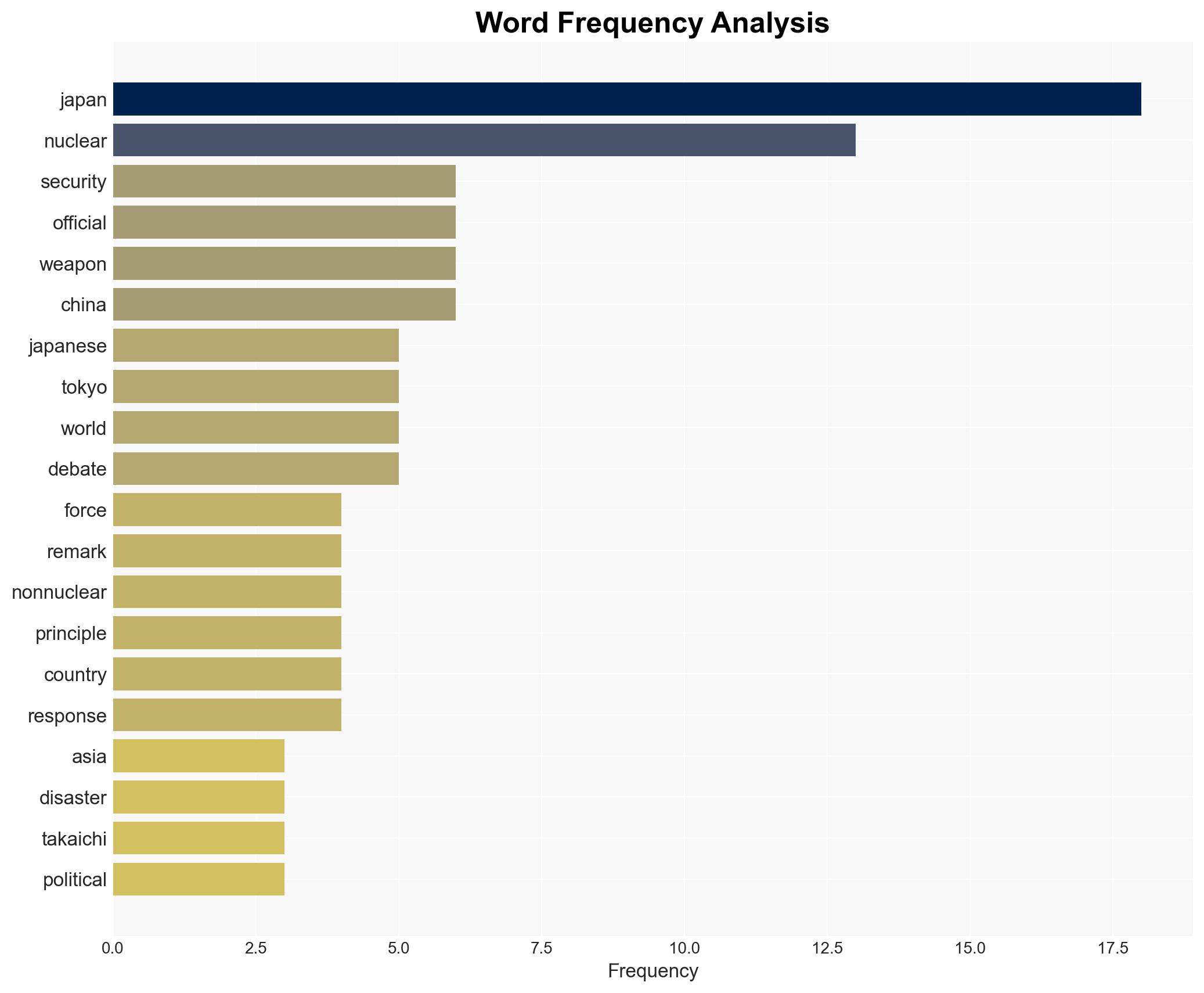
regional conflicts, nuclear policy, regional security, Japan-China relations, non-proliferation, diplomatic tensions, Northeast Asia, public opinion
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us