China-Linked UAT-8099 Exploits IIS Servers in Asia Using BadIIS Malware for SEO Fraud
Published on: 2026-01-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: China-Linked UAT-8099 Targets IIS Servers in Asia with BadIIS SEO Malware
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
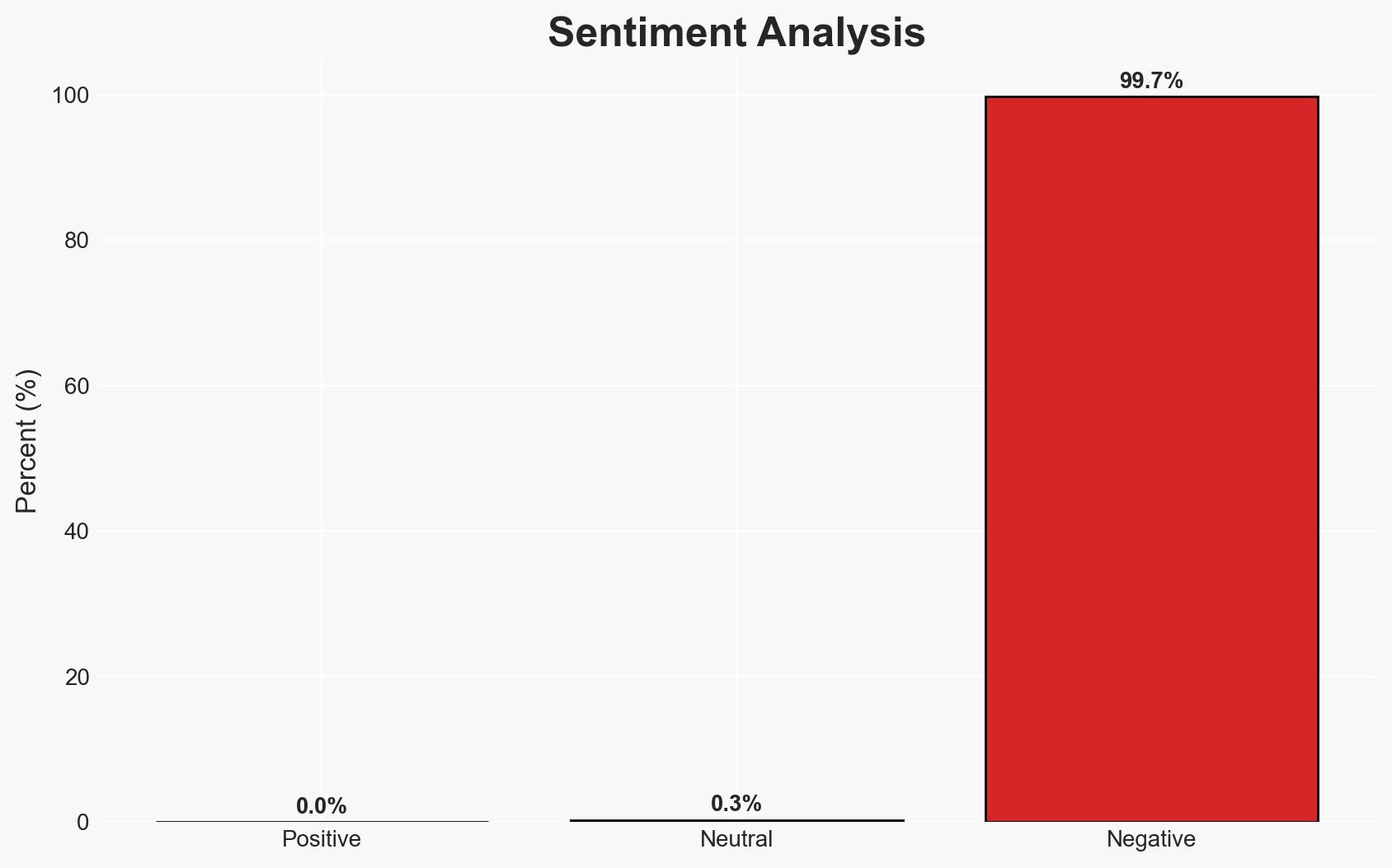
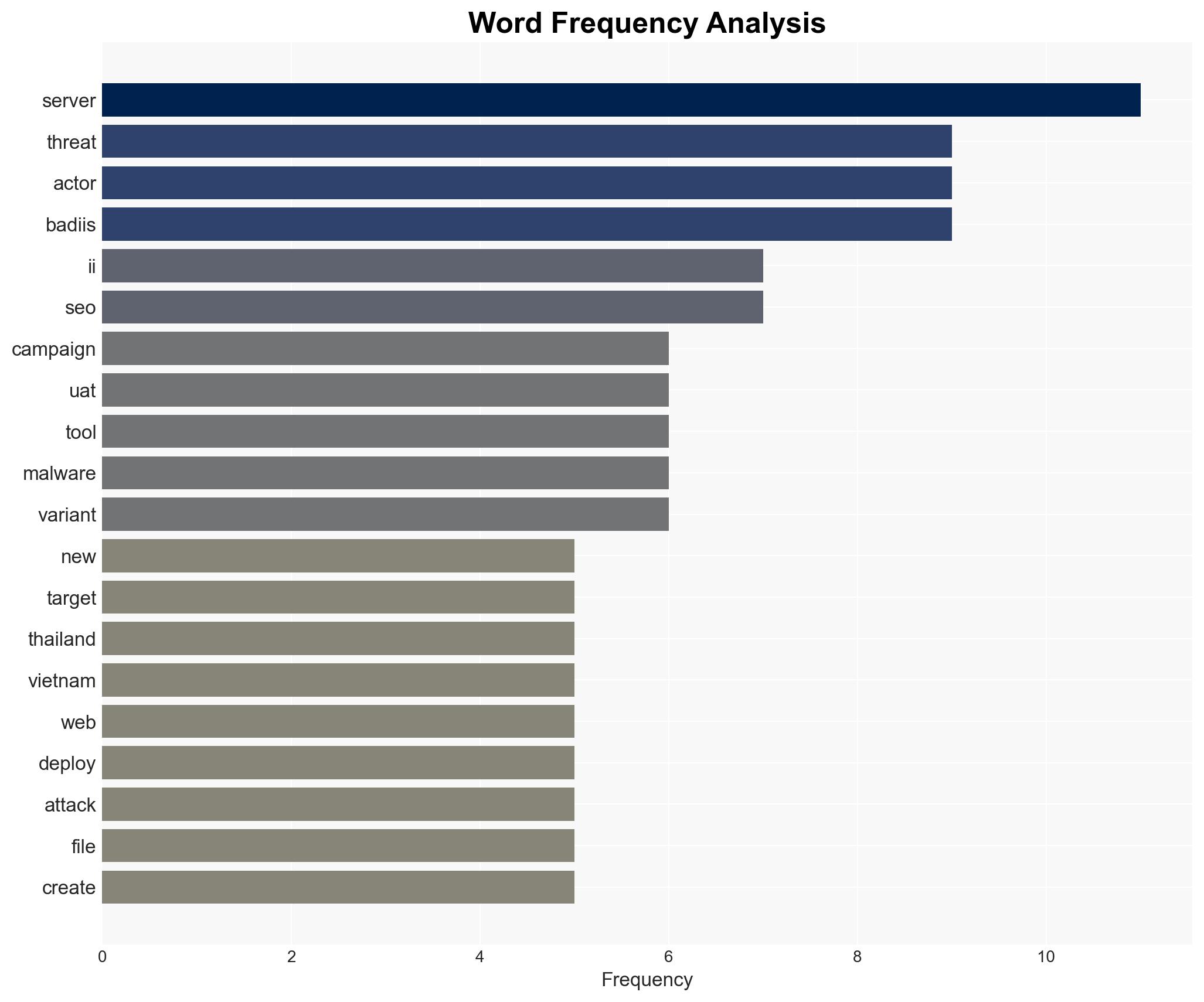
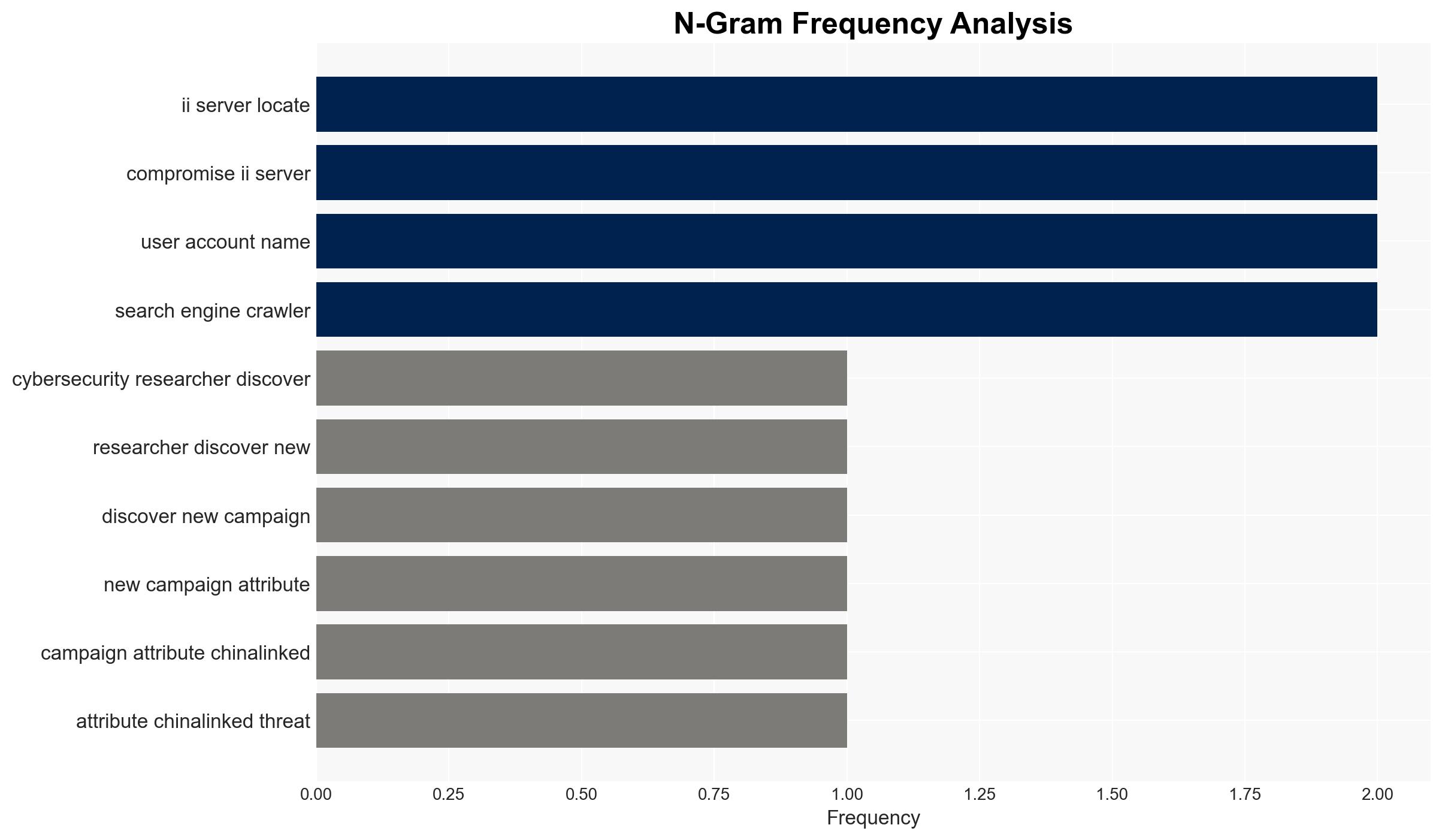
The China-linked threat actor UAT-8099 has been targeting IIS servers in Asia, particularly in Thailand and Vietnam, using BadIIS malware for SEO fraud. The campaign demonstrates a shift towards regional specificity and increased use of legitimate tools to evade detection. The overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the campaign’s scale and potential attribution biases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: UAT-8099 is primarily motivated by financial gain through SEO fraud, leveraging regional server vulnerabilities. This is supported by the focus on SEO tactics and regional targeting but contradicted by the lack of direct financial theft evidence.
- Hypothesis B: UAT-8099’s activities are part of a broader geopolitical strategy to destabilize regional digital infrastructure. This is supported by the strategic targeting of multiple countries but lacks direct evidence linking to state-sponsored objectives.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit use of SEO fraud tactics and the absence of evidence for broader geopolitical aims. Indicators such as changes in targeting patterns or discovery of state affiliations could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: UAT-8099 is of Chinese origin; the primary goal is SEO fraud; the campaign is ongoing; regional focus is intentional.
- Information Gaps: Full scale of the campaign; detailed attribution to Chinese state entities; financial impact assessment.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential attribution bias due to geopolitical tensions; reliance on cybersecurity vendor reports may introduce confirmation bias.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regional cyber vulnerabilities and influence broader geopolitical tensions in Asia. The evolution of UAT-8099’s tactics may inspire similar threat actors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic friction between China and affected countries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for regional digital infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in cyber tactics and potential for copycat operations.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of digital services could impact economic activities and public trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of IIS server vulnerabilities; collaborate with regional cybersecurity entities for intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for critical infrastructure; strengthen international partnerships for cyber defense.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation reduces threat actor’s impact; regional cooperation strengthens cybersecurity.
- Worst: Escalation of cyber activities leads to significant regional instability and economic disruption.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeting with moderate impact, prompting incremental improvements in regional cyber defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- UAT-8099 (China-linked threat actor)
- Cisco Talos (Cybersecurity research team)
- WithSecure (Finnish cybersecurity vendor)
- Joey Chen (Security researcher)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, SEO fraud, China-linked threat actors, IIS servers, regional cyber threats, cyber defense, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us