China’s Legal Warfare Threatens Global Trade and Maritime Sovereignty in the South China Sea
Published on: 2025-12-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chinas Lawfare Is Reshaping Sovereignty And Supply Chain Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
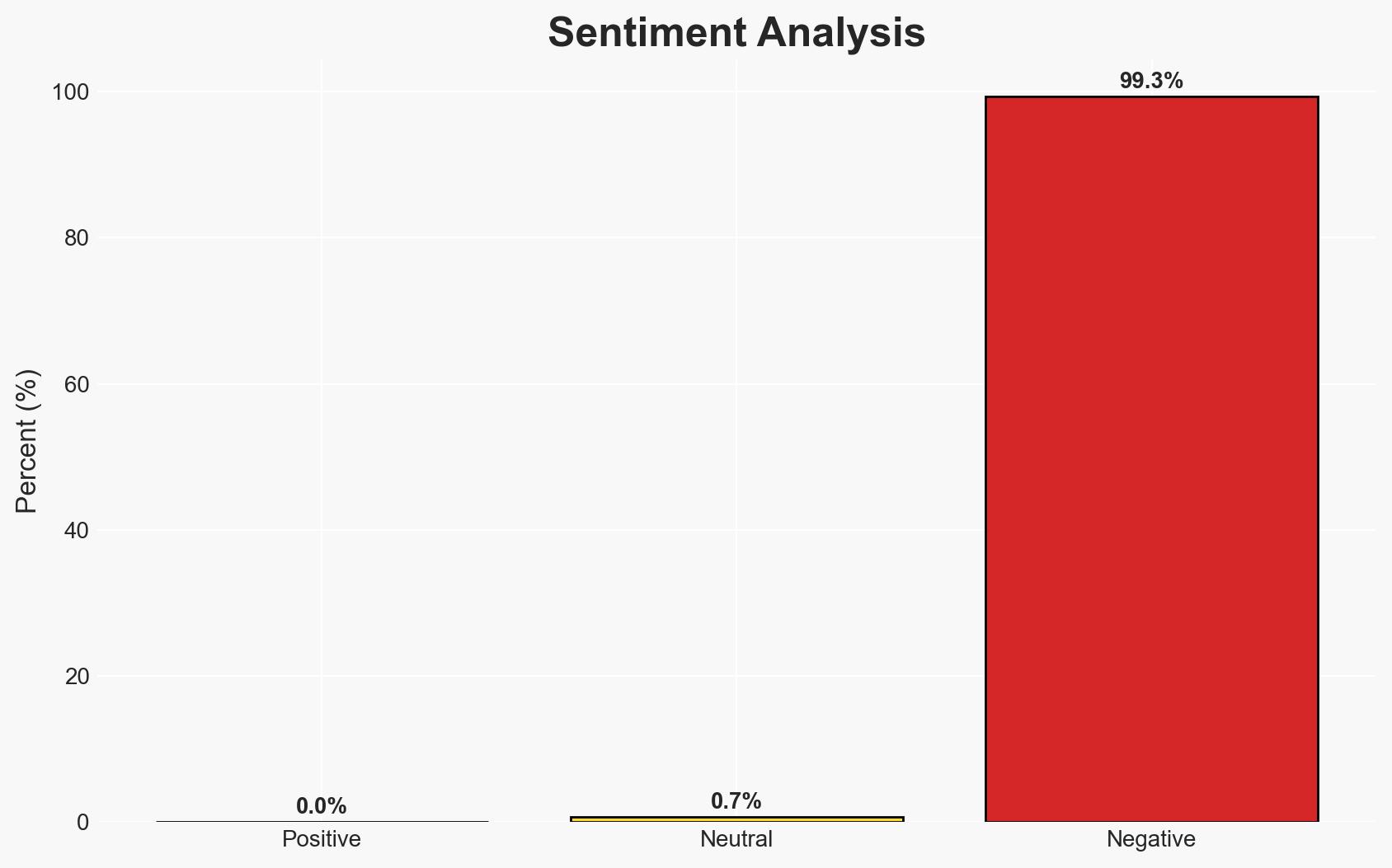
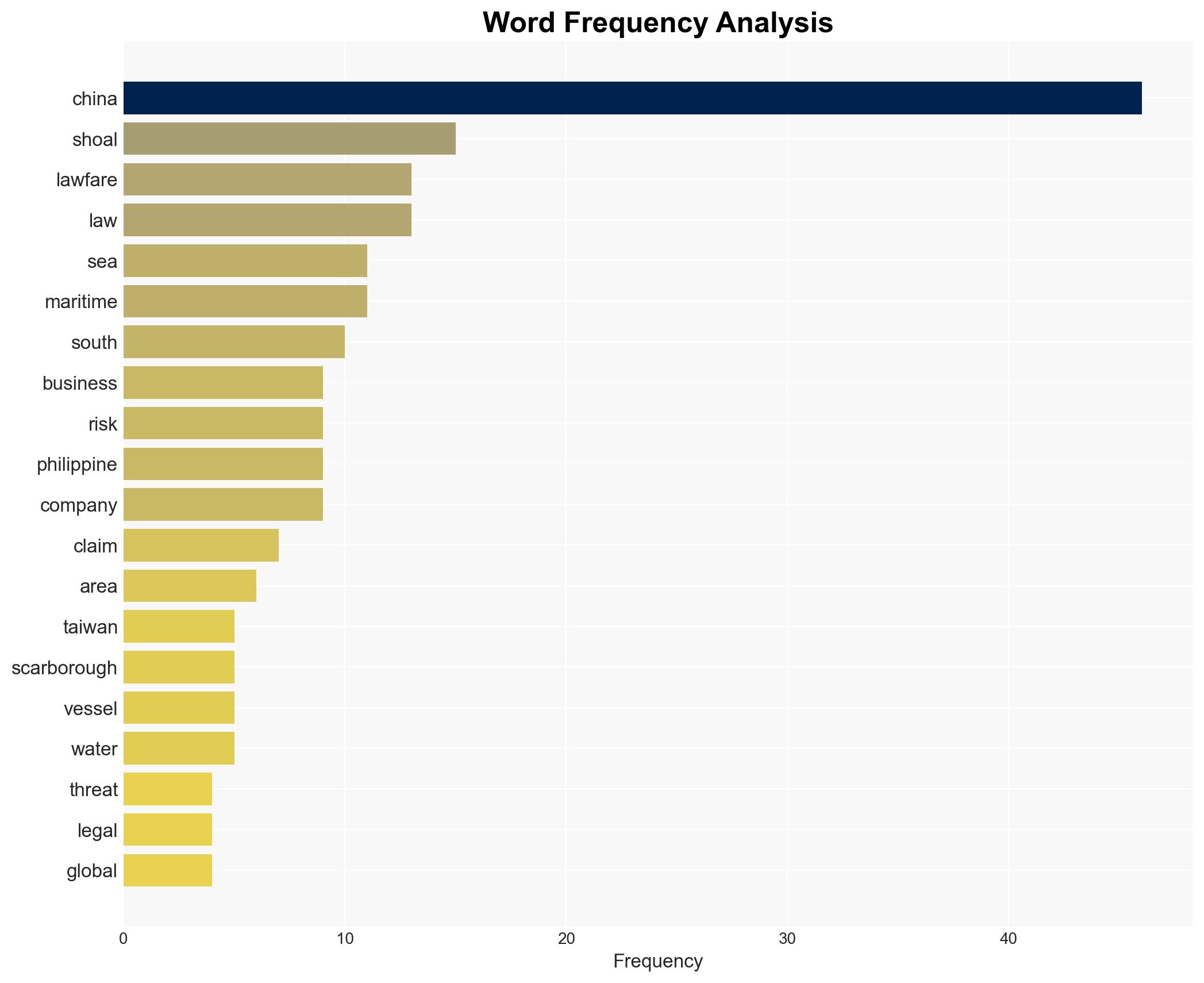
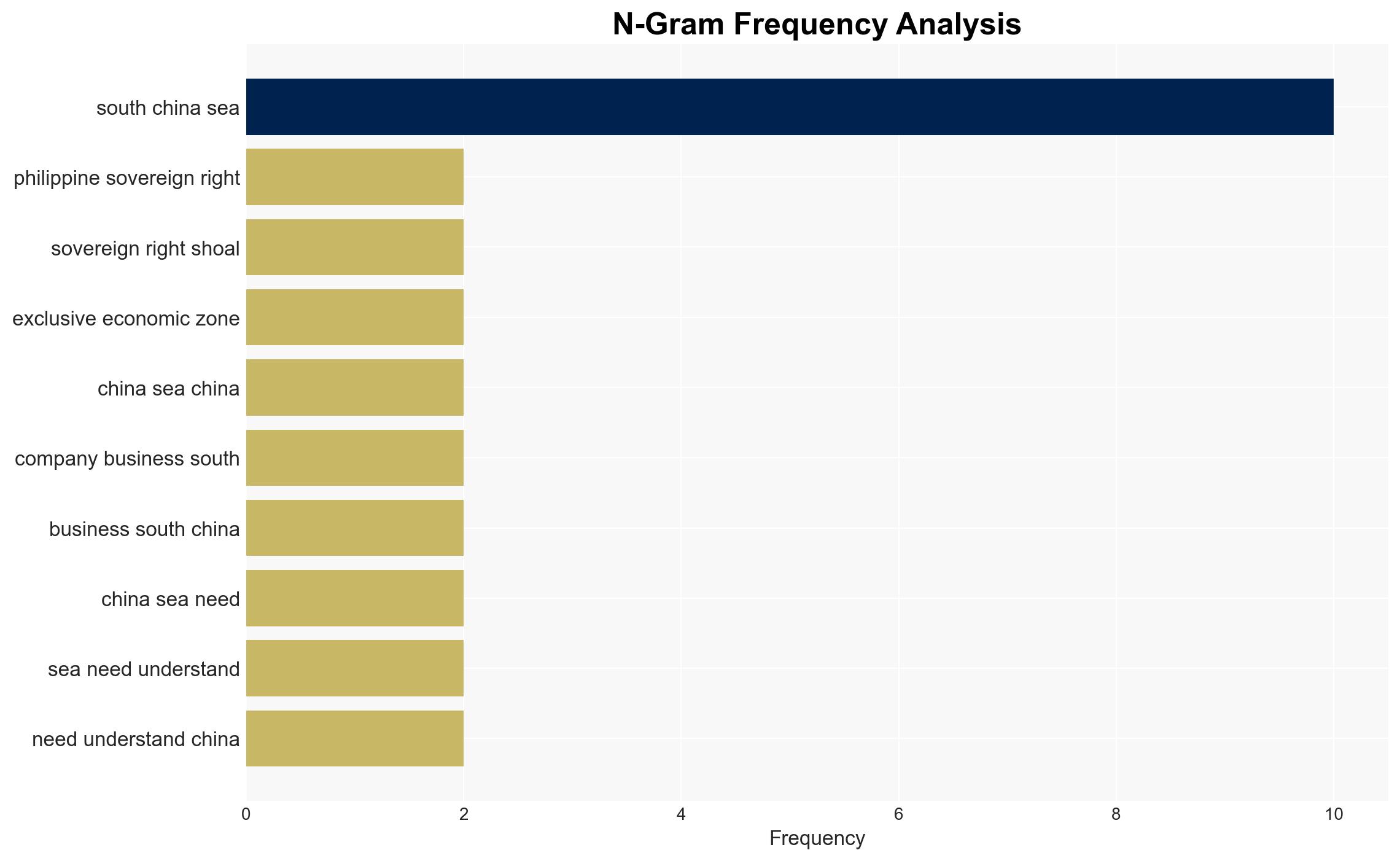
China’s strategic use of lawfare in the South China Sea, particularly around Scarborough Shoal, is reshaping regional sovereignty dynamics and poses significant risks to global supply chain security. The most likely hypothesis is that China will continue to use domestic legal frameworks to assert control over disputed maritime areas, impacting regional stability and international trade. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to ongoing geopolitical tensions and China’s historical actions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: China is using lawfare as a deliberate strategy to assert sovereignty over contested maritime regions, leveraging domestic laws to circumvent international rulings. This is supported by China’s rejection of the 2016 arbitral ruling and its establishment of a nature reserve at Scarborough Shoal. Key uncertainties include the potential for international pushback and regional alliances countering China’s actions.
- Hypothesis B: China’s actions are primarily defensive, aimed at protecting its perceived territorial integrity and responding to external military activities in the region. This is contradicted by the proactive nature of China’s legal maneuvers and military presence in the area.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to consistent patterns of legal and military actions by China to assert control, despite international legal challenges. Indicators that could shift this judgment include significant diplomatic resolutions or changes in China’s domestic policy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: China will continue to prioritize regional dominance; international legal frameworks will remain ineffective in altering China’s behavior; regional actors will not escalate to military conflict.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into China’s internal decision-making processes and potential shifts in regional alliances.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for cognitive bias in underestimating China’s long-term strategic planning; source bias from regional actors with vested interests; possible Chinese information manipulation to justify actions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of China’s lawfare tactics could lead to increased regional tensions and impact global trade routes. The situation may evolve with broader geopolitical shifts, affecting international relations and economic stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for escalation into broader regional conflicts; challenges to international maritime law.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased military presence may heighten regional security risks and complicate counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations and information warfare to support territorial claims.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions to global shipping routes could affect economic stability and supply chain resilience.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of maritime activities; engage in diplomatic efforts to reaffirm international legal standards.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances and partnerships; develop capabilities to counter lawfare tactics.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Diplomatic resolution and adherence to international law; Worst: Military escalation and significant trade disruptions; Most-Likely: Continued legal and military maneuvers by China with regional tensions persisting.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, lawfare, maritime security, South China Sea, international law, regional stability, supply chain security, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us