Chinese Cybersecurity Watchdog Alleges US Stole 132B in Bitcoin Five Years Ago – Decrypt
Published on: 2025-11-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chinese Cybersecurity Watchdog Alleges US Stole 132B in Bitcoin Five Years Ago – Decrypt
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
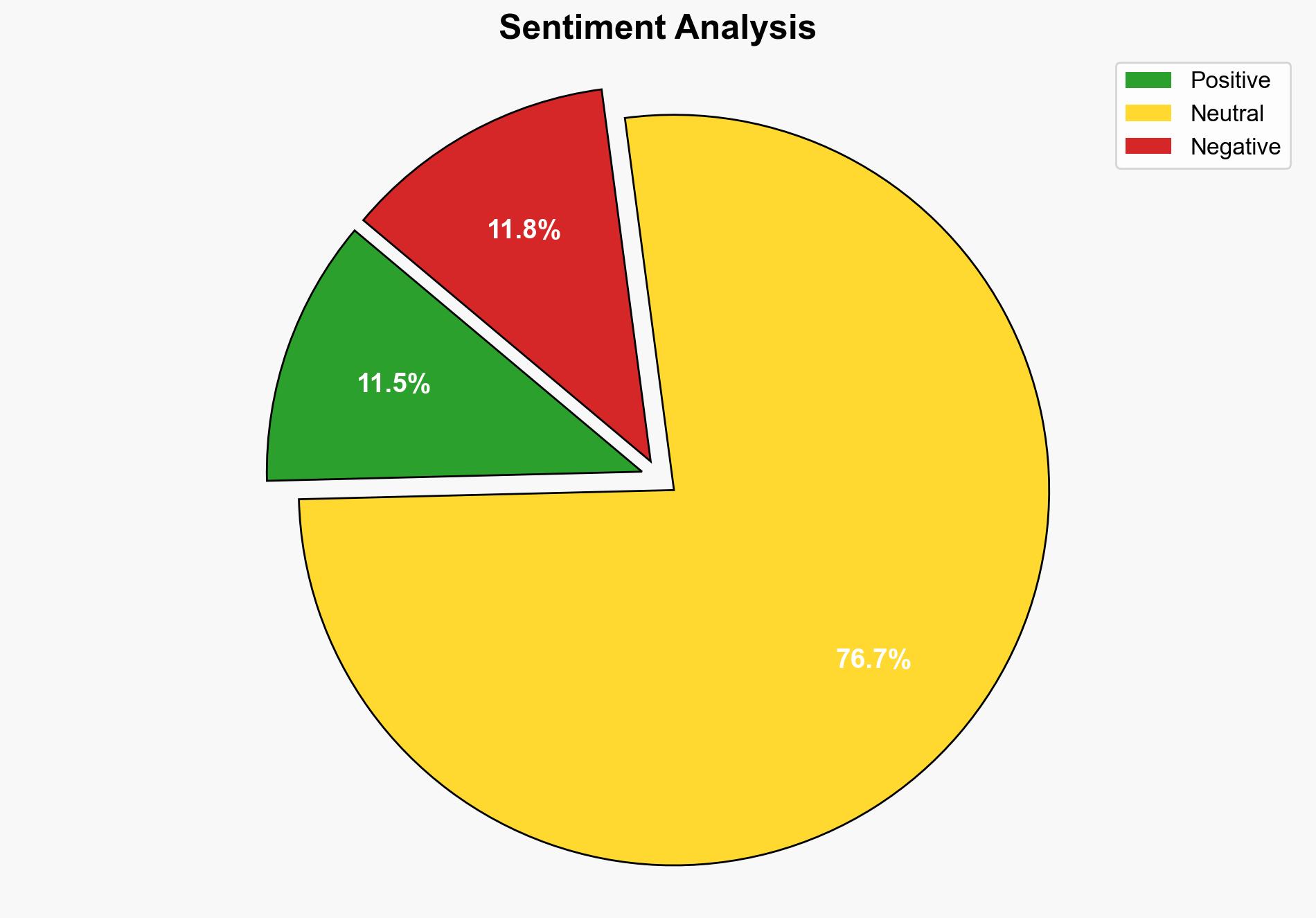
The most supported hypothesis is that the Chinese allegations of the US unlawfully seizing Bitcoin are part of a strategic narrative to undermine US credibility and deflect from domestic issues. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Monitor for further developments and engage in diplomatic channels to address potential misinformation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The allegations by the Chinese cybersecurity watchdog are accurate, and the US government unlawfully seized Bitcoin from Chen Zhi.
Hypothesis 2: The allegations are part of a strategic disinformation campaign by China to undermine US credibility and distract from internal issues.
Hypothesis 2 is more likely due to the lack of corroborative evidence from independent sources and the timing of the allegations coinciding with geopolitical tensions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The US government operates within legal frameworks for asset seizures. The Chinese cybersecurity watchdog’s claims are politically motivated.
Red Flags: Lack of independent verification of the allegations. The use of state-controlled media to propagate the narrative. Timing of the report coinciding with geopolitical tensions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The allegations could exacerbate US-China tensions, potentially impacting diplomatic relations and economic exchanges. There is a risk of retaliatory cyber actions or increased cyber espionage activities. The narrative could also influence global perceptions of US integrity in cyber operations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage in diplomatic dialogue with China to address the allegations and clarify the US position.
- Enhance cybersecurity measures to prevent potential retaliatory cyber actions.
- Monitor Chinese media for further developments and adjust strategic communications accordingly.
- Best-case scenario: The issue is resolved diplomatically, and tensions de-escalate.
- Worst-case scenario: Escalation of cyber conflicts and deterioration of US-China relations.
- Most-likely scenario: Continued rhetorical exchanges with limited tangible impact on bilateral relations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
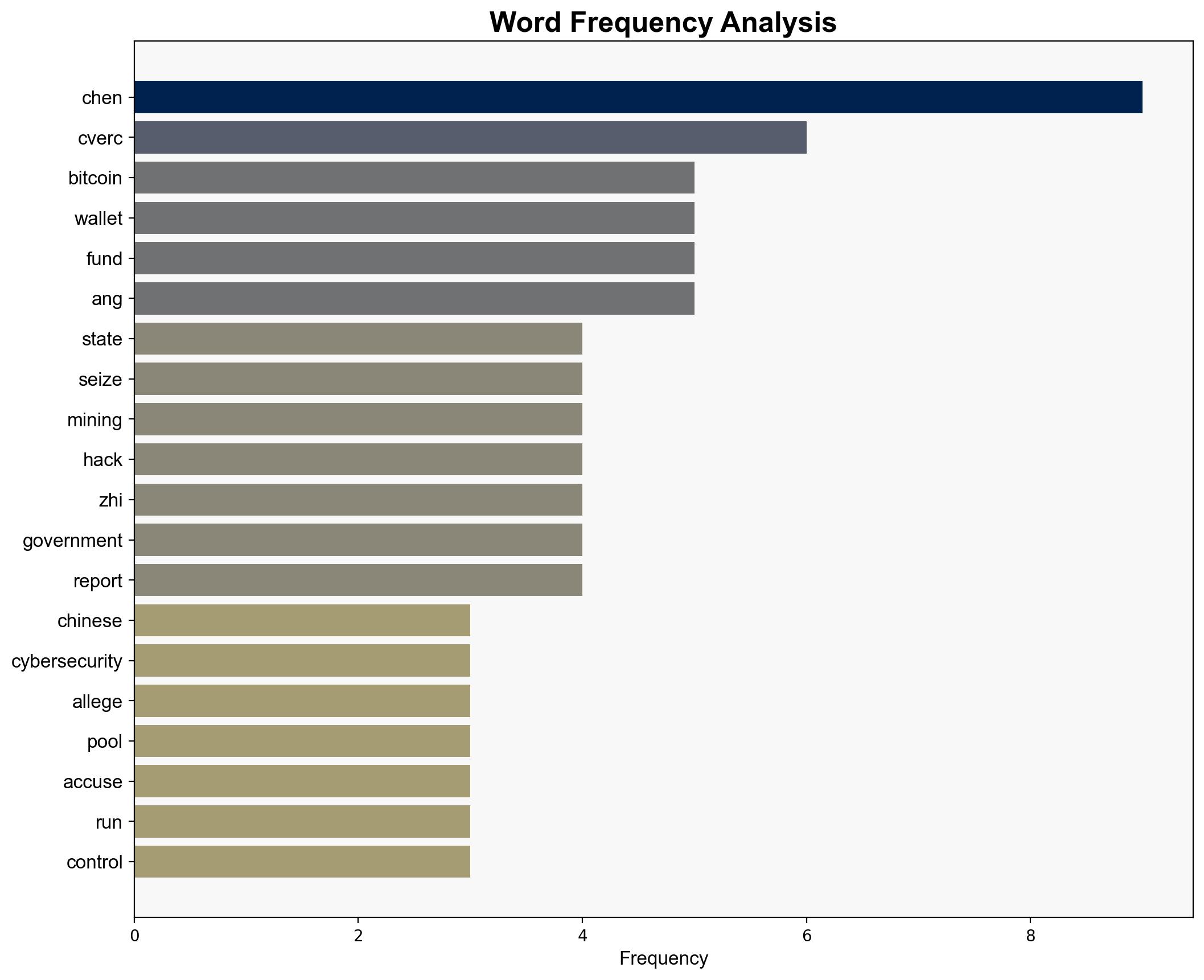
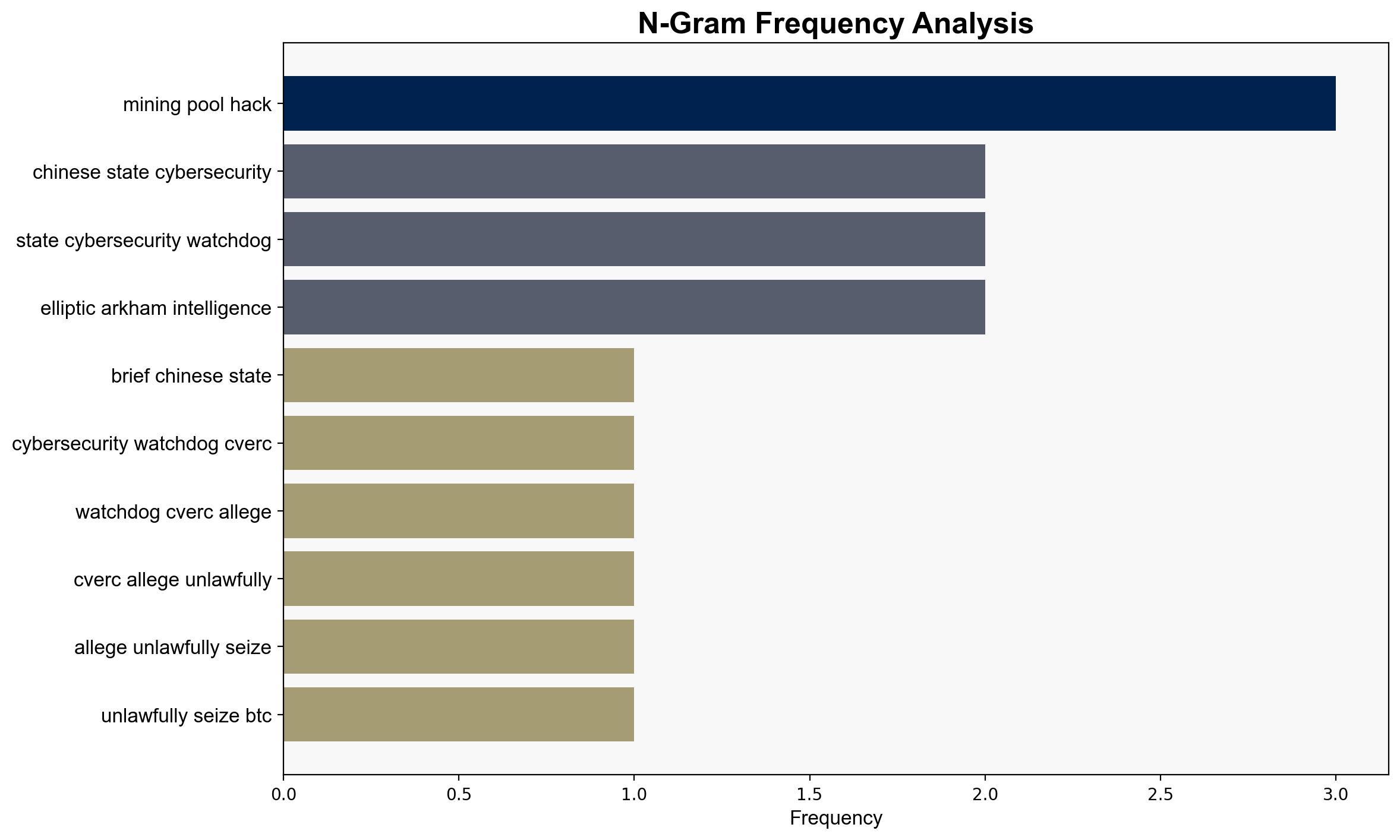
Chen Zhi, Chinese Cybersecurity Watchdog (CVERC), US Department of Justice, Prince Group
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, US-China Relations, Disinformation, Bitcoin, Geopolitics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology