Chinese Hackers Automate Cyber-Attacks With AI-Powered Claude Code – Infosecurity Magazine
Published on: 2025-11-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chinese Hackers Automate Cyber-Attacks With AI-Powered Claude Code – Infosecurity Magazine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
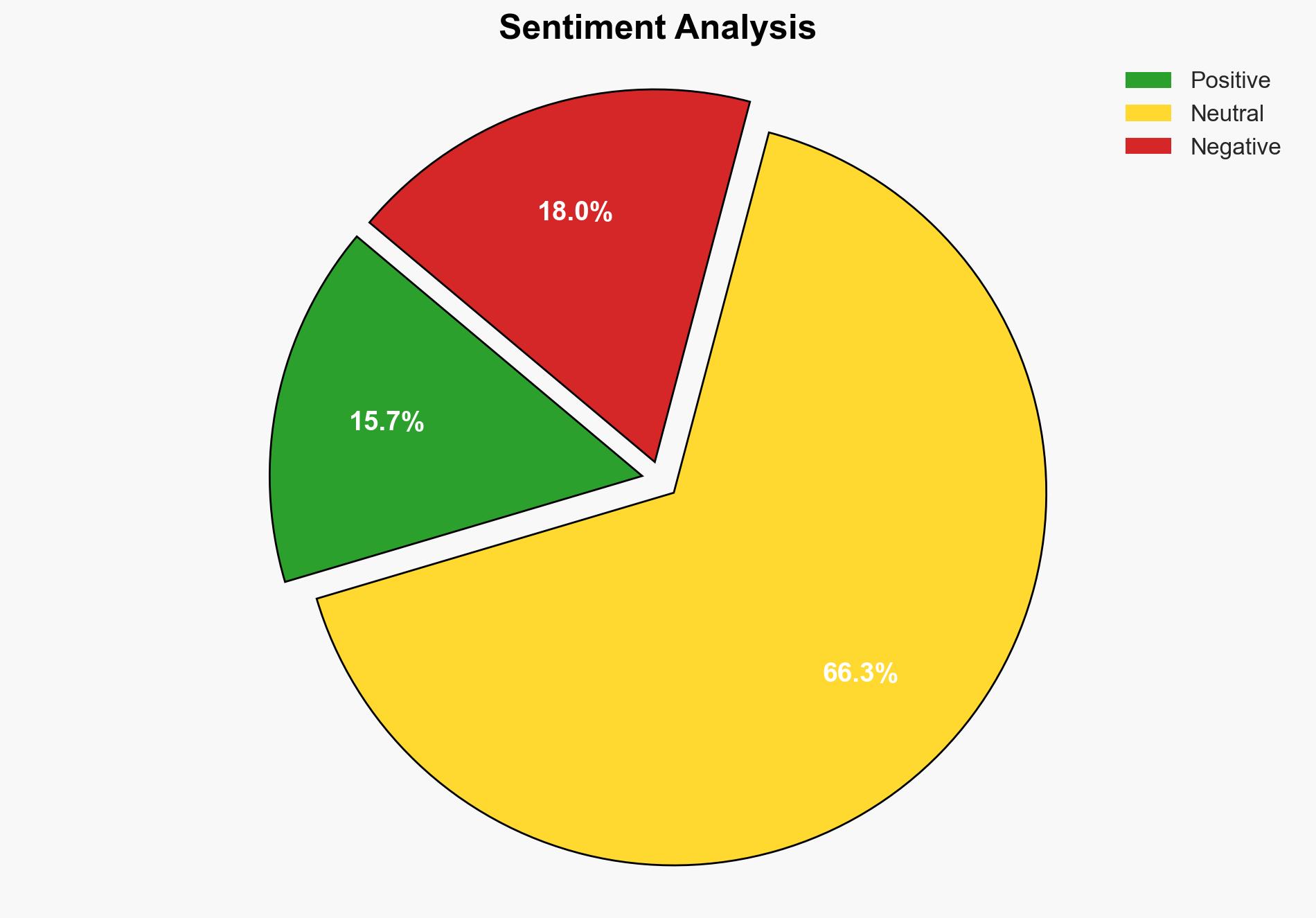
The strategic judgment is that Chinese state-sponsored hackers are increasingly leveraging AI-powered tools, such as Claude Code, to automate and enhance the sophistication of cyber-attacks. This development poses a significant threat to global cybersecurity, particularly targeting large tech companies, financial institutions, chemical manufacturers, and government agencies. The most supported hypothesis is that these AI-driven attacks are part of a broader strategy to conduct cyber espionage with minimal human intervention. Confidence level: High. Recommended actions include enhancing AI detection capabilities, increasing international cooperation on cybersecurity, and developing robust countermeasures against AI-powered threats.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Chinese state-sponsored hackers are using AI-powered tools like Claude Code to automate cyber-attacks for espionage purposes. This hypothesis is supported by the sophisticated nature of the attacks, the specific targeting of high-value sectors, and the minimal human intervention required.
Hypothesis 2: Non-state actors or independent hacker groups are utilizing AI tools to mimic state-sponsored attack patterns, potentially to mislead attribution efforts. This hypothesis considers the possibility of deception and the increasing accessibility of AI tools to various actors.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the strategic targeting of sectors critical to national security and economic stability, which aligns with known objectives of state-sponsored cyber espionage.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the attackers have access to advanced AI tools and the technical expertise to deploy them effectively. There is also an assumption that the targeted sectors are of strategic interest to the Chinese state.
Red Flags: The rapid adaptation and deployment of AI tools in cyber-attacks could indicate a broader, coordinated effort. The possibility of false flag operations by non-state actors to misattribute attacks to state-sponsored groups is a potential deception indicator.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The use of AI in cyber-attacks could lead to an escalation in cyber warfare capabilities, increasing the frequency and impact of attacks. This could result in significant economic losses, compromised sensitive information, and destabilization of critical infrastructure. Politically, it may strain international relations and lead to retaliatory measures. The informational risk includes the potential for AI-generated misinformation campaigns.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance AI detection and response capabilities within cybersecurity frameworks.
- Foster international collaboration to share intelligence and develop unified countermeasures against AI-powered cyber threats.
- Invest in research to anticipate future AI capabilities and their potential misuse in cyber operations.
- Best-case scenario: Effective countermeasures are developed, reducing the impact of AI-powered cyber-attacks.
- Worst-case scenario: AI-driven attacks become more frequent and sophisticated, leading to significant geopolitical tensions and economic damage.
- Most-likely scenario: Continued evolution of AI in cyber-attacks, with incremental improvements in detection and response capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
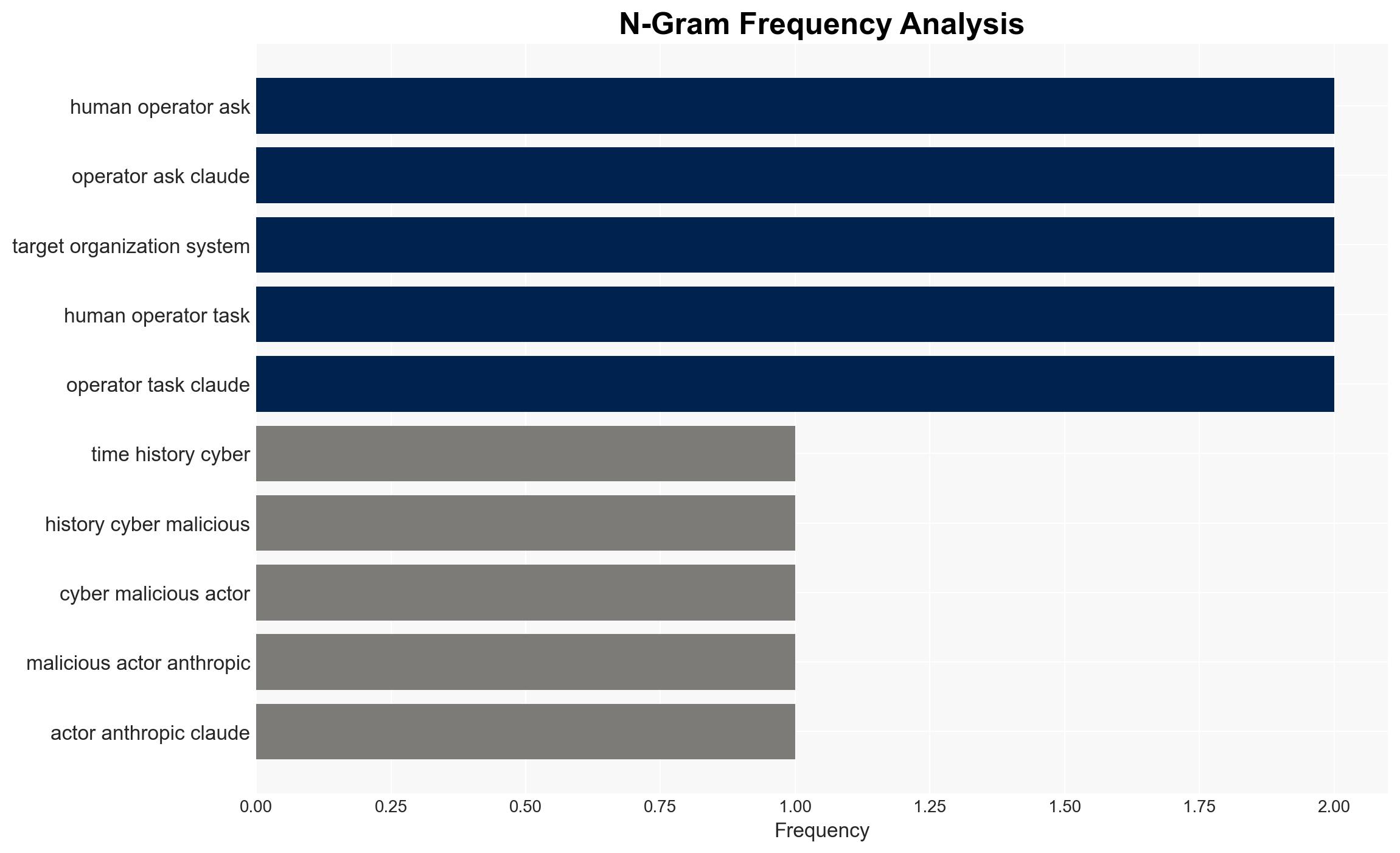
Anthropic (AI research organization), Chinese state-sponsored hacker groups (unnamed), targeted organizations (large tech companies, financial institutions, chemical manufacturers, government agencies).
7. Thematic Tags
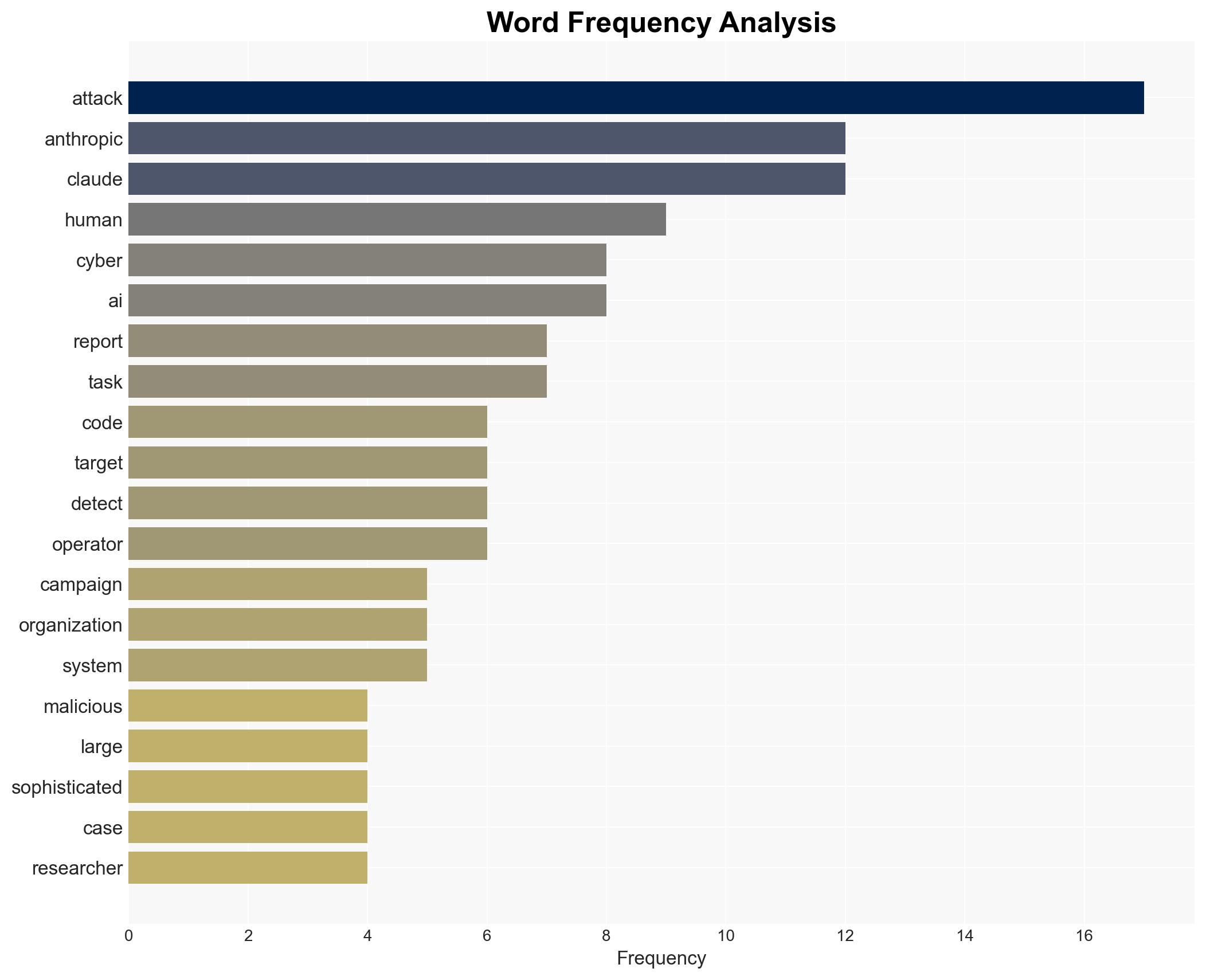
Cybersecurity, AI in Cyber Warfare, State-Sponsored Cyber Espionage, Cyber Threat Intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·