Chinese Hackers Exploit Private Equity Debt to Breach Major VPN Used by US Government and Corporations
Published on: 2026-02-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How Private Equity Debt Left a Leading VPN Open To Chinese Hackers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
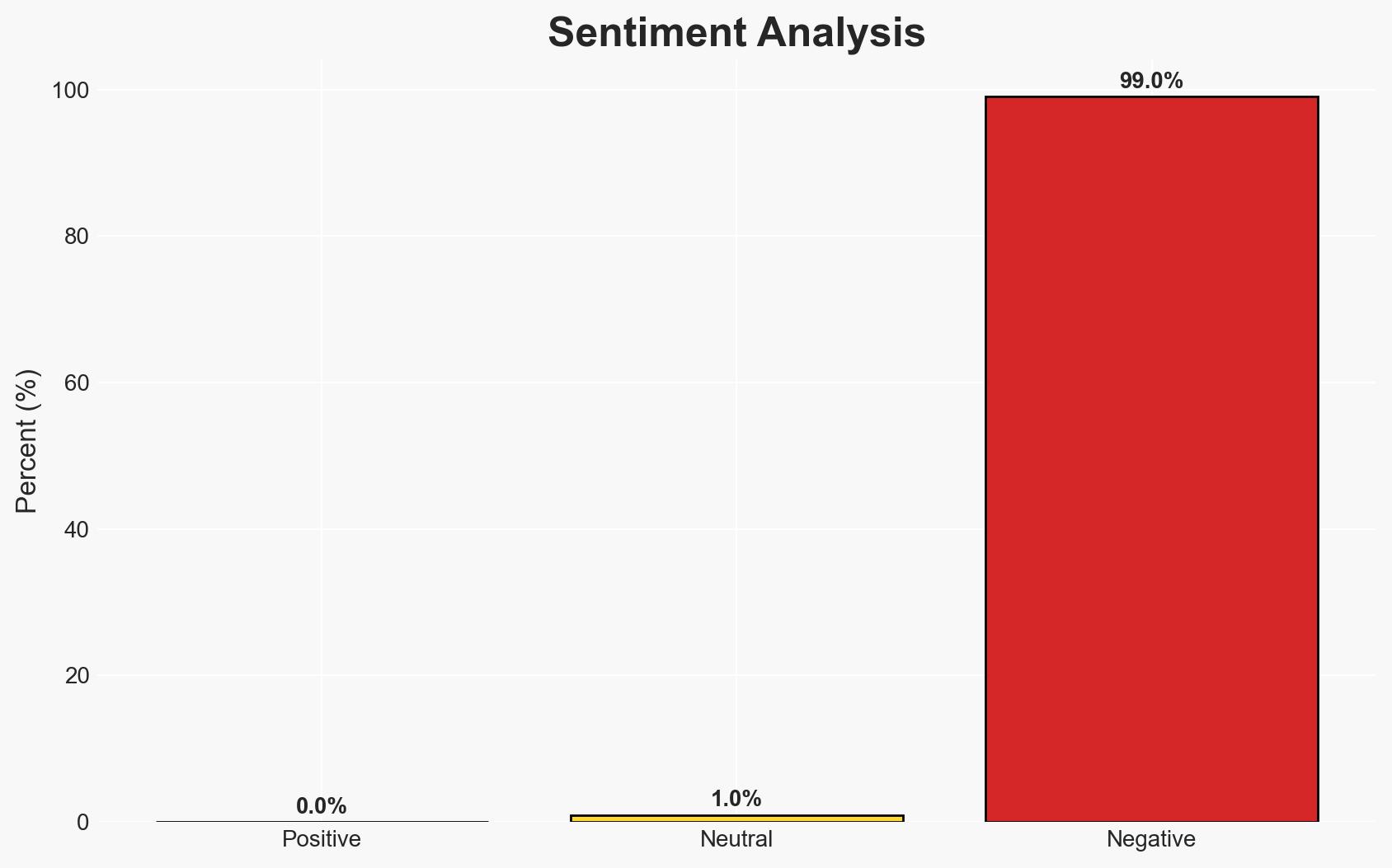
The compromise of Ivanti Inc.’s Connect Secure VPN by Chinese hackers highlights vulnerabilities introduced by private equity-driven cost-cutting in cybersecurity. This incident affects numerous U.S. government agencies and private sector entities, posing significant national security risks. The most likely hypothesis is that private equity ownership led to reduced security measures, facilitating the breach. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily due to private equity-driven cost reductions that compromised the security of Ivanti’s products. Supporting evidence includes reports of reduced security teams at similar firms post-acquisition. However, there is uncertainty about the direct causality between cost-cutting and the breach.
- Hypothesis B: The breach resulted from sophisticated Chinese cyber-espionage efforts independent of corporate ownership changes. While Chinese cyber capabilities are well-documented, this hypothesis lacks direct evidence linking the breach solely to external factors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to documented reductions in security personnel following private equity acquisitions. Indicators such as further breaches or insider testimonies could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Private equity ownership inherently leads to reduced cybersecurity measures; Chinese actors are motivated by strategic gains in cyber-espionage; government agencies rely heavily on commercial VPN solutions.
- Information Gaps: Detailed timelines of security team reductions at Ivanti; specific methods used by Chinese hackers; comprehensive impact assessment on compromised organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing breaches solely to private equity without considering other factors; risk of misinformation from anonymous sources with vested interests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development may lead to increased scrutiny of private equity investments in critical infrastructure sectors and heightened tensions in U.S.-China cyber relations. It could also prompt a reevaluation of cybersecurity strategies across government and private sectors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory measures on foreign investments in sensitive industries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated threat levels for organizations using compromised VPNs, necessitating immediate security overhauls.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber defense spending and policy reforms focusing on supply chain security.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected companies and reputational damage to private equity firms involved.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough security audits of all systems using Ivanti products; enhance monitoring for signs of compromise; engage with cybersecurity experts for mitigation strategies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including diversifying VPN solutions and strengthening public-private cybersecurity partnerships.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid containment and patching of vulnerabilities, leading to minimal long-term impact.
- Worst: Widespread data breaches and loss of sensitive information, resulting in severe national security implications.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in cybersecurity practices with increased regulatory oversight.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Ivanti Inc.
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Elliott Investment Management
- Vista Equity Partners
- Laura Galante, former top cyber official, Office of the Director of National Intelligence
7. Thematic Tags
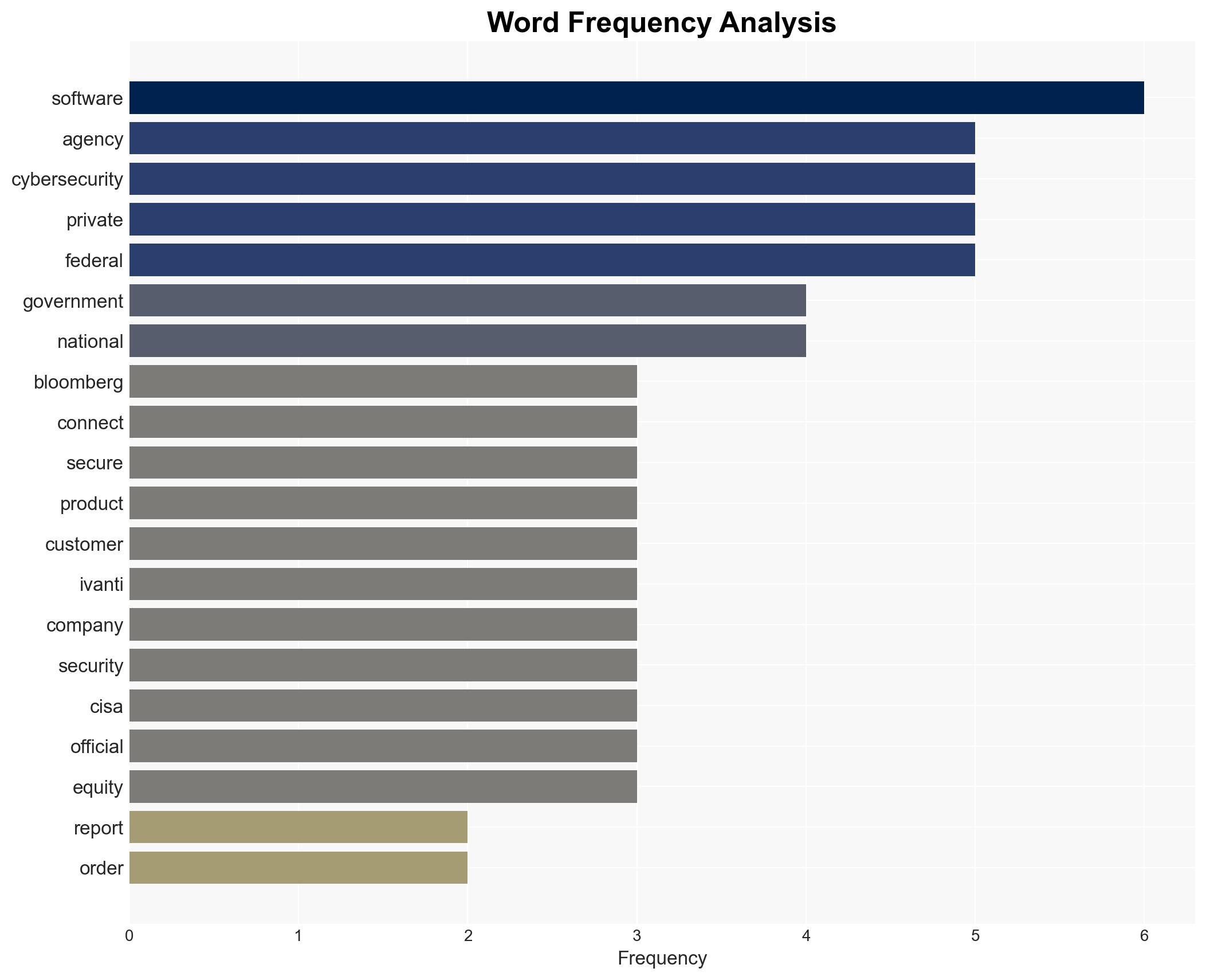
cybersecurity, private equity, cyber-espionage, national security, VPN vulnerabilities, Chinese hackers, regulatory oversight
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us