Chinese-Linked VoidLink Malware Emerges as a Threat to Major Cloud Platforms
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New China Linked VoidLink Linux Malware Targets Major Cloud Providers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
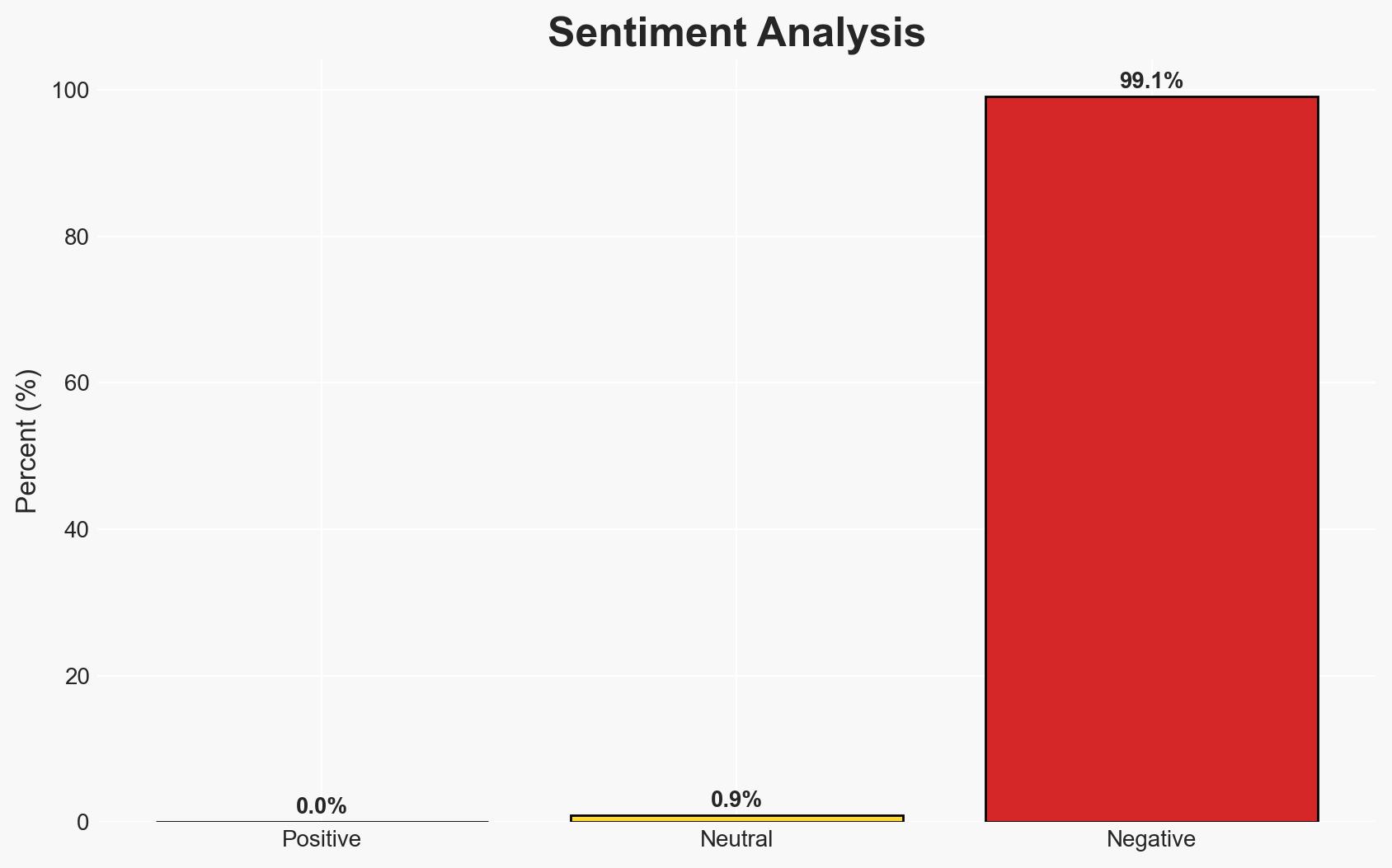
The VoidLink malware, likely developed by a Chinese-affiliated group, poses a significant threat to major cloud providers by targeting Linux-based environments. This sophisticated toolkit is designed for stealth and adaptability, potentially impacting global corporations reliant on cloud services. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the absence of confirmed real-world victims and the potential for further developments.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: VoidLink is a state-sponsored tool developed by Chinese-affiliated actors to conduct cyber-espionage against major cloud providers. Supporting evidence includes the high level of sophistication, the use of a Chinese web dashboard, and the targeting of key infrastructure. However, the lack of direct attribution to state entities and the absence of confirmed victims introduce uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: VoidLink is a commercially developed malware intended for sale to cybercriminals, not directly linked to state activities. This is supported by the polished and well-documented code, suggesting a product designed for broader use. Contradicting this is the strategic targeting of cloud environments, which may imply a more focused agenda.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic nature of the targets and the technical capabilities indicative of state-sponsored operations. Indicators such as confirmed use in espionage activities or direct links to state actors could further solidify this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The developers are Chinese-affiliated; VoidLink’s primary purpose is cyber-espionage; the malware’s sophistication implies state-level resources.
- Information Gaps: Lack of confirmed victims; absence of direct attribution to state actors; limited insight into the full operational scope of VoidLink.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive bias towards attributing sophisticated cyber tools to state actors; source bias from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; possible deception in the malware’s origin or intended use.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
VoidLink’s emergence could lead to increased cyber tensions and necessitate enhanced security measures across cloud platforms. Its adaptability and stealth capabilities may inspire similar developments in cyber threats.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in cyber warfare tactics, impacting international relations, particularly with China.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to critical infrastructure and potential exploitation by non-state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on cloud security and potential proliferation of similar malware tools.
- Economic / Social: Possible disruptions to cloud-reliant businesses, affecting economic stability and trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cloud environments, update security protocols, and conduct threat assessments for potential VoidLink indicators.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing, invest in advanced threat detection technologies, and strengthen international cybersecurity cooperation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: VoidLink is contained with minimal impact, leading to improved cloud security practices.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation of VoidLink results in significant data breaches and geopolitical tensions.
- Most-Likely: Incremental increase in targeted attacks, prompting gradual enhancements in cybersecurity measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, cloud security, state-sponsored threats, malware, China, Linux
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us