Chrome to Make HTTPS Mandatory by Default in 2026 – Infosecurity Magazine
Published on: 2025-10-29
Intelligence Report: Chrome to Make HTTPS Mandatory by Default in 2026 – Infosecurity Magazine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
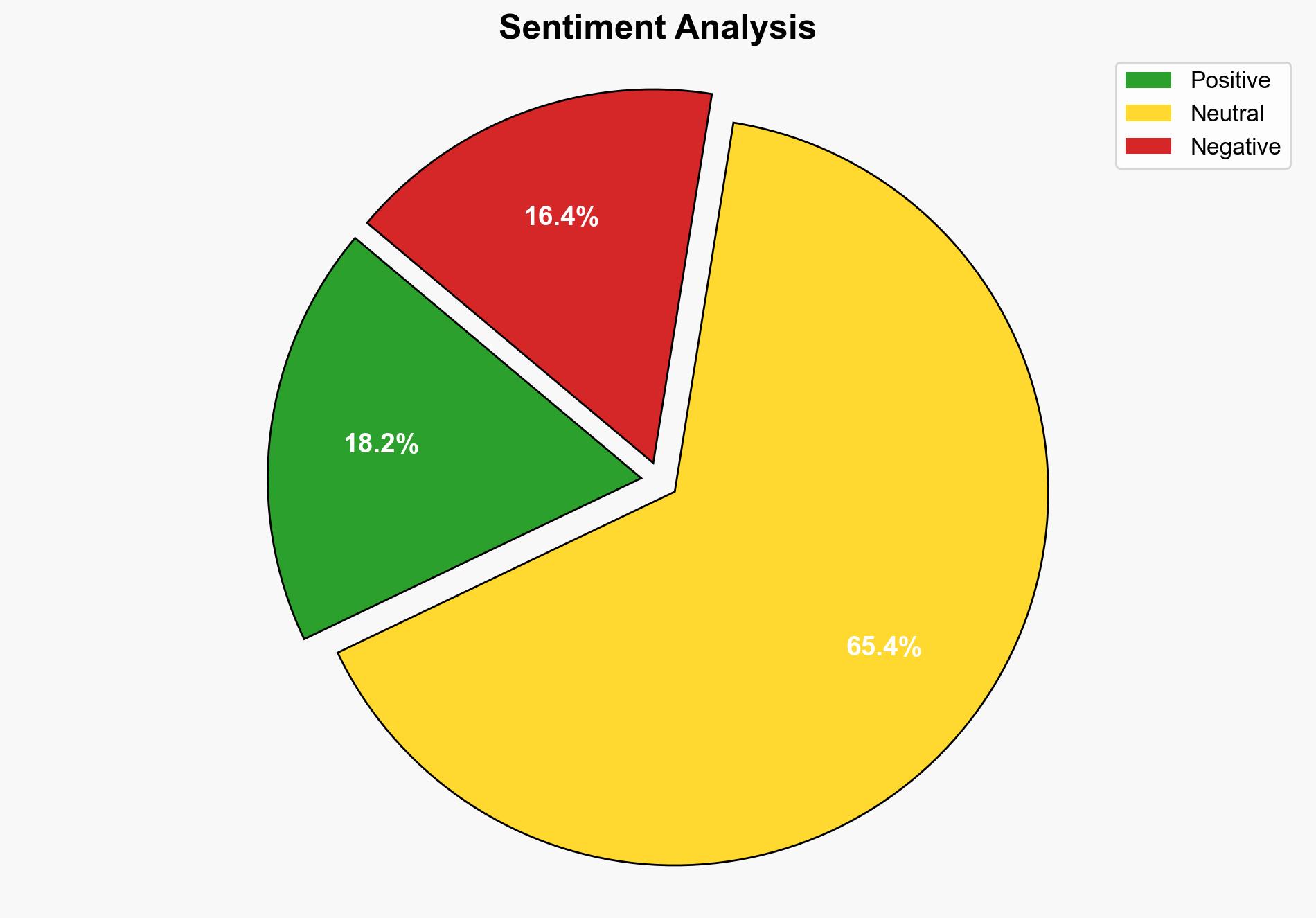
Google’s decision to make HTTPS mandatory in Chrome by 2026 is a strategic move to enhance web security. The most supported hypothesis is that this shift will significantly reduce the risk of data interception and manipulation, thereby improving user trust and security. Confidence level: High. Recommended action: Stakeholders should prepare for this transition by ensuring their websites support HTTPS to avoid disruptions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Google’s mandatory HTTPS policy will lead to a significant decrease in cyber threats by reducing the number of insecure connections, thereby enhancing overall web security.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The mandatory HTTPS policy may lead to initial disruptions and increased costs for website operators, particularly small businesses, potentially slowing down the adoption of secure connections.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported due to Google’s historical success in increasing HTTPS adoption and the minimal disruption reported in early experiments.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that all public websites will be able to transition to HTTPS without significant technical or financial barriers.
– **Red Flags**: The potential for increased phishing attacks on HTTPS sites is not fully addressed. Additionally, the impact on small businesses and local network sites remains uncertain.
– **Blind Spots**: The report does not consider the potential for new types of cyber threats that could arise from universal HTTPS adoption.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The transition to mandatory HTTPS could lead to:
– **Economic Impact**: Increased costs for website operators to obtain and maintain SSL certificates.
– **Cybersecurity**: A reduction in data interception risks but potential for new attack vectors targeting HTTPS vulnerabilities.
– **Geopolitical**: Countries with restrictive internet policies may face challenges in implementing these changes, leading to potential diplomatic tensions.
– **Psychological**: Increased user trust in web security could enhance digital engagement and e-commerce activities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Website operators should begin transitioning to HTTPS to avoid future disruptions.
- Conduct awareness campaigns to educate users and businesses about the benefits and requirements of HTTPS.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Smooth transition with widespread adoption, leading to enhanced security and trust.
- Worst Case: Technical and financial barriers slow adoption, leaving gaps in security.
- Most Likely: Gradual adoption with initial disruptions, but eventual normalization and improved security.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Google (as the entity driving the change)
– Mamun Sheikh (credited for image)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus