CISA alerts on critical SmarterMail vulnerability exploited in ransomware operations
Published on: 2026-02-06
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA warns of SmarterMail RCE flaw used in ransomware attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
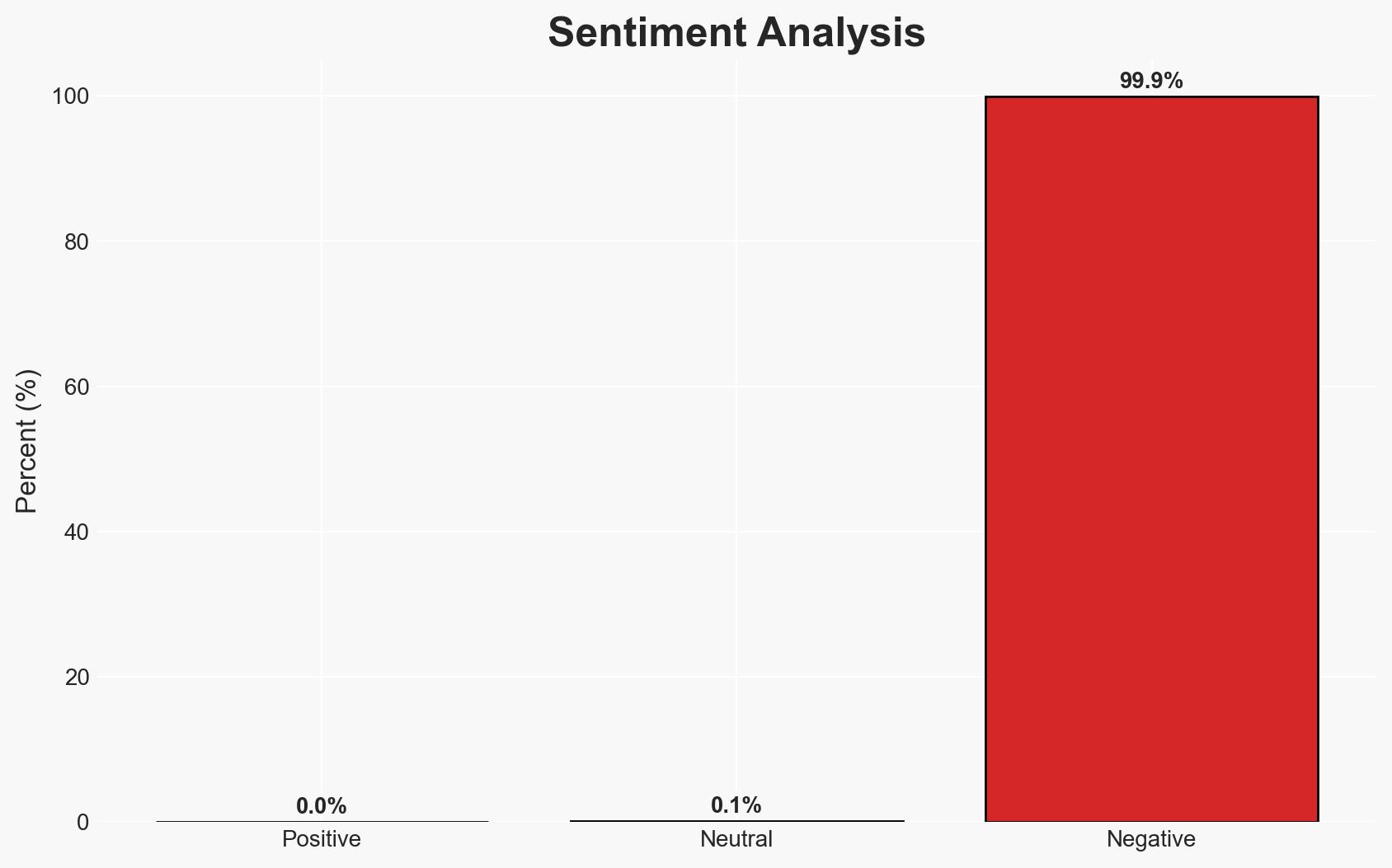
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has identified a critical vulnerability in SmarterMail, exploited in ransomware attacks, affecting numerous users globally. The vulnerability allows remote code execution without authentication, posing significant security risks, particularly to MSPs and small businesses. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors will continue to exploit this flaw until all affected systems are patched. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the ongoing exploitation and recent patch releases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors will continue to exploit the SmarterMail vulnerability (CVE-2026-24423) until all systems are patched. This is supported by CISA’s warning and the active exploitation in ransomware campaigns. However, the rate of patch adoption is uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation of the SmarterMail vulnerability will decrease rapidly as organizations apply patches and mitigations. This is supported by the availability of patches and CISA’s guidance, but contradicts the ongoing reports of exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the active exploitation of the vulnerability and the historical lag in patch adoption by some organizations. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant increase in patch adoption rates or new vulnerabilities being discovered.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will prioritize patching based on CISA’s guidance; threat actors have the capability to exploit the vulnerability effectively; SmarterTools will continue to release timely patches for new vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: The exact number of unpatched systems and the timeline for patch adoption remain unclear.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests in highlighting vulnerabilities; no clear indicators of deception from CISA or SmarterTools.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of the SmarterMail vulnerability could lead to increased ransomware incidents, affecting global business operations and potentially escalating geopolitical tensions if state actors are involved.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated in exploiting the vulnerability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for MSPs and small businesses, increasing the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on patch management and vulnerability disclosure processes; potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging the vulnerability.
- Economic / Social: Disruption to business operations and potential economic losses for affected entities; increased demand for cybersecurity services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for signs of exploitation, apply patches and mitigations, and enhance network monitoring for suspicious activities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, strengthen public-private partnerships for information sharing, and invest in cybersecurity training and awareness.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption leads to a decline in exploitation incidents.
- Worst: New vulnerabilities are discovered, leading to widespread disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation at a reduced rate as patches are gradually applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- SmarterTools
- watchTowr, CODE WHITE, VulnCheck (cybersecurity firms)
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
- Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, vulnerability management, patch management, SmarterMail, CISA, remote code execution
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us