CISA alerts on critical vulnerabilities in HPE OneView and legacy PowerPoint, urging immediate patching
Published on: 2026-01-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA warns of active attacks on HPE OneView and legacy PowerPoint
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
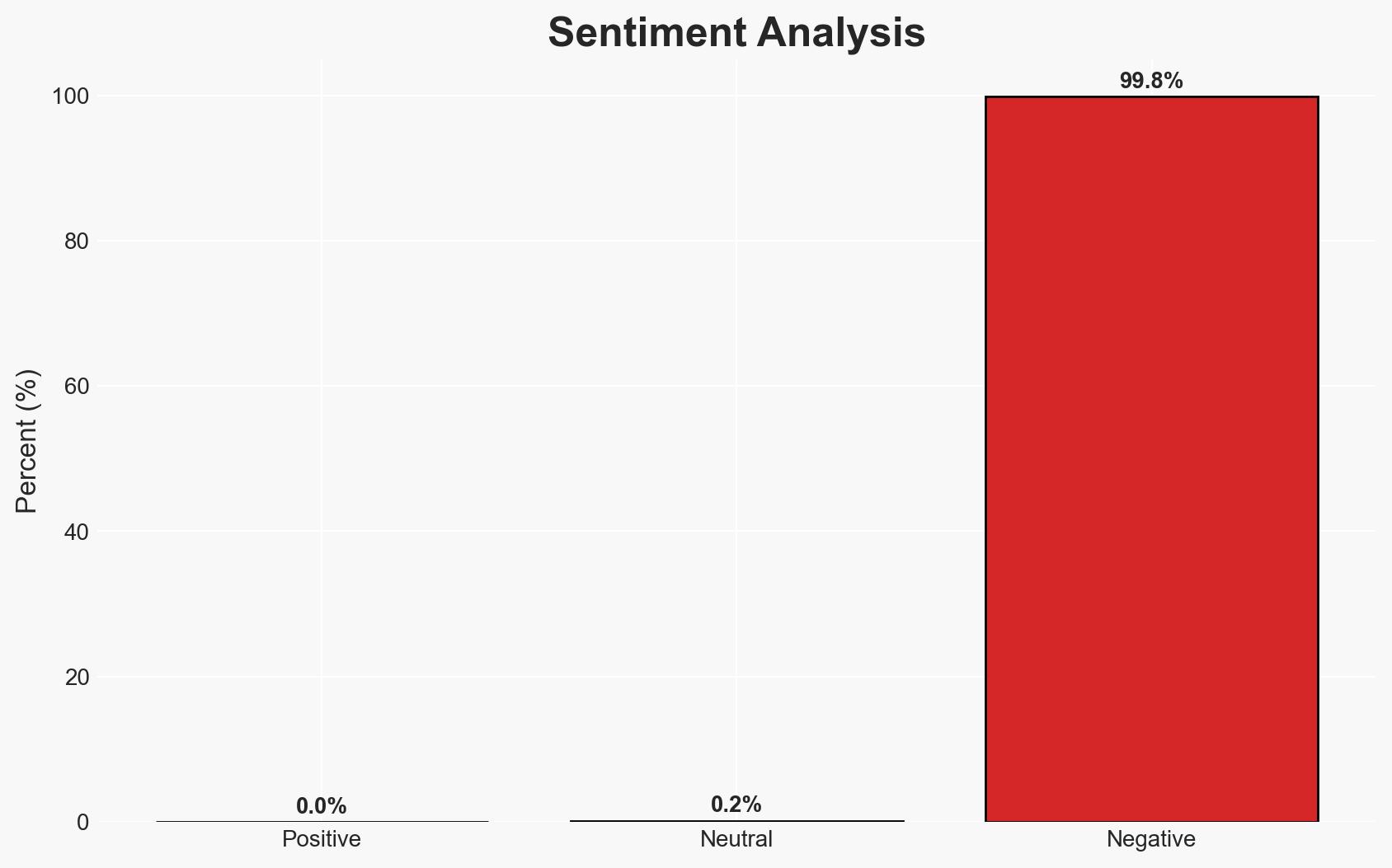
The CISA has identified critical vulnerabilities in HPE OneView and a legacy Microsoft PowerPoint flaw, both actively exploited. The HPE OneView vulnerability poses a significant risk due to its potential for remote code execution and deep network penetration. The PowerPoint vulnerability, though older, indicates ongoing threats to legacy systems. Moderate confidence in the assessment due to limited visibility on the extent of exploitation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The resurgence of the PowerPoint vulnerability indicates a targeted campaign against legacy systems, exploiting organizations with outdated software. Supporting evidence includes the unusual addition of an old vulnerability to the KEV catalog. Uncertainties include the scale and specific targets of the campaign.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are being exploited opportunistically by various threat actors rather than a coordinated campaign. This is supported by the broad applicability of the vulnerabilities across different systems. Contradicting evidence is the specific focus on legacy systems, which may suggest targeted intent.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the targeted nature of exploiting legacy systems, which aligns with the strategic interest of threat actors in accessing less-secured networks. Indicators such as increased reports of legacy system breaches could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have not universally patched the identified vulnerabilities; threat actors are capable of exploiting these flaws; legacy systems remain in use within critical infrastructure.
- Information Gaps: The identity and motives of the threat actors exploiting these vulnerabilities; the full scope of affected entities; detailed incident reports from affected organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overreliance on CISA’s catalog as a comprehensive threat indicator; underestimation of the threat posed by legacy systems due to their age.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to significant disruptions in IT infrastructure management and data integrity, with potential cascading effects on operational capabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated, potentially leading to diplomatic confrontations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with potential for increased cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened vulnerability of digital networks, necessitating increased cybersecurity measures and awareness.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to disruptions in services and increased costs for patching and upgrading systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently patch affected systems, particularly HPE OneView; conduct vulnerability assessments on legacy systems; enhance monitoring for signs of exploitation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience strategies for legacy systems; invest in cybersecurity training and awareness; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity agencies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patching reduces exploitation; Worst: Widespread breaches due to unpatched systems; Most-Likely: Continued exploitation of unpatched systems with sporadic breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
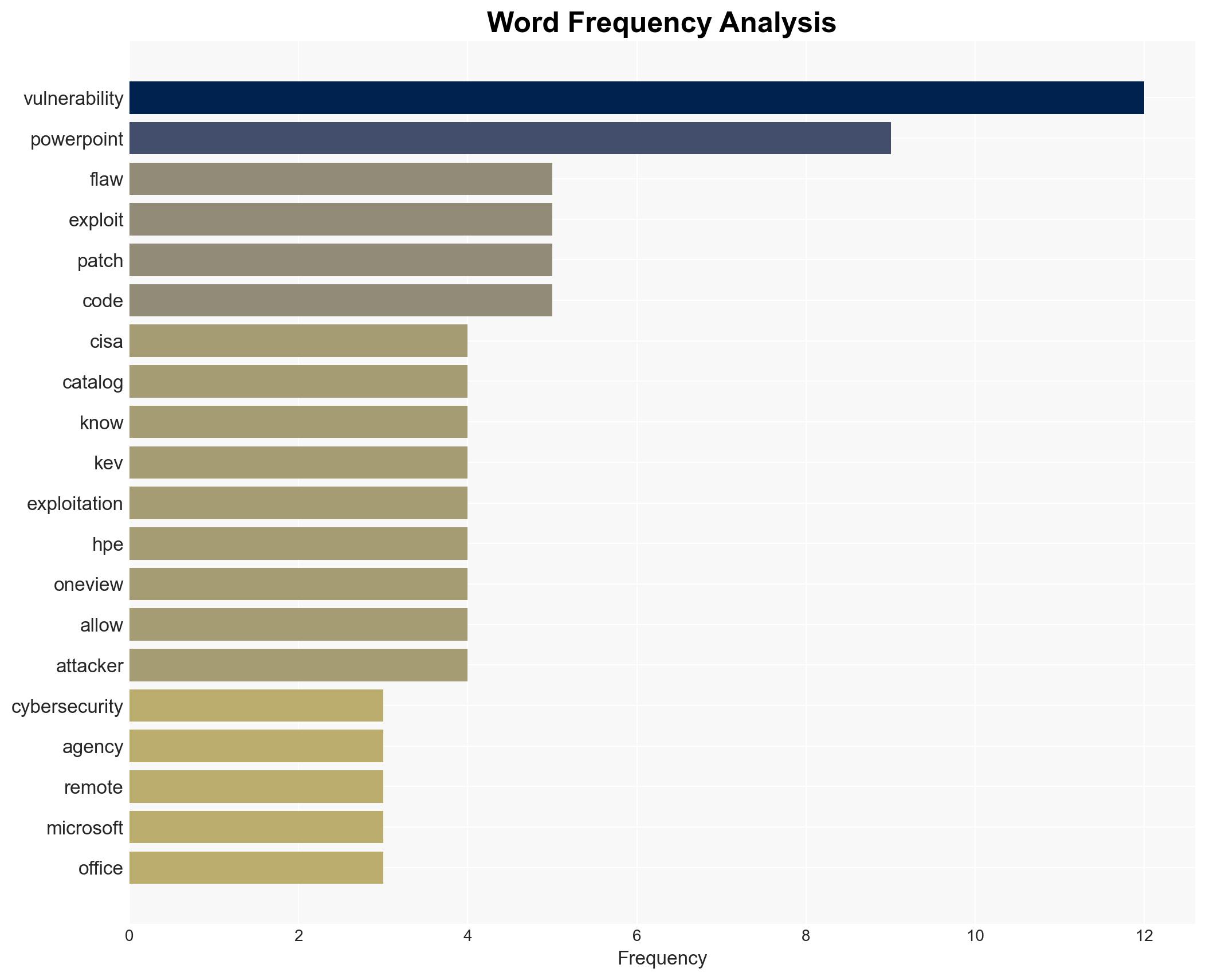
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, legacy systems, IT infrastructure, threat intelligence, cyber exploitation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us