CISA alerts on exploitation of four vulnerabilities in enterprise software from Versa, Zimbra, and others
Published on: 2026-01-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA confirms active exploitation of four enterprise software bugs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
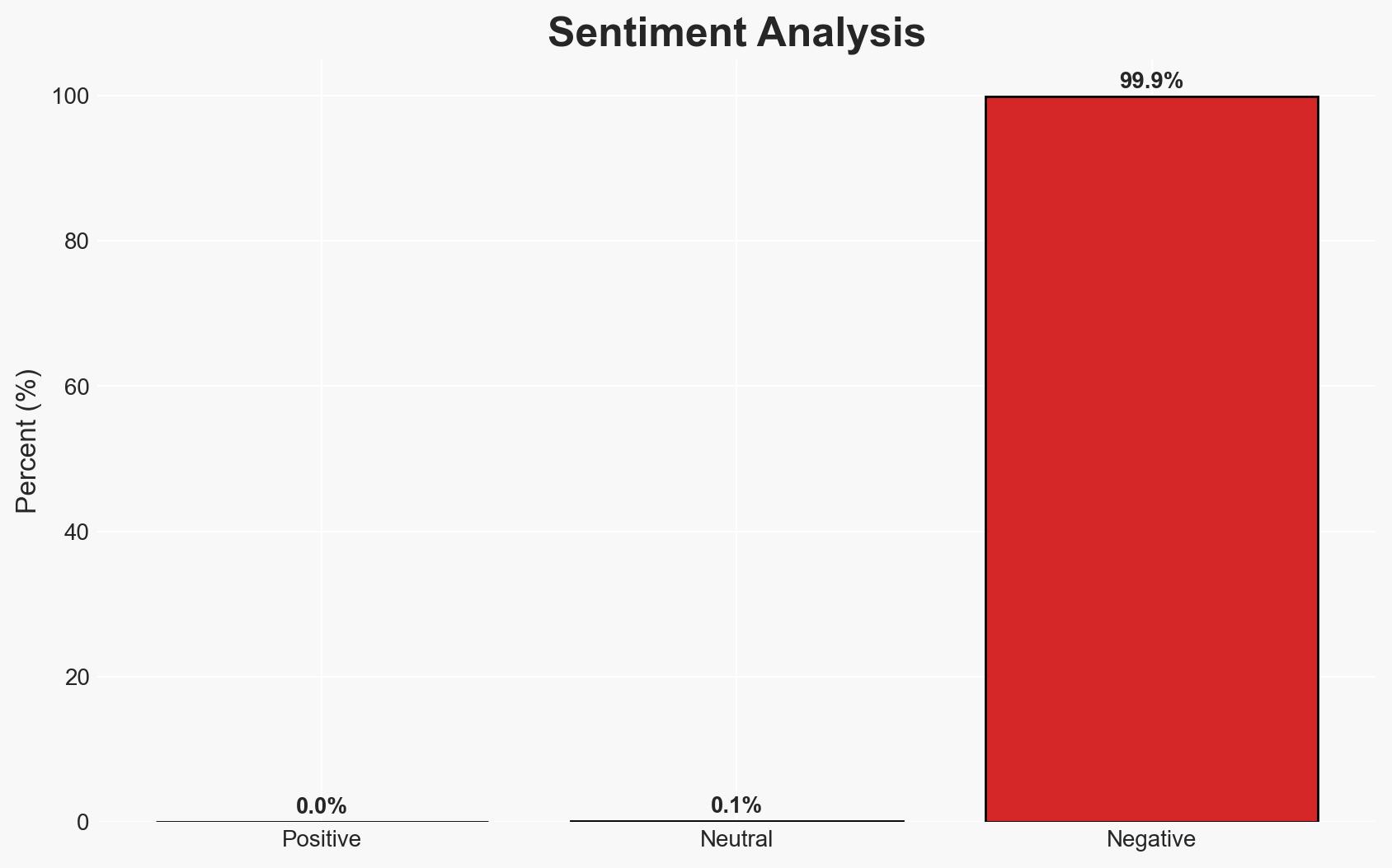
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has confirmed the active exploitation of four vulnerabilities in enterprise software, affecting systems from Versa, Zimbra, and others. These vulnerabilities pose significant risks to enterprise networks, potentially leading to unauthorized access and data breaches. The most likely hypothesis is that these exploits are being utilized by cybercriminals for financial gain or espionage. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of detailed exploitation activity data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities are being exploited primarily by financially motivated cybercriminals. This is supported by the nature of the vulnerabilities, which allow unauthorized access and data theft, typical targets for financial gain. However, the lack of specific exploitation details introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: State-sponsored actors are exploiting these vulnerabilities for espionage purposes. This is plausible given the strategic value of enterprise data, but there is no direct evidence linking state actors to these specific exploits.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the typical profile of such exploits aligning with financially motivated cybercrime. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of targeted attacks on high-value geopolitical targets.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerabilities are being actively exploited in the wild; affected organizations have not yet fully mitigated these vulnerabilities; the exploits are primarily financially motivated.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the exploitation methods and the identity of the actors involved; the extent of the impact on affected organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in assuming financial motives without concrete evidence; risk of underestimating state-sponsored involvement due to lack of direct attribution.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to increased cyber threats to enterprise systems, affecting data integrity and confidentiality. As organizations respond, there may be broader impacts on cybersecurity policies and practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored involvement is confirmed, impacting international cybersecurity relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert levels and increased resource allocation to cybersecurity defenses.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible surge in cyber defense measures and information sharing among affected entities.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for affected companies and erosion of trust in digital infrastructure.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently apply patches and mitigations as advised by CISA; enhance monitoring for unusual activity related to these vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including regular vulnerability assessments and strengthening of incident response capabilities; foster partnerships for information sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patching and mitigation efforts minimize impact, with no significant breaches reported.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to major data breaches and financial losses, with potential geopolitical ramifications if state actors are involved.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation by cybercriminals with sporadic breaches, prompting ongoing cybersecurity enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Versa Networks
- Zimbra
- ProjectDiscovery
- BleepingComputer
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
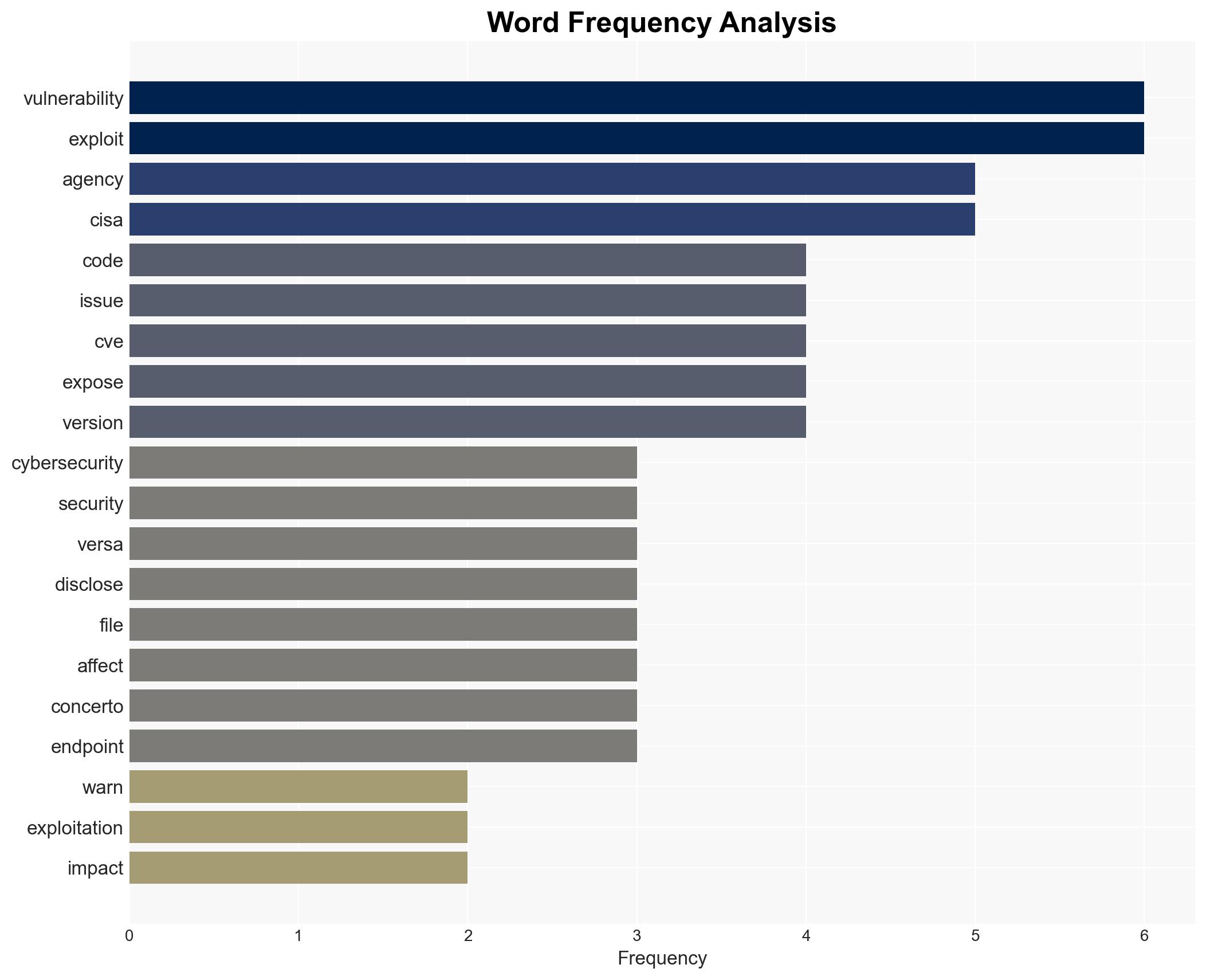
cybersecurity, vulnerabilities, enterprise software, cybercrime, state-sponsored threats, information security, patch management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us