CISA identifies critical HPE OneView vulnerability as under active exploitation in cyberattacks
Published on: 2026-01-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA tags max severity HPE OneView flaw as actively exploited
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
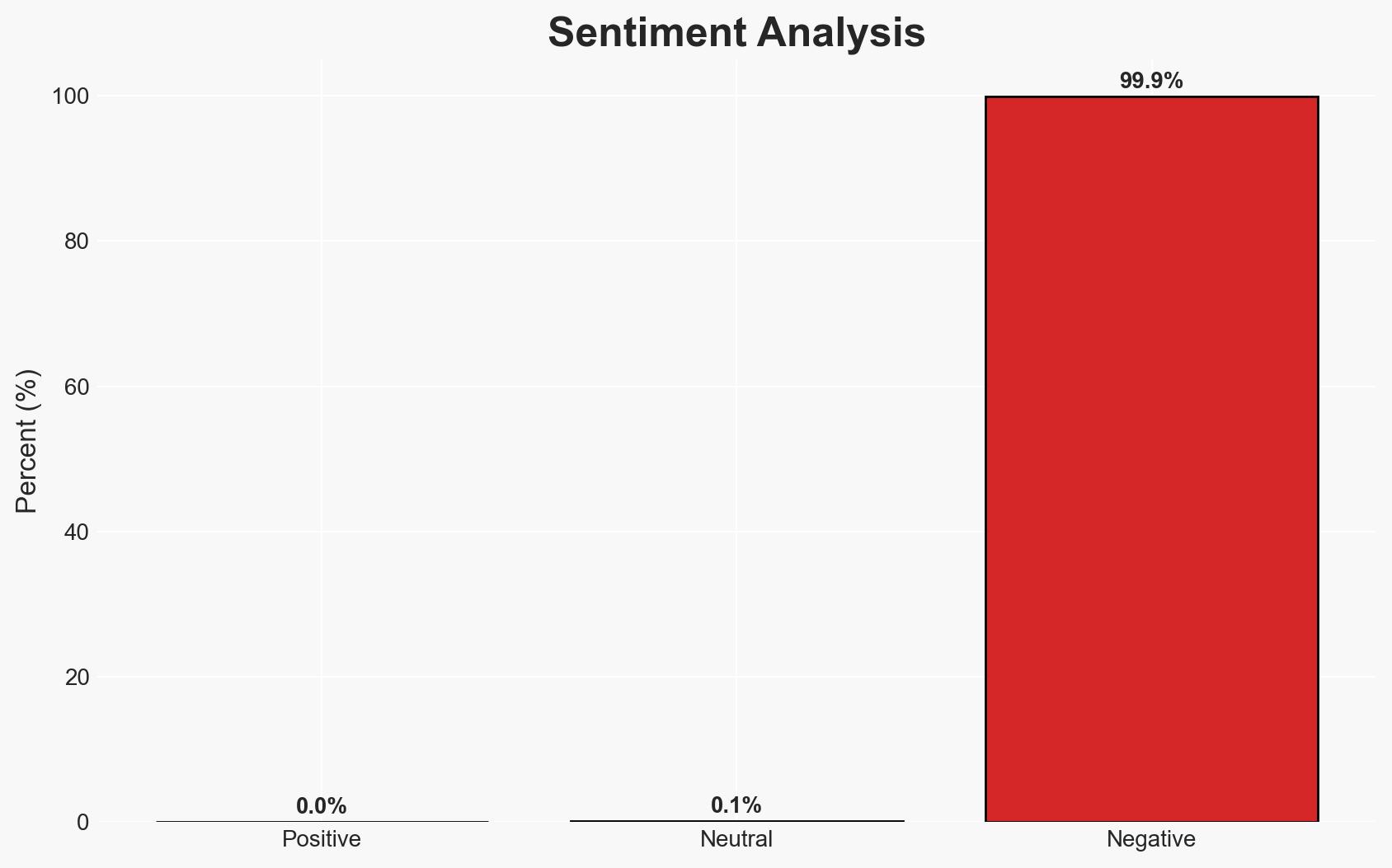
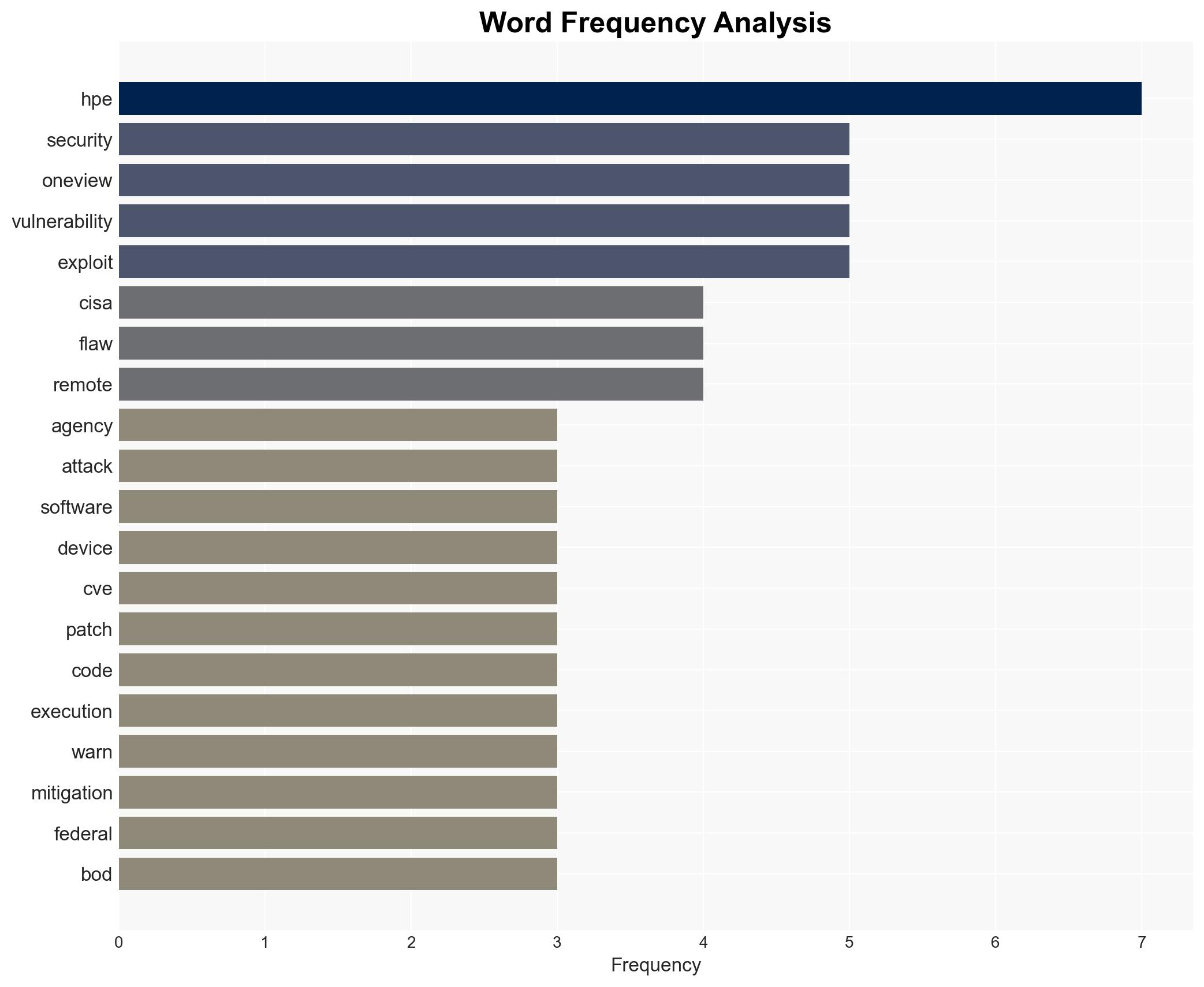
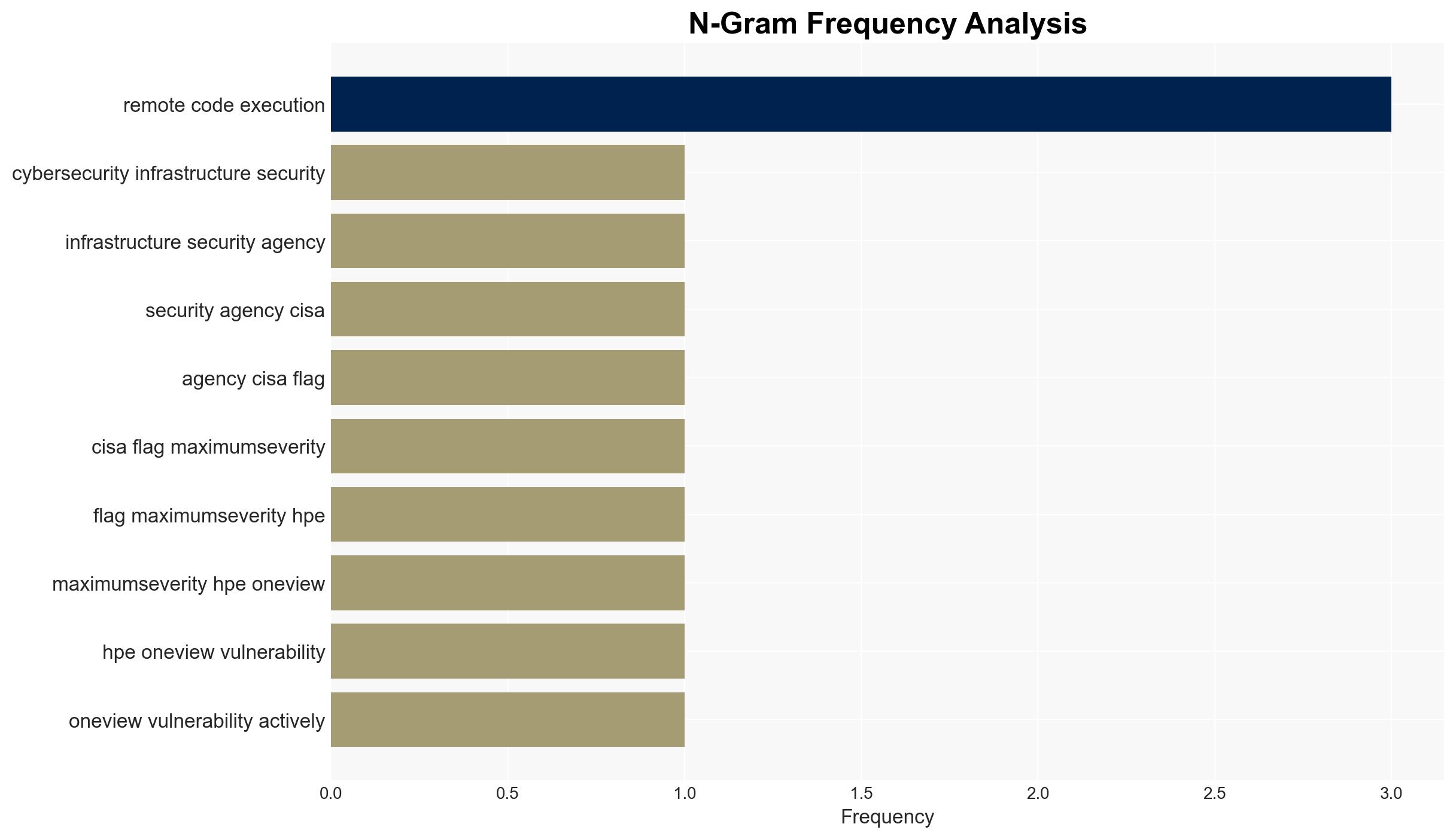
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has identified a critical vulnerability in HPE OneView, actively exploited in cyber-attacks, affecting IT infrastructure management globally. This flaw poses significant risks to federal and private sector systems, necessitating immediate patching. We assess with moderate confidence that the vulnerability could lead to widespread disruptions if not addressed promptly.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The exploitation of the HPE OneView vulnerability is primarily driven by financially motivated cybercriminals seeking to leverage remote code execution for data theft or ransomware attacks. Supporting evidence includes the nature of the vulnerability allowing unauthenticated access and the lack of mitigations, which are attractive to such actors. Key uncertainties involve the identity and specific motivations of the threat actors.
- Hypothesis B: State-sponsored actors are exploiting the HPE OneView vulnerability to gather intelligence or disrupt critical infrastructure. This is supported by the strategic value of targeting infrastructure management software used by major organizations, including government entities. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of specific attribution to state actors at this time.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate financial incentives and the typical pattern of cybercriminals exploiting such vulnerabilities. However, indicators such as increased targeting of government systems or geopolitical tensions could shift this assessment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will prioritize patching the vulnerability; the vulnerability is not yet widely exploited by state actors; HPE will continue to provide timely updates and support.
- Information Gaps: Specific identities and motivations of the exploiting threat actors; the extent of the exploitation across different sectors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of incidents due to reputational concerns; reliance on vendor-provided information which may downplay risks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The active exploitation of the HPE OneView vulnerability could lead to significant operational disruptions and data breaches, affecting both public and private sectors. The situation could evolve with increased sophistication of attacks or broader targeting.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are implicated in exploiting the vulnerability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for critical infrastructure protection; possible shifts in threat actor tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing IT management systems; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the vulnerability.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses from data breaches or operational downtime; potential erosion of trust in IT management solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently patch affected systems; enhance monitoring for signs of exploitation; communicate risks to stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for IT management systems; foster public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patch adoption mitigates risks. Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant disruptions. Most-Likely: Continued targeted attacks with gradual mitigation as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nguyen Quoc Khanh (brocked200) – Vietnamese security researcher
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, federal agencies, IT infrastructure, cybercrime, state-sponsored threats, public-private partnerships
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us