CISA Includes MongoDB Server Vulnerability CVE-2025-14847 in Its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities List
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US CISA adds a flaw in MongoDB Server to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
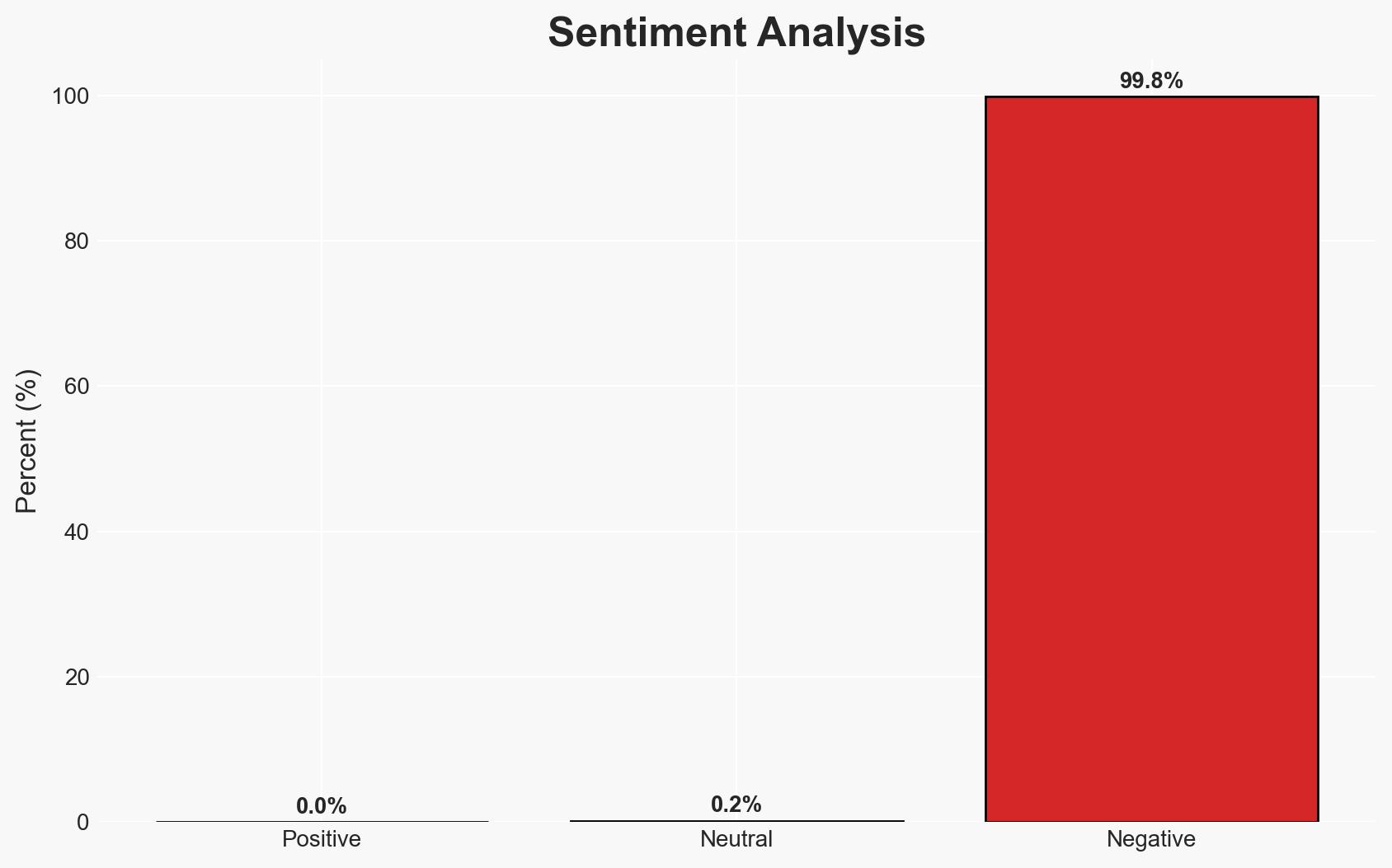
The addition of the MongoDB vulnerability CVE-2025-14847 to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog indicates an active exploitation threat with significant potential impact, particularly in the U.S., China, Germany, and India. The vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code and leak sensitive data. Immediate mitigation is critical to prevent data breaches. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete exploitation details.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is being exploited primarily by state-sponsored actors to gather intelligence. This is supported by the widespread geographic distribution of vulnerable instances and the potential for significant data extraction. However, the lack of specific attribution to state actors limits certainty.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation is primarily driven by cybercriminal groups seeking financial gain through data theft and subsequent sale on the dark web. The public availability of the exploit and the nature of the data at risk (user details, passwords) support this hypothesis, though direct evidence of cybercriminal involvement is lacking.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the nature of the vulnerability and the typical motivations of cybercriminals targeting such flaws. Indicators such as increased dark web activity related to MongoDB data could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability affects a significant number of critical systems; affected entities have not yet fully mitigated the risk; the exploit will continue to be used in the near term.
- Information Gaps: Specific actor attribution and detailed exploitation methodologies are not fully known; the extent of data already compromised remains unclear.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting due to reliance on cybersecurity firm assessments; risk of underestimating state actor involvement due to lack of direct evidence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to significant data breaches, impacting both private and public sectors. The exploitation may evolve into more sophisticated attacks if not mitigated promptly.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored involvement is confirmed, particularly among affected nations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of data being used for identity theft or to facilitate further cyber-attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber threat landscape complexity; potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging stolen data.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected businesses; erosion of public trust in digital infrastructure security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urge organizations to upgrade affected MongoDB versions or disable zlib compression; enhance monitoring for suspicious activity related to MongoDB instances.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for intelligence sharing; invest in workforce training to improve incident response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid mitigation reduces exploitation, with minimal data loss.
- Worst: Widespread data breaches lead to significant economic and security impacts.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation with moderate data loss until mitigation measures are widely adopted.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Joe Desimone (Cybersecurity Researcher)
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Wiz (Cybersecurity Firm)
- Censys (Cybersecurity Firm)
7. Thematic Tags
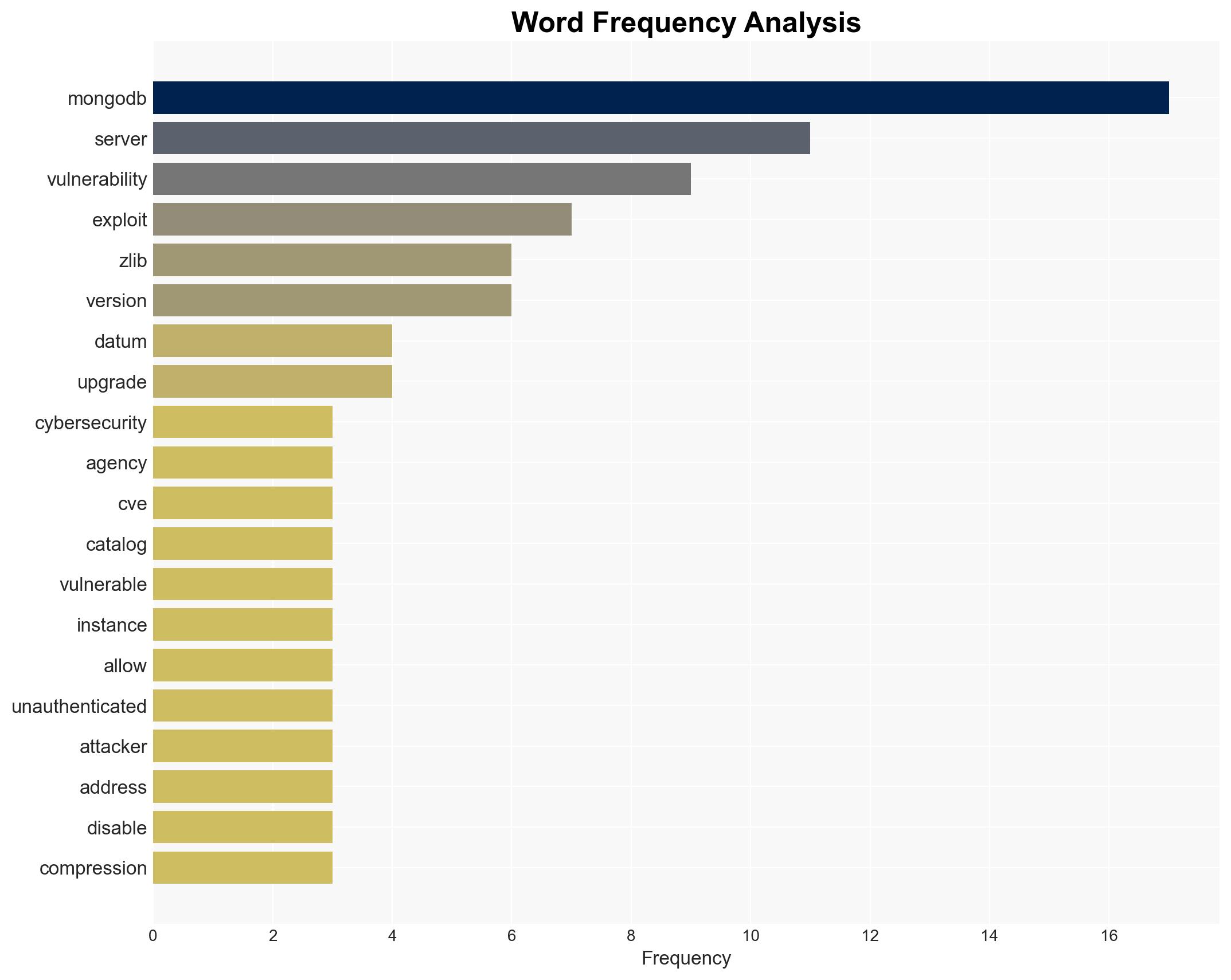
cybersecurity, data breach, vulnerability management, cybercrime, state-sponsored threats, MongoDB, CISA
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us