CISA includes SolarWinds, Sangoma FreePBX, and GitLab vulnerabilities in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities…
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
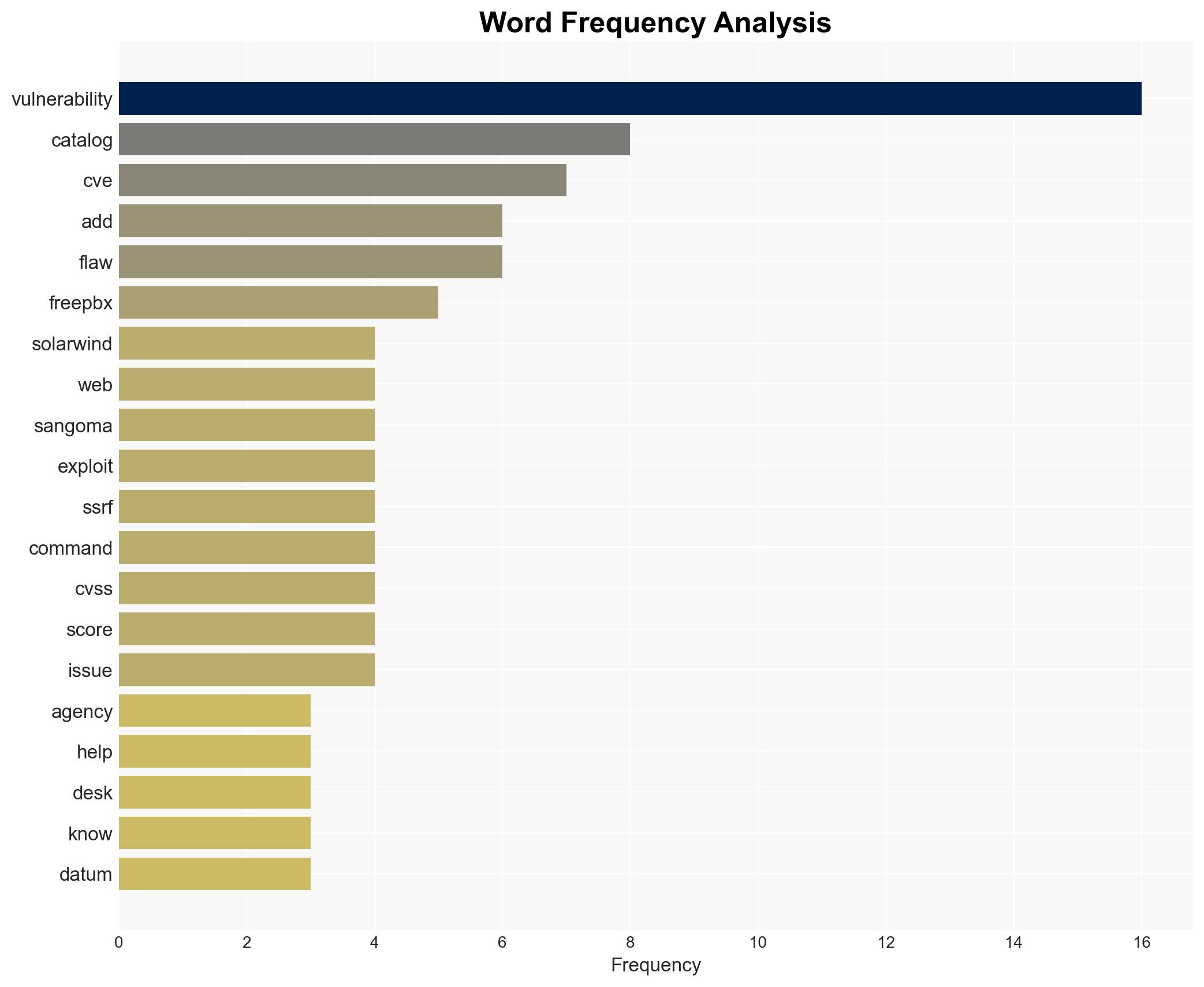
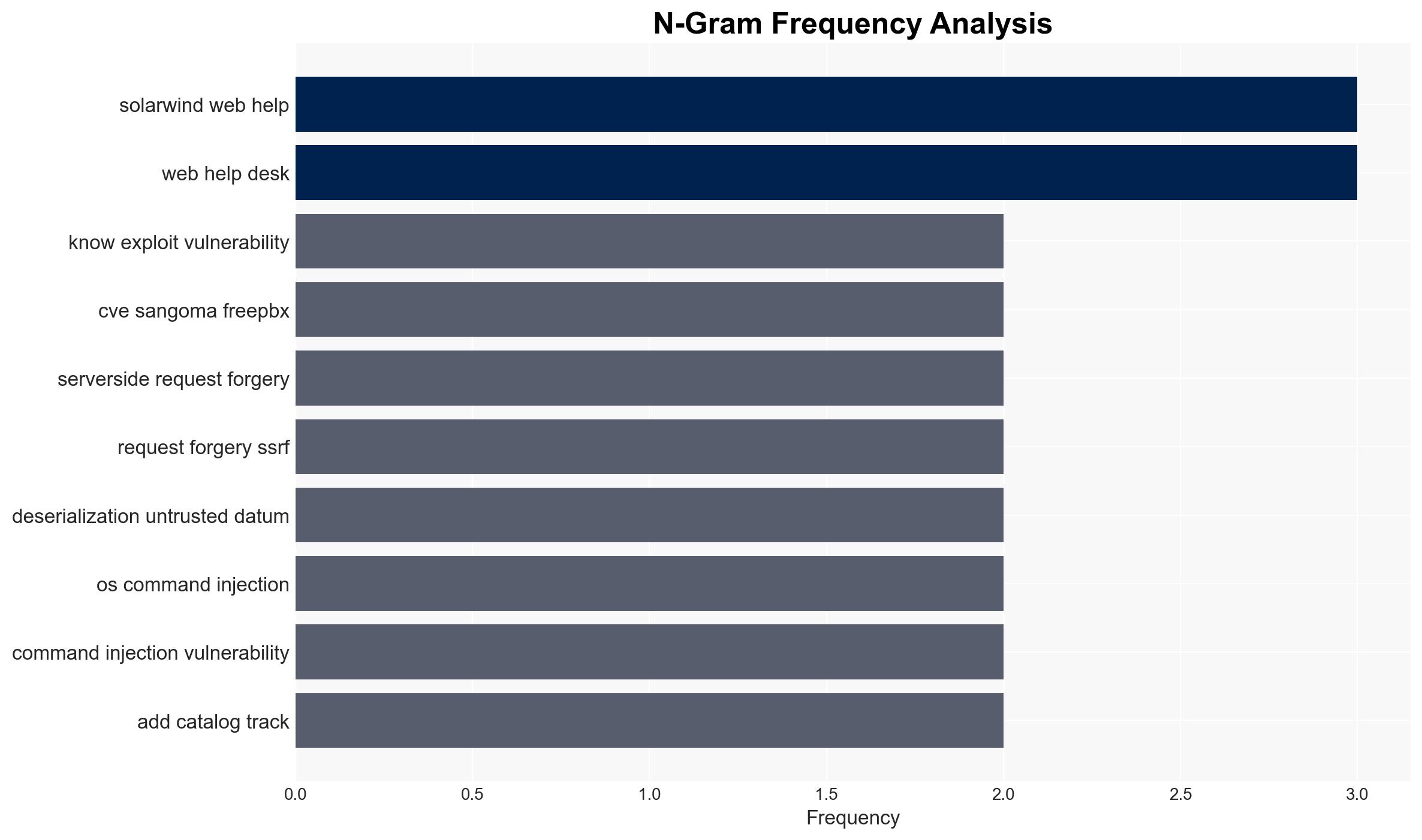
Intelligence Report: US CISA adds SolarWinds Web Help Desk Sangoma FreePBX and GitLab flaws to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
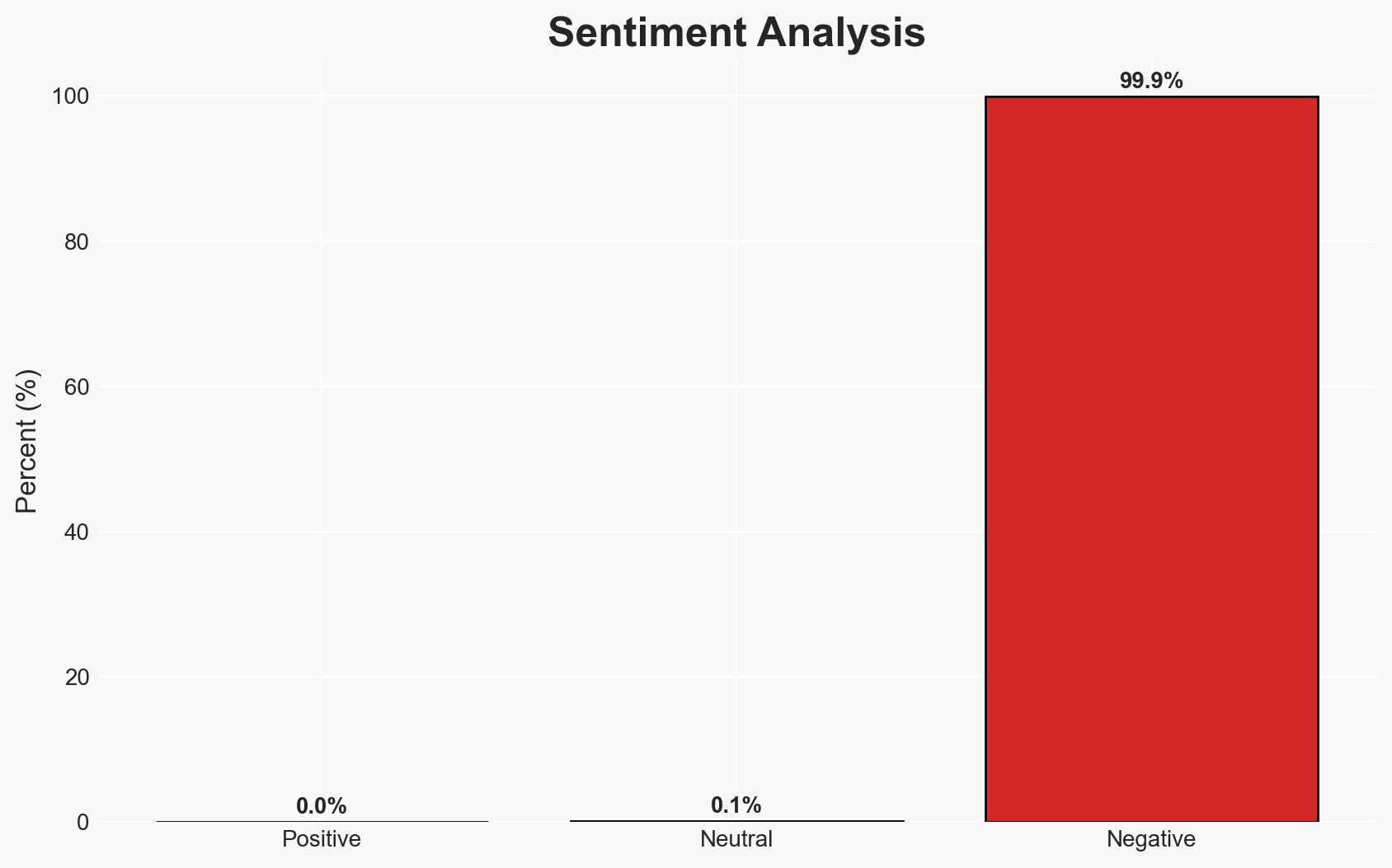
The addition of vulnerabilities in SolarWinds Web Help Desk, Sangoma FreePBX, and GitLab to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog underscores a significant threat to U.S. federal networks and private sector infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities are being actively exploited by cyber actors for reconnaissance and potential network compromise. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to observed exploitation patterns and the high CVSS scores of the vulnerabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities are being exploited primarily by state-sponsored actors aiming to infiltrate U.S. networks for espionage purposes. Evidence includes the high severity of the vulnerabilities and the strategic value of the targeted systems. However, there is uncertainty regarding the specific actors involved.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are being exploited by cybercriminal groups for financial gain, using compromised systems for ransomware or data theft. This is supported by the broad targeting of multiple vulnerabilities and the automation observed in exploitation attempts. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of direct financial motives observed in current exploitation patterns.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic nature of the targeted systems and the potential for significant geopolitical impact. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include attribution of specific actors or discovery of financial exploitation motives.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerabilities are being actively exploited; the exploitation is coordinated; the affected systems are critical to U.S. infrastructure.
- Information Gaps: Specific attribution of the actors exploiting these vulnerabilities; detailed impact assessments of compromised systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing state-sponsored motives; reliance on open-source data that may be incomplete or misleading.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to significant disruptions in U.S. federal and private sector operations, with potential cascading effects on national security and economic stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation of cyber tensions between the U.S. and potential adversary states, leading to diplomatic strains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vulnerability of critical infrastructure, potentially exploited for disruptive or destructive purposes.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened risk of data breaches and cyber espionage, undermining trust in digital systems.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic losses from disrupted services and increased cybersecurity costs for affected organizations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of network traffic for signs of exploitation; apply patches and mitigations for identified vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen public-private partnerships to improve threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity resilience measures.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patching and mitigation prevent significant exploitation, maintaining network integrity.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to major data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation with moderate impact, prompting increased cybersecurity measures and policy responses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jimi Sebree, Researcher at Horizon3.ai
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other individuals or entities.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerabilities, cyber-espionage, infrastructure protection, state-sponsored actors, cybercrime, network security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us