CISA Includes SolarWinds Web Help Desk RCE Vulnerability in KEV Catalog Amid Active Exploitation Concerns
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISA Adds Actively Exploited SolarWinds Web Help Desk RCE to KEV Catalog
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
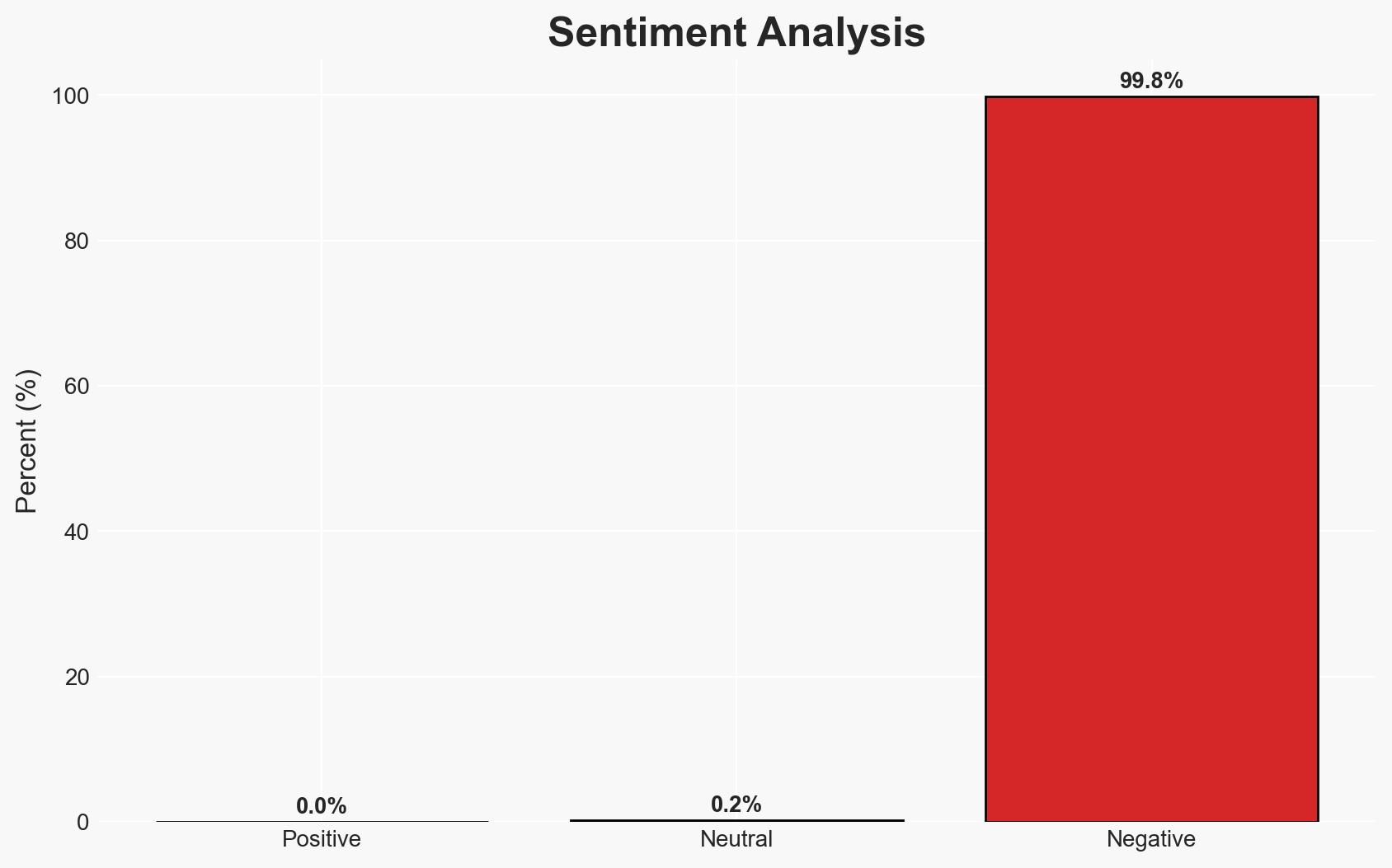
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has identified a critical vulnerability in SolarWinds Web Help Desk (WHD) that is being actively exploited. This vulnerability allows remote code execution without authentication, posing a significant threat to affected systems. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors are rapidly exploiting this flaw to gain unauthorized access to systems. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to the lack of detailed exploitation reports.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors are exploiting the SolarWinds WHD vulnerability primarily for espionage and data exfiltration purposes. This is supported by the high CVSS score indicating severe impact and the historical targeting of SolarWinds products by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups. However, the absence of specific exploitation details introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation is opportunistic, with actors aiming to deploy ransomware or other malware for financial gain. This is plausible given the common use of such vulnerabilities for monetary purposes, but lacks direct evidence in the current context.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic value of SolarWinds products in IT environments, which are attractive targets for espionage. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of financial extortion or ransomware deployment linked to this vulnerability.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is being exploited by sophisticated threat actors; SolarWinds WHD is widely used in critical sectors; Patches are not yet fully deployed across all affected systems.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the exploitation methods, targeted sectors, and geographical distribution of affected systems are missing.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on historical patterns of APT behavior; lack of independent verification of exploitation claims could lead to misinterpretation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to significant disruptions in IT operations and data breaches, affecting both public and private sectors. Over time, this may erode trust in software supply chains and increase regulatory scrutiny.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated, leading to diplomatic strains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert levels and resource allocation to counter cyber threats; potential for cascading effects if critical infrastructure is compromised.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber defense posturing and information sharing among cybersecurity communities; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the vulnerability.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses due to data breaches and operational disruptions; potential impact on consumer confidence in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgent patching of affected systems, enhanced monitoring for indicators of compromise, and dissemination of threat intelligence to stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthening of software supply chain security, development of incident response capabilities, and fostering public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch deployment mitigates exploitation, with minimal impact.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most Likely: Continued exploitation with gradual containment as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, remote code execution, SolarWinds, threat intelligence, software supply chain, cyber espionage
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us