Client’s Neglect of Password Security Leads to Major Cybersecurity Breach and Data Loss
Published on: 2026-01-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: IT Employee Explained The Importance Of Strong Passwords To A Client But They Ignored Him And Their Systems Got Hacked
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
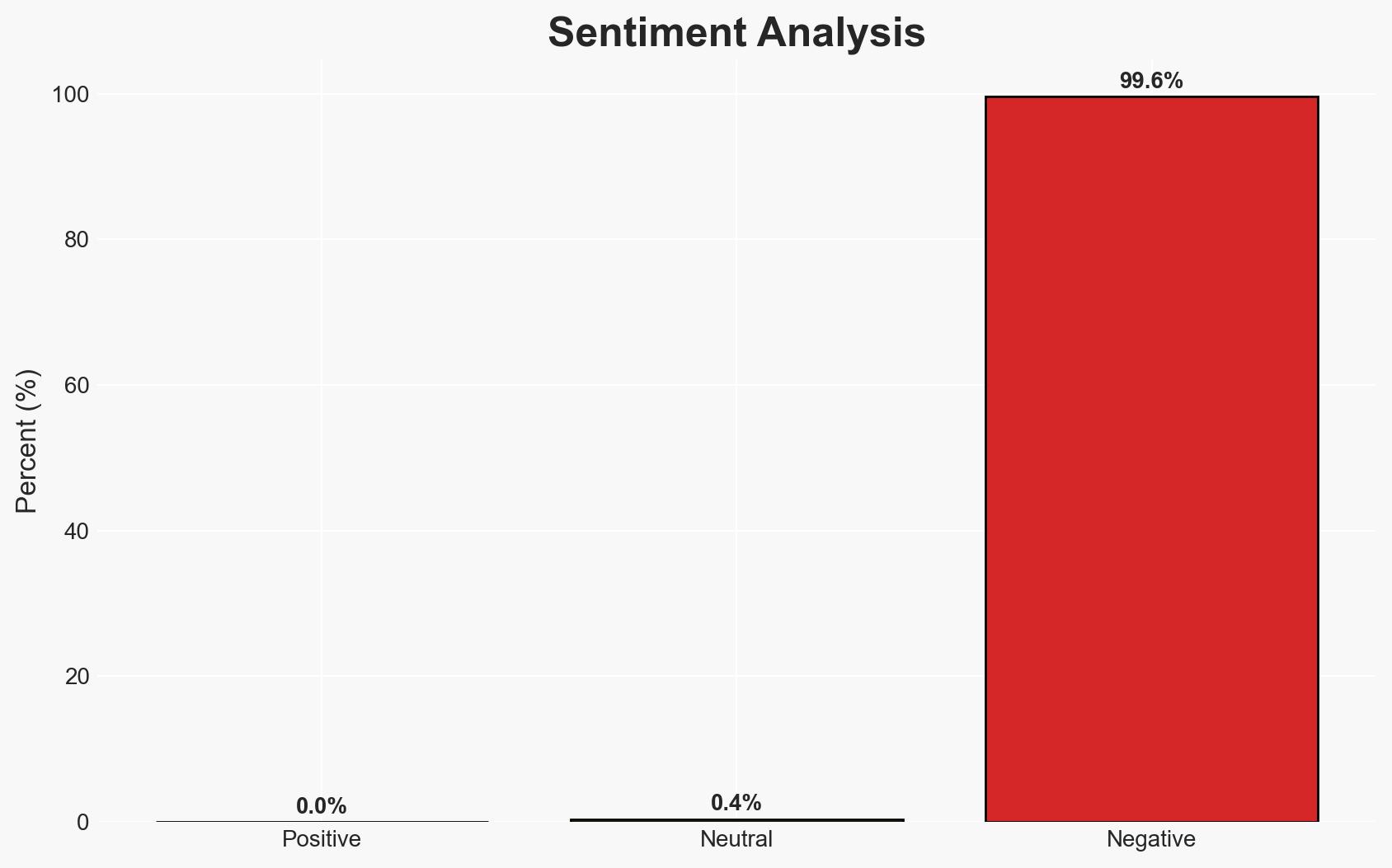
The failure of a small manufacturing company to adhere to strong password policies resulted in a ransomware attack, compromising critical data. The most likely hypothesis is that the owner’s decision to simplify passwords led to the breach. This incident highlights the importance of cybersecurity practices in small enterprises. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
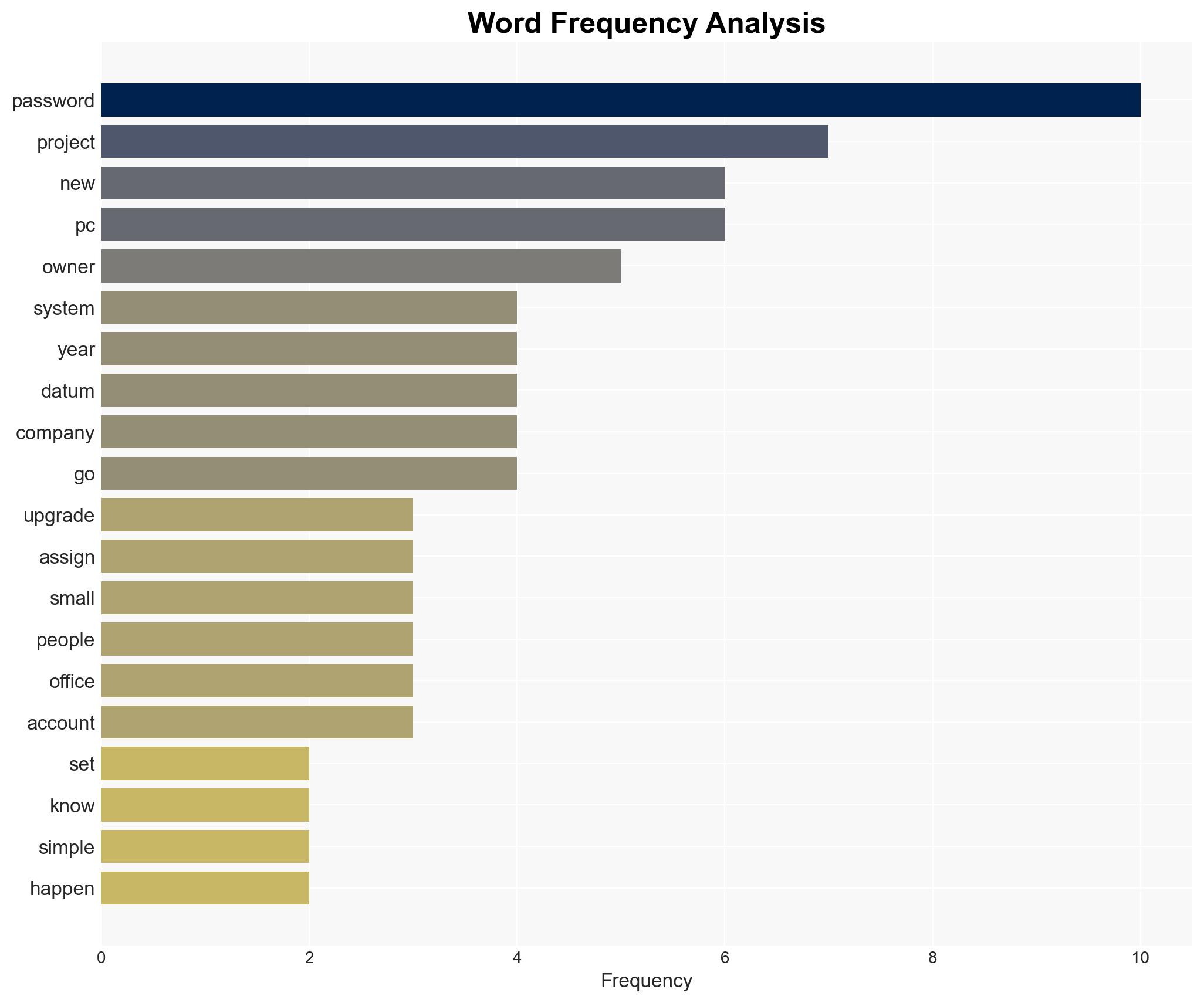
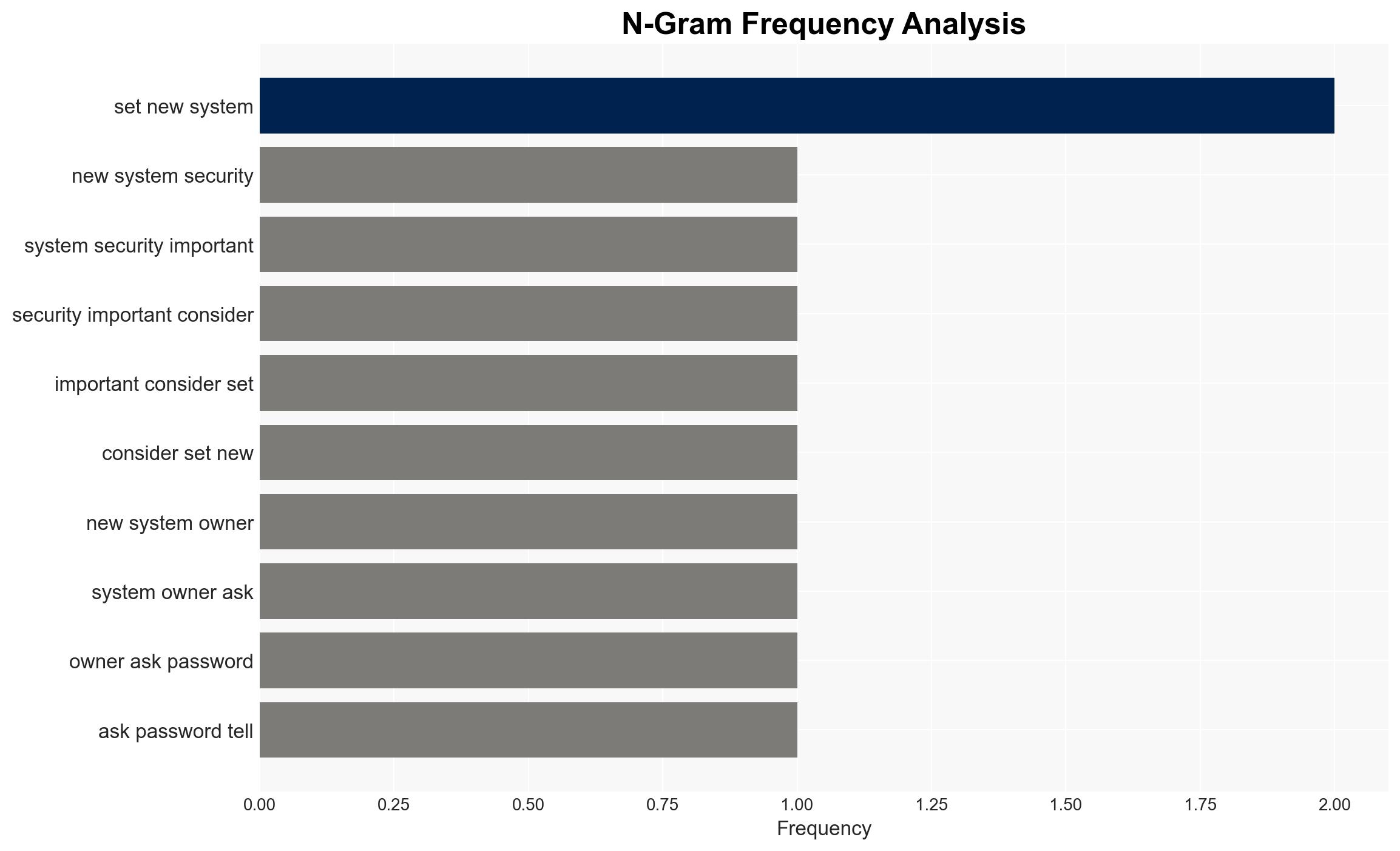
- Hypothesis A: The company’s systems were compromised due to the owner’s decision to simplify passwords, making them vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Supporting evidence includes the owner’s documented actions to reduce password complexity. However, the exact timeline of the breach relative to the password change is uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The breach occurred due to an external factor unrelated to password complexity, such as the nephew’s download of a malicious PDF viewer. While this could have been an entry point, the simplified passwords likely facilitated the spread of ransomware.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct link between password simplification and increased vulnerability. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of external targeting or sophisticated attack vectors unrelated to password strength.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The password change directly led to the breach; the nephew’s actions were unintentional and not part of a coordinated attack; the company did not have additional cybersecurity measures in place.
- Information Gaps: Details on the exact timeline of events post-password change; information on any other cybersecurity measures in place; specifics of the ransomware used.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from the IT consultant’s perspective; lack of direct evidence from the company’s internal security logs; possible underreporting of other security incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development underscores the vulnerability of small businesses to cyber threats due to inadequate cybersecurity practices. It may prompt increased scrutiny on cybersecurity standards in small enterprises.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications, but potential for increased regulatory focus on cybersecurity in small businesses.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Highlights the need for improved cybersecurity awareness and training to prevent similar incidents.
- Cyber / Information Space: Demonstrates the ease with which ransomware can exploit weak security practices, potentially encouraging similar attacks.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for the company and reputational damage, affecting business operations and employee trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit of the company; enforce strong password policies; provide cybersecurity training to all employees.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing support; implement advanced threat detection systems; establish a response plan for future incidents.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: The company strengthens its cybersecurity posture, preventing future breaches.
- Worst: Continued neglect of cybersecurity leads to repeated incidents, causing severe financial and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: The company improves security measures, but remains a potential target due to industry-wide vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, small business, password policy, IT consultancy, data breach, cyber awareness
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us