Cloud security struggles to keep pace with rapid cloud advancements and evolving threats
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cloud security is stuck in slow motion
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
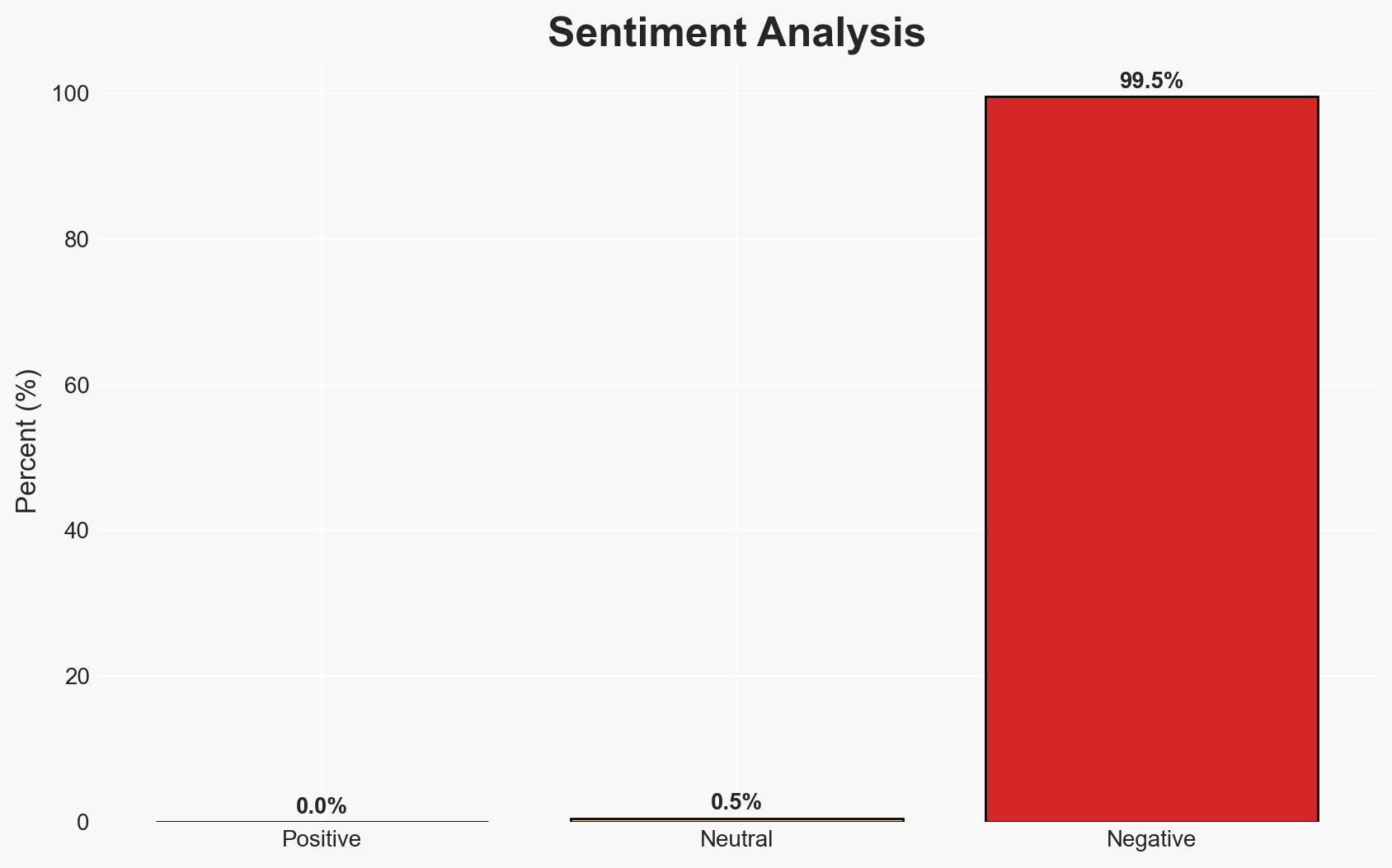
The rapid evolution of cloud environments outpaces current security measures, leading to increased vulnerabilities and operational complexity. This affects enterprises using multi-cloud and hybrid architectures, with moderate confidence in the assessment. Security teams face challenges in keeping up with fast development cycles and managing identity and data sprawl, increasing the risk of breaches.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The primary risk to cloud security is the speed of cloud adoption and development cycles outpacing security measures. Evidence includes the routine nature of weekly deployments and the use of generative AI tools, which complicate security enforcement. However, uncertainty remains about the specific impact of these factors on different types of organizations.
- Hypothesis B: The main threat stems from the complexity of managing multi-cloud and hybrid environments, leading to identity and data management issues. Supporting evidence includes concerns about fragmented environments and identity permissions. Contradicting evidence includes the ability of some organizations to detect and contain threats quickly.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent reporting of security teams struggling with the pace of development and the integration of security controls. Indicators that could shift this judgment include improvements in security tooling or changes in cloud adoption rates.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cloud environments will continue to grow in complexity; security measures will lag behind development cycles; identity and data management will remain challenging.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the effectiveness of current security measures across different sectors; detailed impact of generative AI on security vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from security vendors; over-reliance on self-reported data from organizations; lack of independent verification of breach timelines.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing lag in cloud security could lead to increased frequency and severity of breaches, impacting organizational trust and operational stability. Over time, this may necessitate regulatory interventions and increased investment in security technologies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international collaboration on cloud security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks exploiting cloud vulnerabilities, potentially used by state and non-state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber espionage activities targeting cloud environments; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting security breaches.
- Economic / Social: Economic impact from data breaches; potential loss of consumer trust in cloud services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cloud environments; prioritize patching and vulnerability management; increase training for security teams on cloud-specific threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cloud providers for improved security solutions; invest in automation and AI-driven security tools; advocate for standardized security protocols across cloud services.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid advancements in security technologies mitigate risks, leading to reduced breach incidents.
- Worst: Significant breaches occur, leading to regulatory crackdowns and loss of trust in cloud services.
- Most-Likely: Continued struggle with security adaptation, with incremental improvements as organizations adjust.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
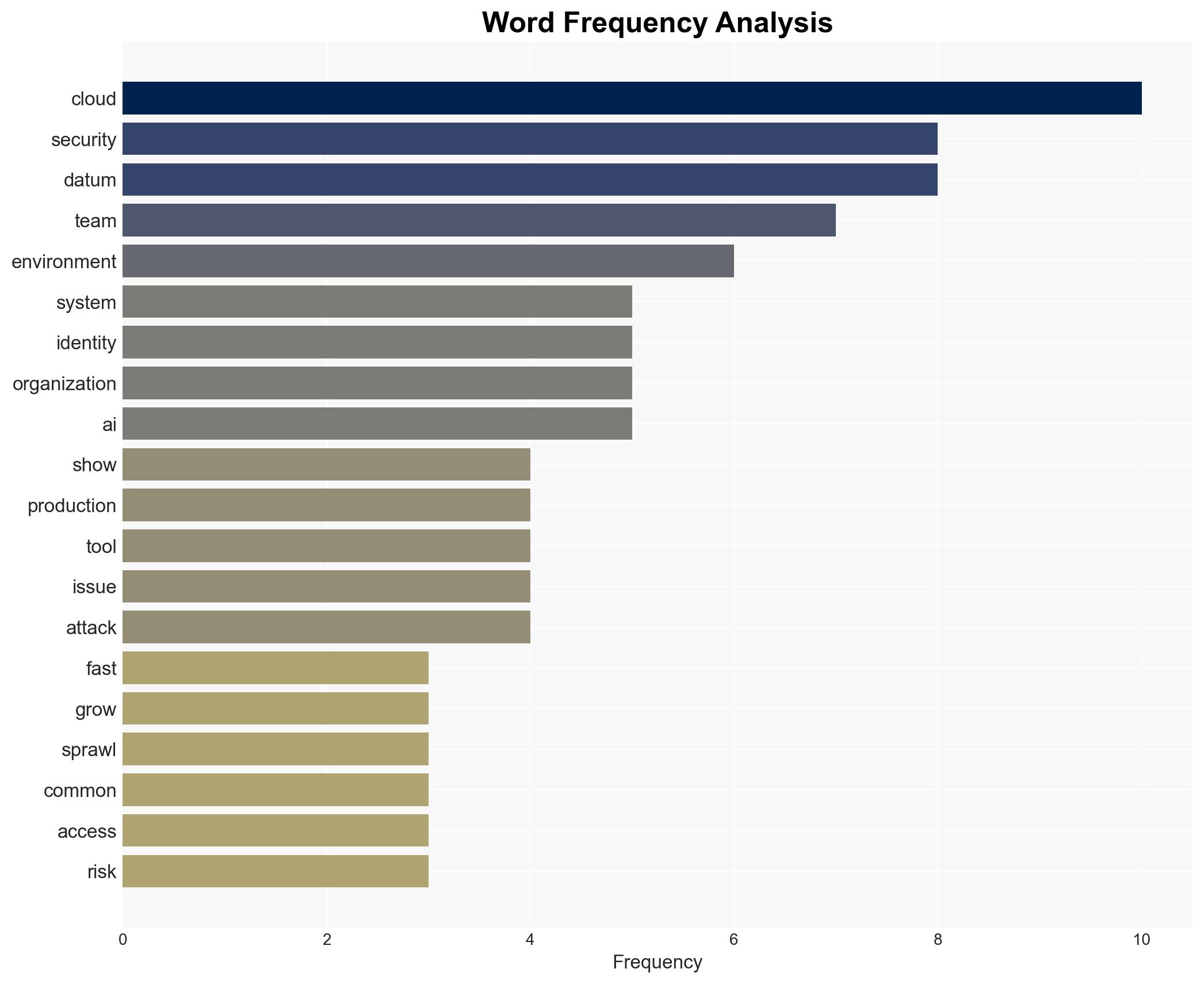
cybersecurity, cloud security, cyber risk, identity management, data protection, multi-cloud environments, generative AI, regulatory implications
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us