Comparing U.S. Maritime Actions to Houthi Interceptions: A Study in Double Standards and Sovereignty Issues
Published on: 2025-12-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Who are the real ocean outlaws Trumps regime or the Houthis
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
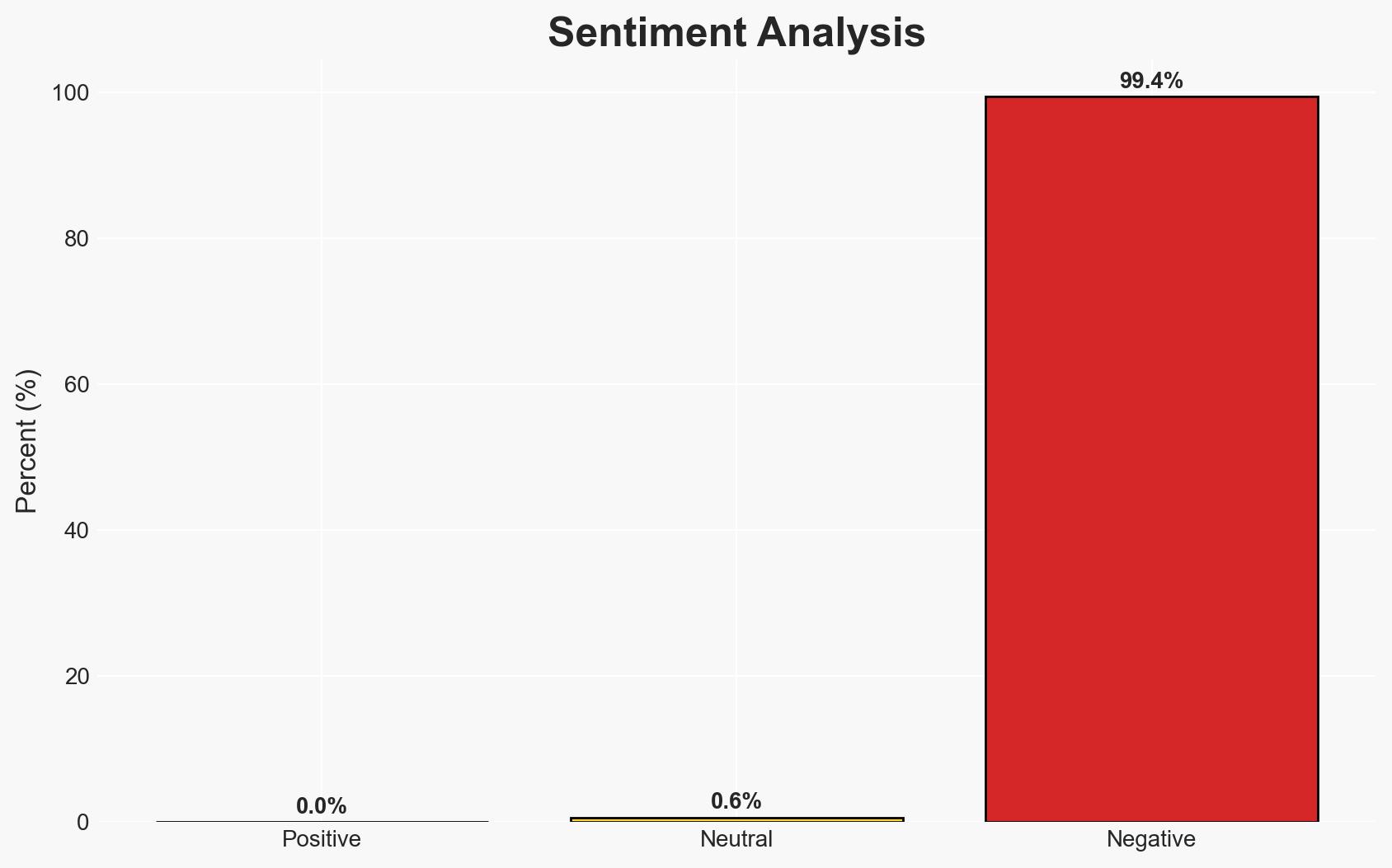
The U.S. and Houthi naval actions reflect contrasting legal and ethical interpretations of maritime interdiction. The U.S. actions against Venezuelan oil tankers and small boats under drug enforcement pretexts contrast with its condemnation of Houthi actions in the Red Sea. The most likely hypothesis is that both parties are leveraging maritime operations for strategic geopolitical gains, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to limited transparency and potential bias in reporting.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. naval actions are primarily driven by legitimate security concerns, including drug enforcement and regional stability. Supporting evidence includes the U.S. framing of operations under international law enforcement. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of transparency and potential civilian casualties.
- Hypothesis B: The Houthis’ naval campaign is a strategic response to perceived Israeli aggression, justified under international humanitarian law. Supporting evidence includes the Houthis’ legal framing and targeted criteria. Contradicting evidence involves potential overreach and civilian harm.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the Houthis’ explicit legal justifications and criteria, although both hypotheses are influenced by significant geopolitical interests. Indicators such as international legal rulings or shifts in U.S. policy could alter this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. actions are primarily security-driven; the Houthis are acting in response to Israeli actions; international law interpretations are consistent.
- Information Gaps: Detailed casualty reports, specific legal justifications for U.S. actions, and independent verification of vessel connections to Israel.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential U.S. narrative bias in framing operations as lawful; Houthi claims may omit unlawful actions or civilian impacts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development may exacerbate regional tensions and influence international maritime law interpretations. It could also affect global perceptions of U.S. and Houthi legitimacy.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased geopolitical friction between U.S. and Middle Eastern actors; potential for broader conflict escalation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment in maritime regions; potential for retaliatory actions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for disinformation campaigns and cyber operations targeting maritime infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of maritime trade routes; potential economic impacts on regional economies reliant on maritime commerce.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on maritime operations; engage in diplomatic dialogues to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for maritime security; strengthen international legal frameworks and partnerships.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: De-escalation through diplomatic engagement; Worst: Escalation into broader regional conflict; Most-Likely: Continued low-intensity maritime confrontations with intermittent diplomatic efforts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
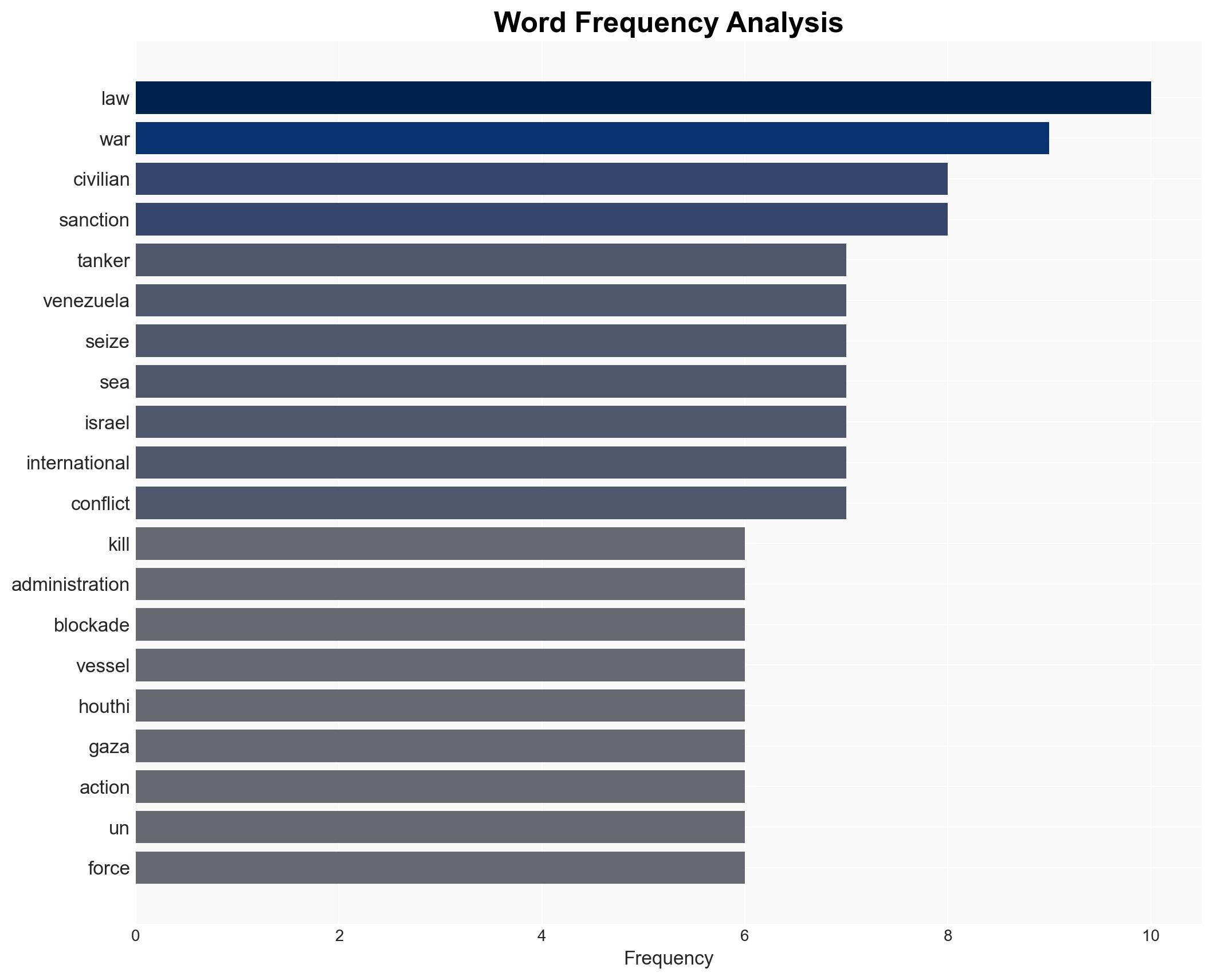
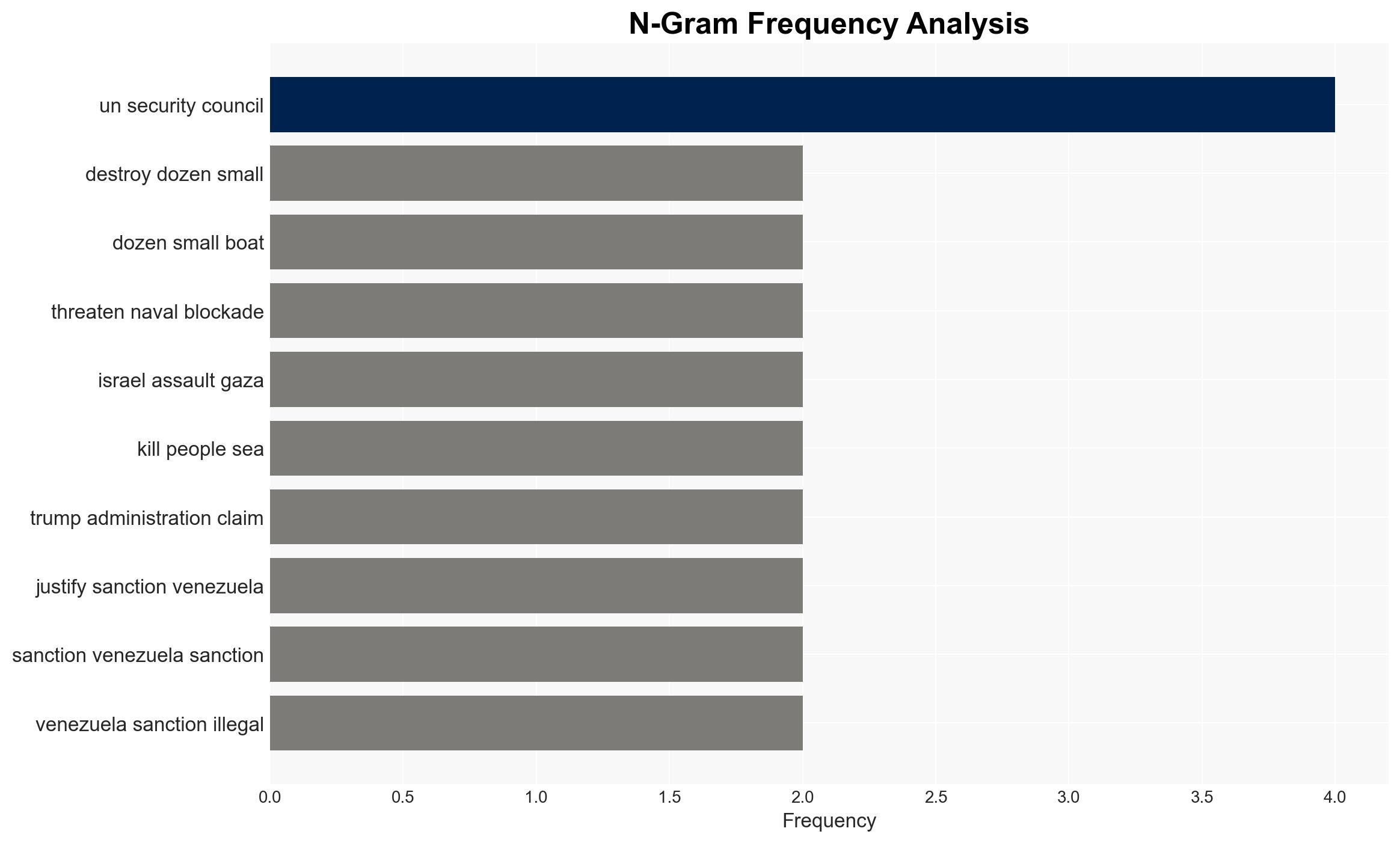
Counter-Terrorism, maritime security, international law, geopolitical tensions, U.S. foreign policy, Middle East conflict, naval operations, humanitarian law
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us