Compromised Developer Account Fuels Supply Chain Attack on Open VSX with GlassWorm Malware Distribution
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Open VSX Supply Chain Attack Used Compromised Dev Account to Spread GlassWorm
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
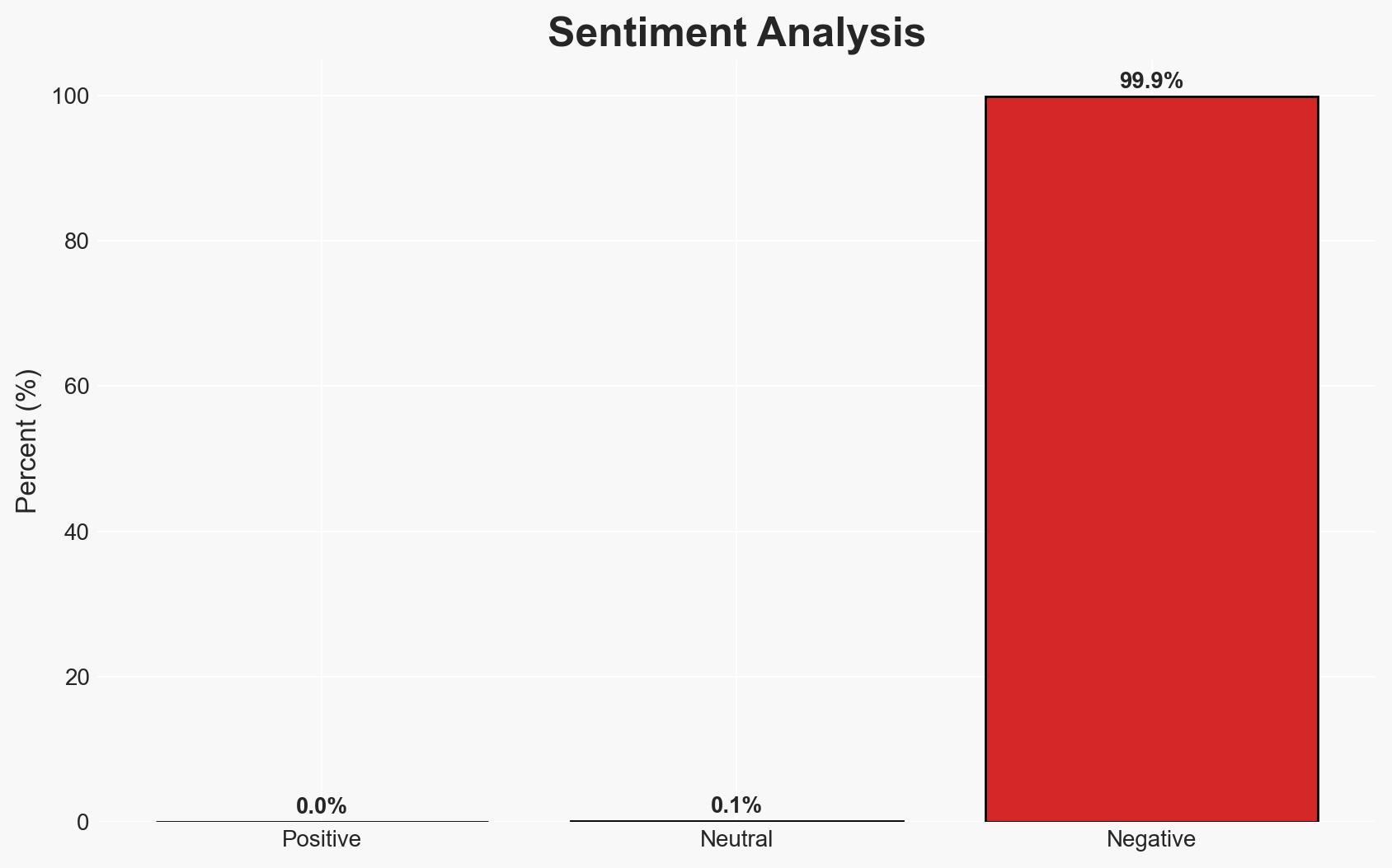
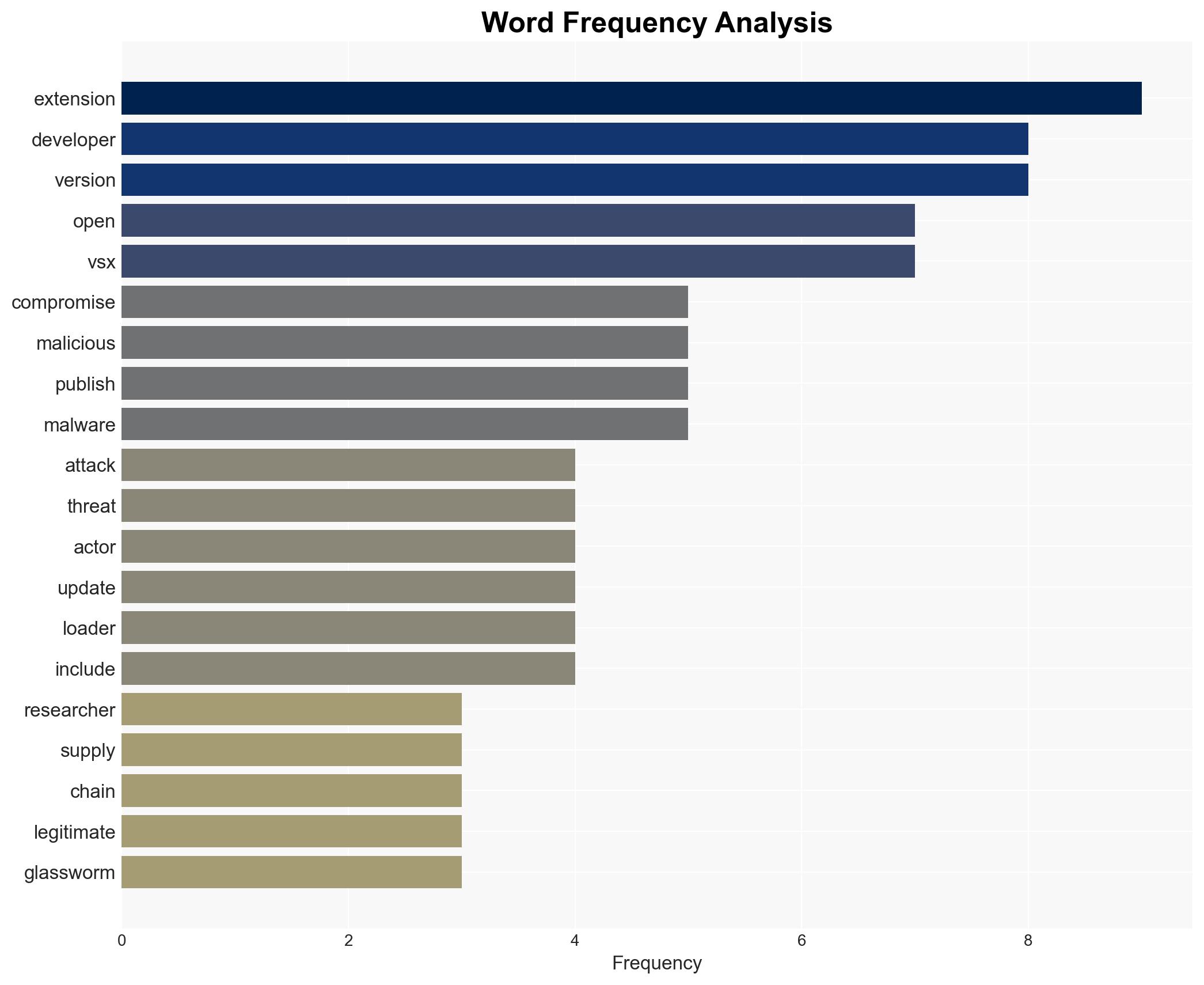
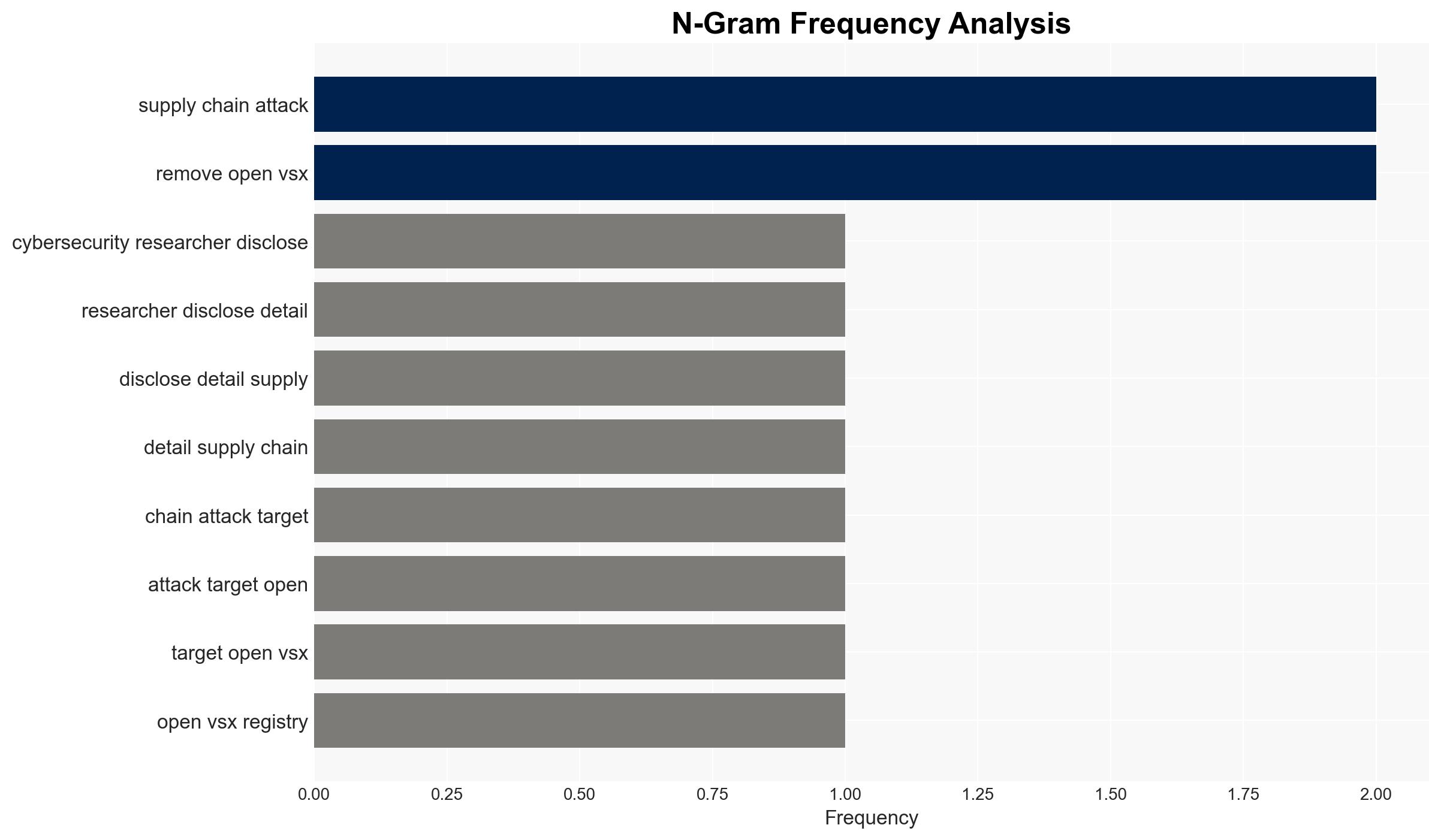
The Open VSX Registry experienced a supply chain attack where threat actors used compromised developer credentials to distribute the GlassWorm malware. This incident poses significant risks to enterprise environments due to potential cloud account compromises and lateral movement attacks. The attack appears to be associated with Russian-speaking threat actors, given the malware’s avoidance of Russian locales. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was orchestrated by Russian-speaking threat actors leveraging compromised developer credentials to target enterprise environments. This is supported by the malware’s avoidance of Russian locales and its sophisticated techniques. However, the exact identity of the threat actors remains unknown, creating uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was conducted by non-state actors or cybercriminal groups seeking financial gain through credential theft and cryptocurrency wallet access. This hypothesis is supported by the focus on stealing financial data but lacks direct evidence linking it to specific groups.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the malware’s specific avoidance of Russian locales, a common tactic among Russian-speaking threat actors. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include attribution evidence or changes in the malware’s targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The threat actors are motivated by financial gain; the compromised credentials were obtained through unauthorized access; the malware’s targeting is intentional and strategic.
- Information Gaps: Precise attribution of the threat actors; details on how the credentials were compromised; the full scope of affected users and systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias towards attributing the attack to Russian-speaking actors; reliance on open-source data that may be incomplete or manipulated.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny on supply chain security and heightened tensions in cyber defense strategies. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in developer ecosystems and the potential for widespread impact through compromised software updates.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased cyber tensions between Russia and affected nations if attribution is confirmed.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar supply chain attacks and increased focus on protecting developer credentials.
- Cyber / Information Space: Emphasis on improving supply chain security and monitoring for unauthorized access to developer accounts.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected enterprises and individuals, leading to calls for stronger cybersecurity measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Strengthen monitoring of developer credential use; audit and secure supply chain processes; inform affected users and provide remediation guidance.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced threat detection capabilities; enhance credential security protocols.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved security measures prevent further incidents; threat actors are identified and neutralized.
- Worst: Continued exploitation of supply chain vulnerabilities leads to widespread data breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security posture with ongoing threat actor activity.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Kirill Boychenko, Socket security researcher
- Open VSX Registry
- oorzc, developer account
- Unidentified threat actors
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain security, malware, cyber-espionage, credential theft, Russian-speaking threat actors, enterprise security, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us