Critical Flaw Exposes 60000 Redis Servers to Remote Exploitation – Infosecurity Magazine
Published on: 2025-10-07
Intelligence Report: Critical Flaw Exposes 60000 Redis Servers to Remote Exploitation – Infosecurity Magazine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that the Redis vulnerability, identified as CVE-nicknamed “Redishell,” poses an immediate and significant threat to global cybersecurity infrastructure, particularly due to its potential for exploitation by cybercriminals. Given the widespread exposure and historical targeting of Redis servers, there is a high confidence level that immediate patching and enhanced security measures are necessary to mitigate risks. It is recommended that organizations prioritize patching, enforce strict access controls, and monitor for suspicious activities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The Redis vulnerability will be rapidly exploited by cybercriminals, leading to widespread attacks involving data theft, ransomware, and cryptomining.
Hypothesis 2: The vulnerability will be contained quickly due to proactive patching and security measures, minimizing potential exploitation and impact.
Using Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH), Hypothesis 1 is better supported by historical data on previous Redis exploits and the current exposure of servers. The persistent targeting of Redis by malware such as Ppinfect and Redigo suggests a high likelihood of exploitation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that organizations will act swiftly to patch vulnerabilities and that attackers have the capability to exploit the flaw. A red flag is the reliance on organizations to implement security measures without external enforcement. The lack of evidence of current exploitation could indicate either underreporting or a delay in attack execution.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The vulnerability could lead to significant economic losses and damage to organizational reputations if exploited. It may also escalate into geopolitical tensions if state-sponsored actors leverage the flaw for cyber espionage. The psychological impact on public trust in cloud services could be substantial if high-profile breaches occur.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate patching of Redis servers and implementation of security updates.
- Enforce network segmentation and access controls to limit exposure.
- Monitor network traffic for anomalies and set up alerts for suspicious activities.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Swift patching leads to minimal exploitation and quick containment.
- Worst Case: Delayed response results in widespread attacks and significant data breaches.
- Most Likely: Moderate exploitation occurs before full patching is achieved, leading to isolated incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned in the source text. Key entities include Redis, Wiz (the cloud security firm), and Palo Alto Networks.
7. Thematic Tags
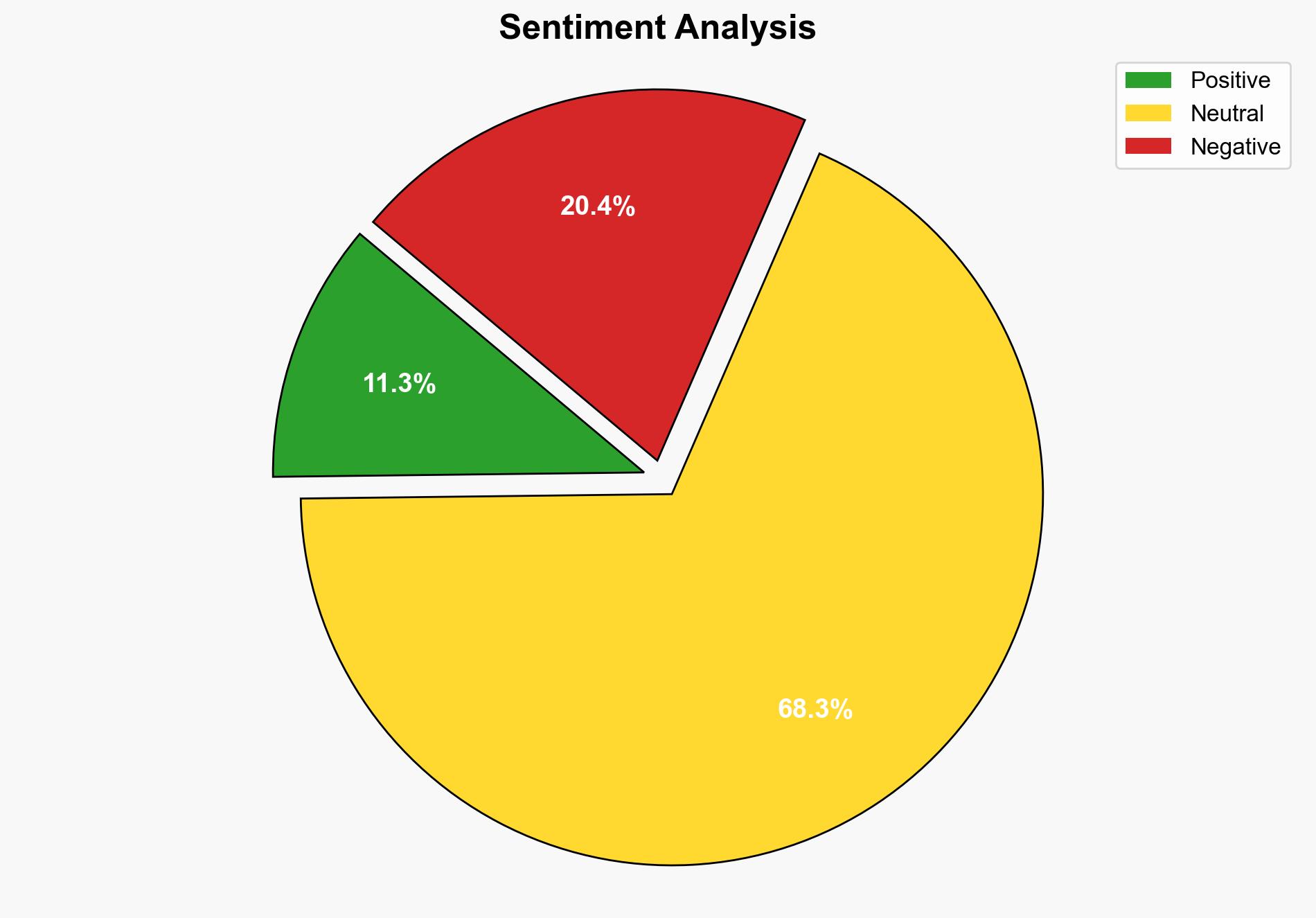
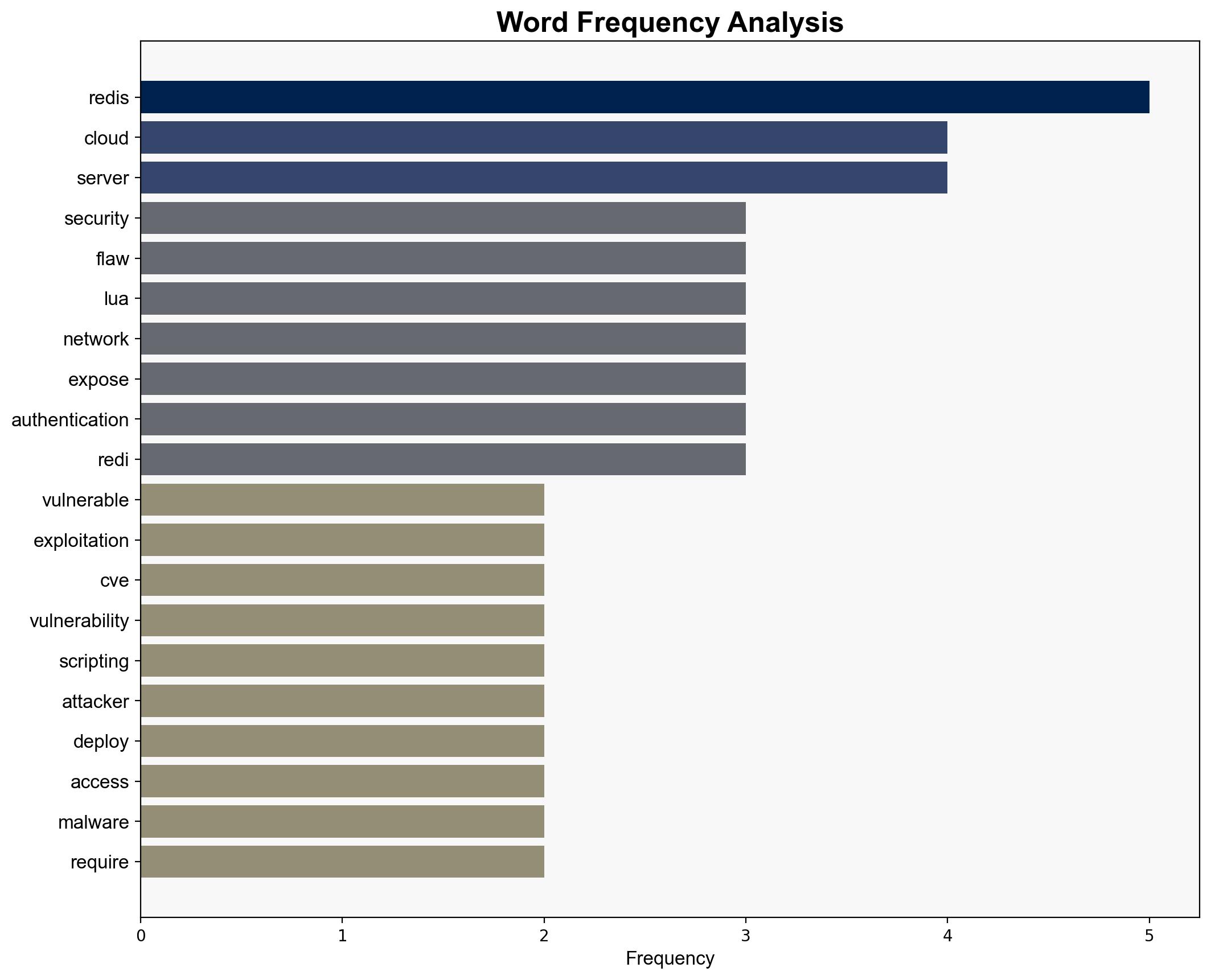
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus