Critical RCE Vulnerability Discovered in OpenClaw Exposing User Data and Access Keys
Published on: 2026-02-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
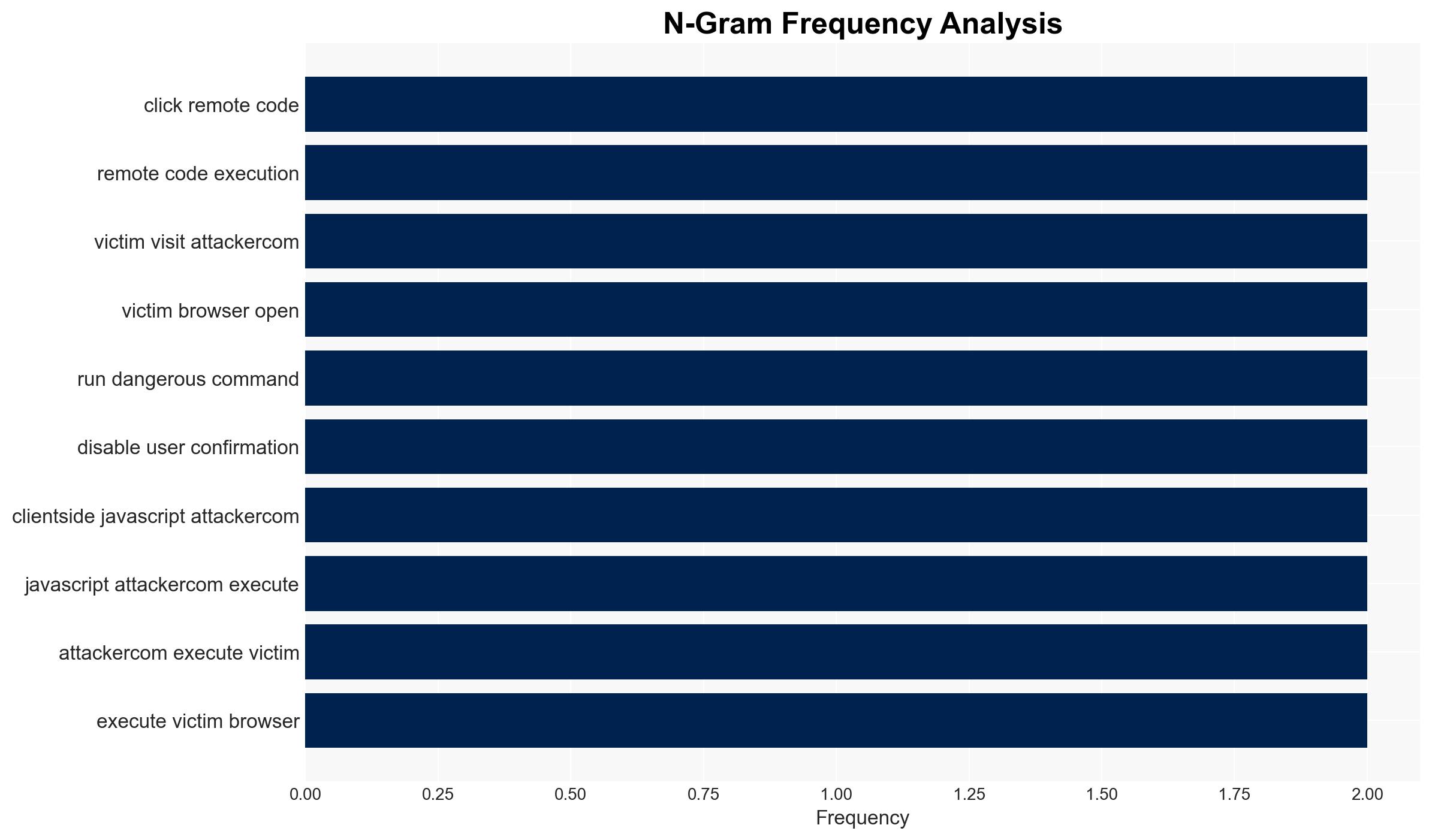
Intelligence Report: 1-Click RCE to steal your Moltbot data and keys
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The discovery of a critical 1-Click Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in OpenClaw, an AI personal assistant, poses a significant cyber threat to over 100,000 developers. This vulnerability allows attackers to access sensitive data and perform actions on behalf of users. The most likely hypothesis is that this vulnerability will be exploited by cybercriminals for data theft and unauthorized access. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and potential bias in the source.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will be exploited primarily by cybercriminals for data theft and unauthorized access. This is supported by the ease of exploitation and the high value of the data accessible through OpenClaw. However, the extent of exploitation is uncertain due to potential defensive measures by users.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability will be quickly patched and exploitation will be minimal. This is supported by the proactive identification of the vulnerability and potential rapid response from the OpenClaw community. However, the speed and effectiveness of patch deployment remain uncertain.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate availability of the exploit and the high incentive for attackers. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the release of a patch and widespread user adoption of security measures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: OpenClaw users are not immediately aware of the vulnerability; attackers have the capability to exploit the vulnerability; a patch has not yet been deployed.
- Information Gaps: The timeline for patch deployment and user adoption of security measures; the extent of current exploitation activities.
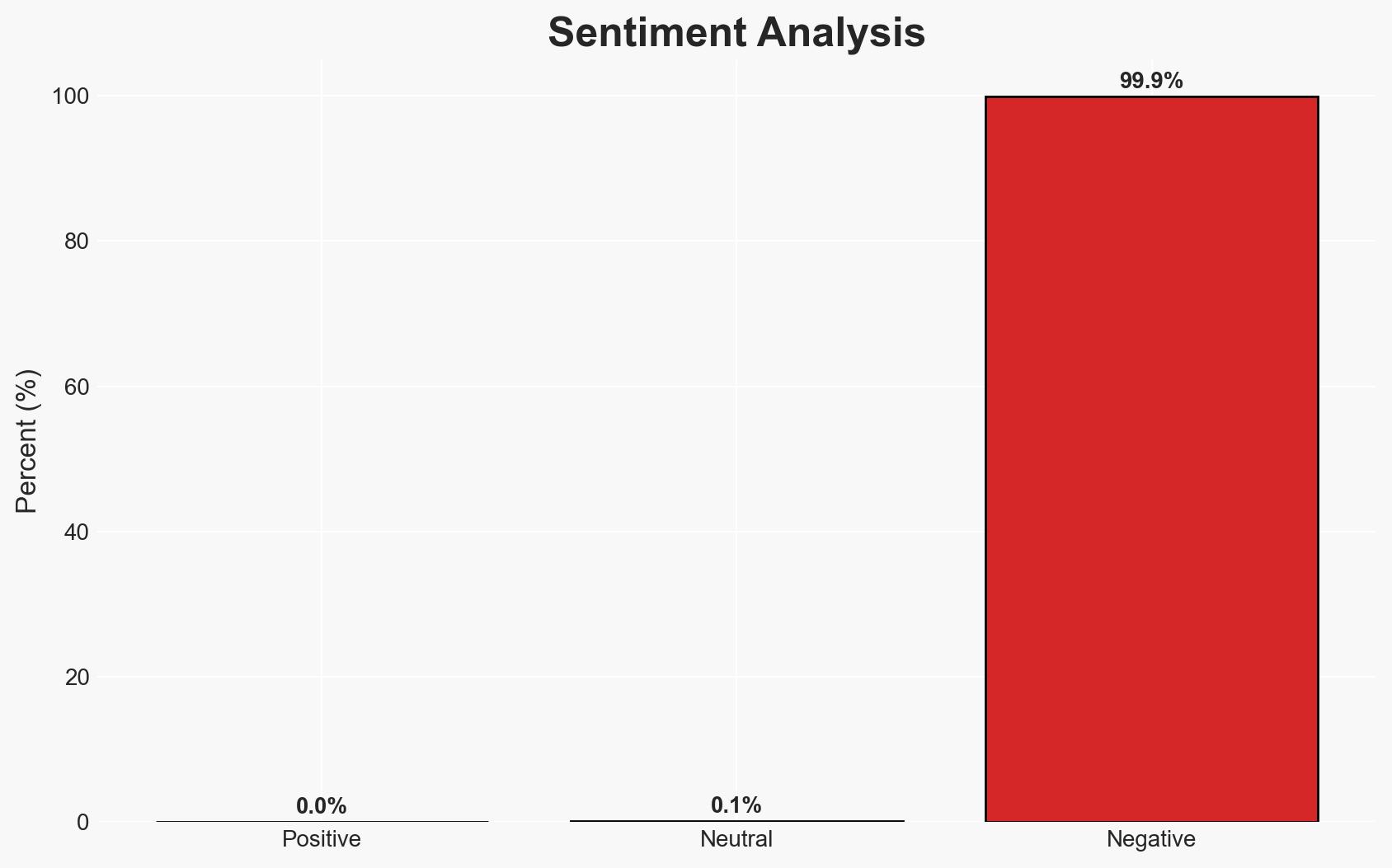
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the source due to vested interests in highlighting vulnerabilities; lack of corroborating sources increases the risk of misinformation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to significant data breaches and unauthorized actions, affecting user trust and system integrity. The broader implications depend on the response from the OpenClaw community and affected users.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications, but potential for increased scrutiny on AI security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cybercriminal activity targeting OpenClaw users.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on businesses relying on OpenClaw for operations; erosion of user trust in AI systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for signs of exploitation; encourage users to apply any available security updates; increase awareness of the vulnerability among OpenClaw users.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance detection and response capabilities; invest in user education on security best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch deployment and user adoption minimize exploitation.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and loss of trust.
- Most Likely: Moderate exploitation with gradual mitigation as patches are deployed.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- OpenClaw (formerly Moltbot and ClawdBot)
- Depthfirst General Security Intelligence
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
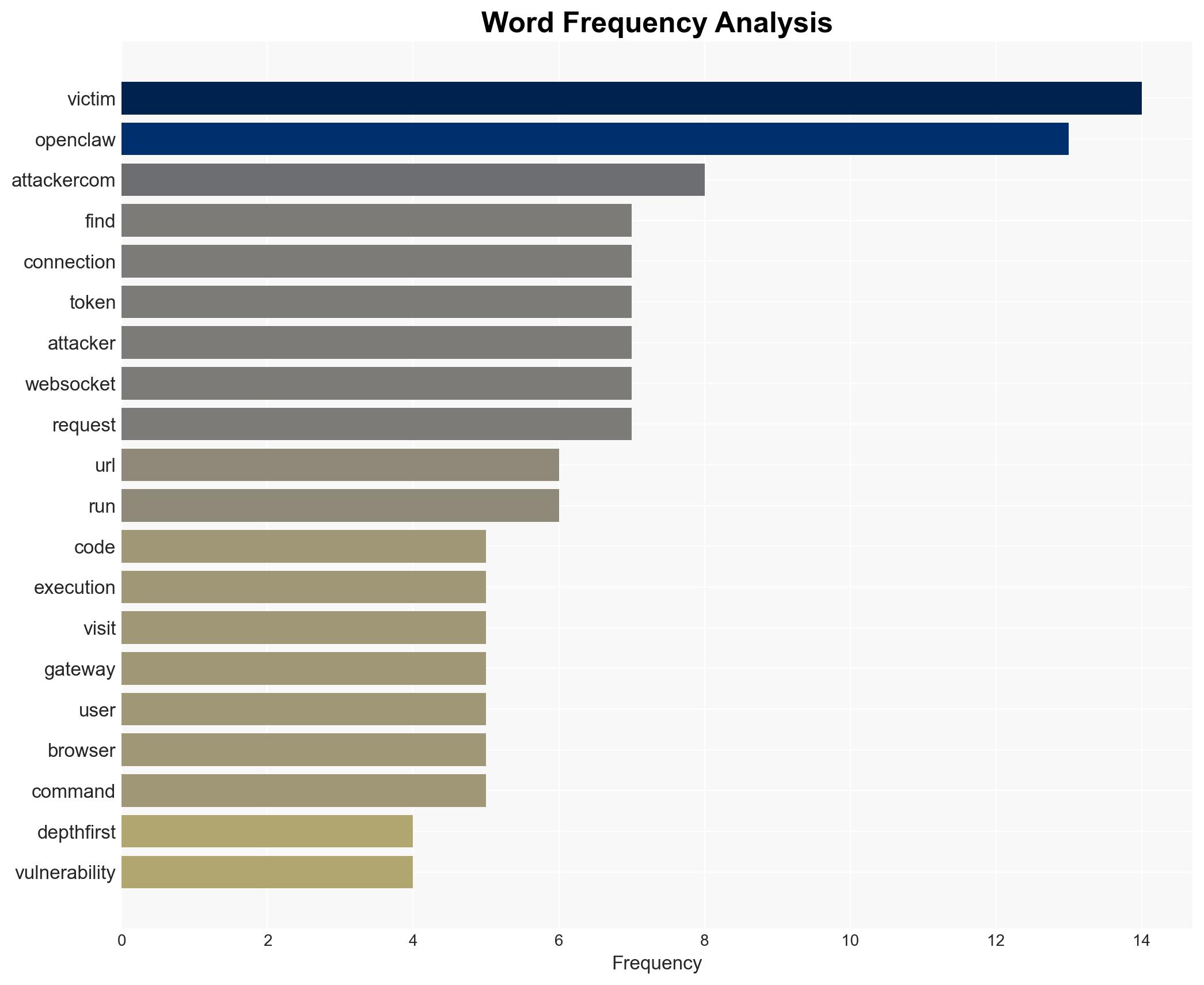
cybersecurity, remote code execution, AI vulnerabilities, data breach, cybercrime, software security, user trust
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us