Critical vulnerabilities expose thousands of systems to exploitation, highlighting rising cyber risks.
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: News brief Security flaws put thousands of systems at risk
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
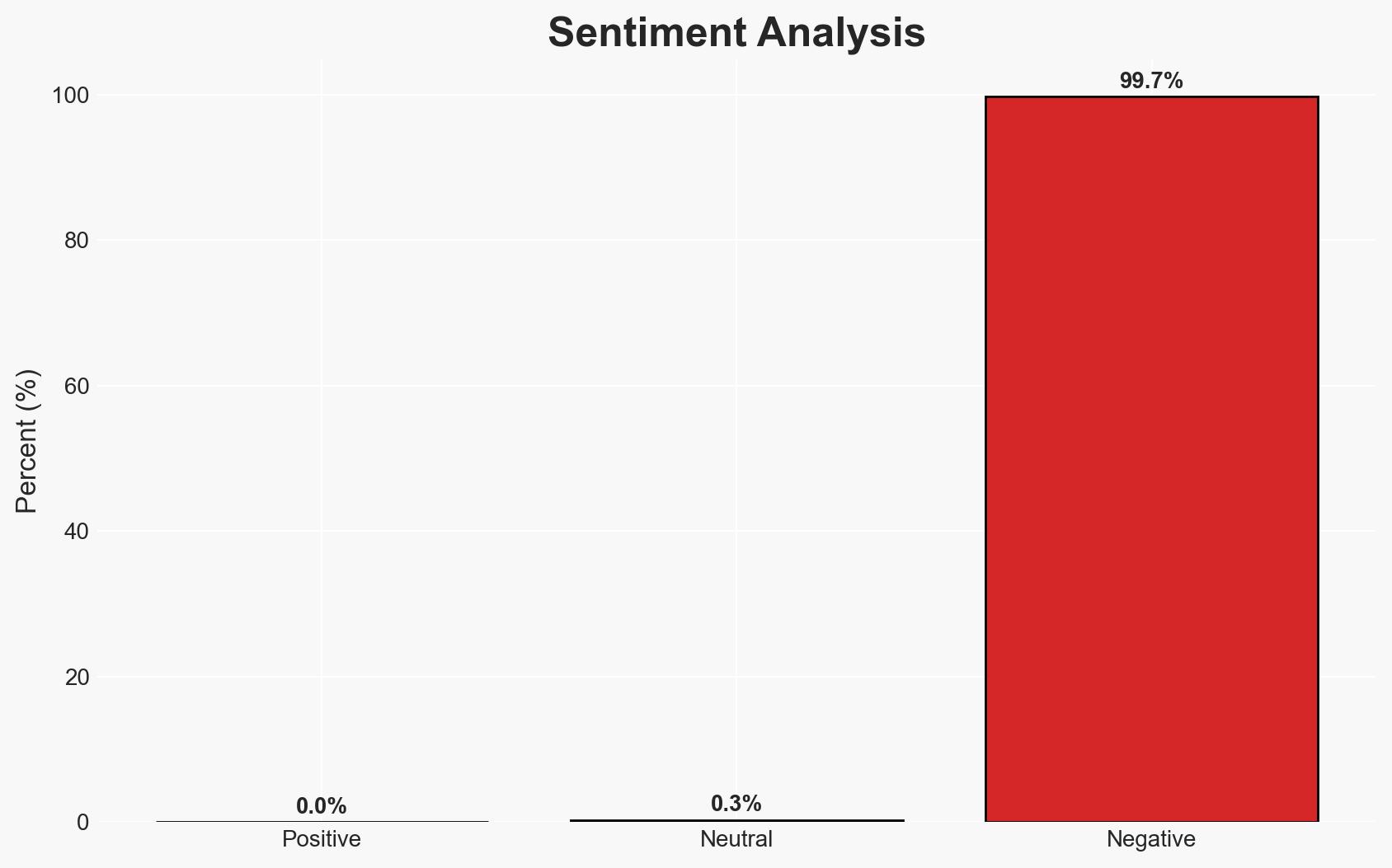
The discovery of critical vulnerabilities in widely used platforms such as ServiceNow, n8n, and AWS poses significant cyber risks to enterprise systems globally. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities are a result of increased reporting and scrutiny rather than a rise in cyber threats, with moderate confidence. Organizations using these platforms are primarily affected, with potential impacts on data security and operational integrity.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in reported vulnerabilities is primarily due to improved detection and reporting mechanisms rather than an actual increase in cyber threats. This is supported by expert opinions suggesting thorough reporting as the cause. However, the vast number of vulnerabilities remains a concern.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in vulnerabilities indicates a genuine increase in cyber threats, possibly due to more sophisticated attack vectors and tools. The presence of advanced AI-driven vulnerabilities and the emergence of new malware frameworks support this view.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to expert analysis indicating improved reporting. Indicators such as a sudden increase in exploitation incidents could shift this judgment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will act promptly to patch vulnerabilities; the vulnerabilities have not been widely exploited yet; reporting improvements are consistent across the industry.
- Information Gaps: Lack of detailed exploitation data; unclear if all affected organizations have implemented patches; limited information on the scope of potential damage.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in expert opinions towards minimizing perceived threat levels; risk of underreporting or delayed disclosure by affected companies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing discovery of vulnerabilities could lead to increased scrutiny on software vendors and pressure for rapid security enhancements. If unaddressed, these vulnerabilities could be exploited, leading to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cybersecurity standards and responsibilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with potential for exploitation by state and non-state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on cybersecurity measures and potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting vulnerability news.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on affected companies and loss of consumer trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Organizations should immediately apply available patches, conduct security audits, and limit AI agent capabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing, enhance incident response capabilities, and invest in AI security research.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch adoption and no significant exploitation incidents.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leading to major data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most Likely: Continued discovery of vulnerabilities with sporadic exploitation incidents, prompting ongoing security enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Aaron Costello, Chief of Security Research, AppOmni
- ServiceNow
- n8n
- AWS
- Check Point Research
- Cyera
- Wiz Researchers
7. Thematic Tags
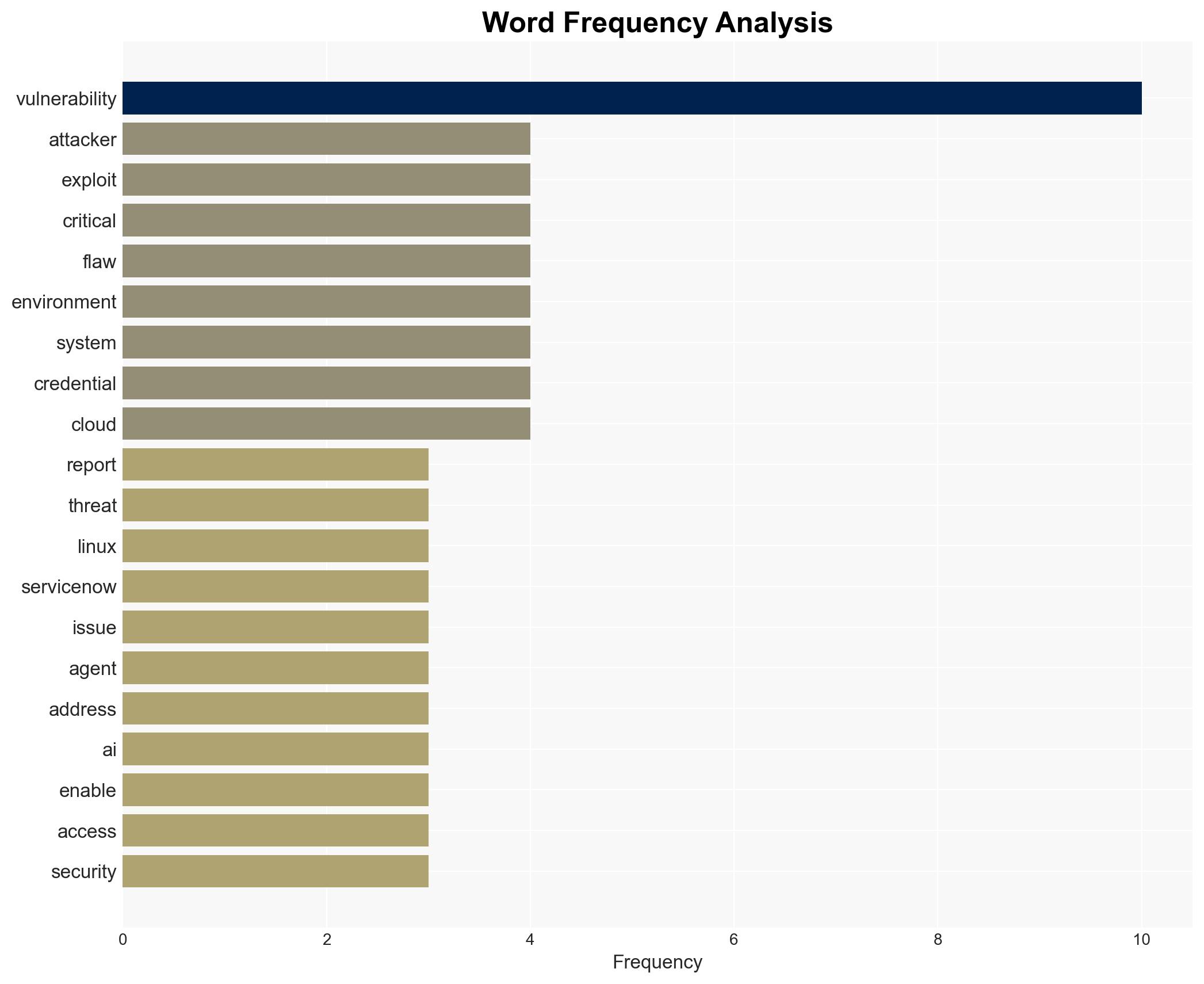
cybersecurity, vulnerabilities, AI-driven threats, enterprise systems, software patches, data security, malware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us