Critical Vulnerability in Grandstream GXP1600 VoIP Phones Enables Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
Published on: 2026-02-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Grandstream GXP1600 VoIP Phones Exposed to Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
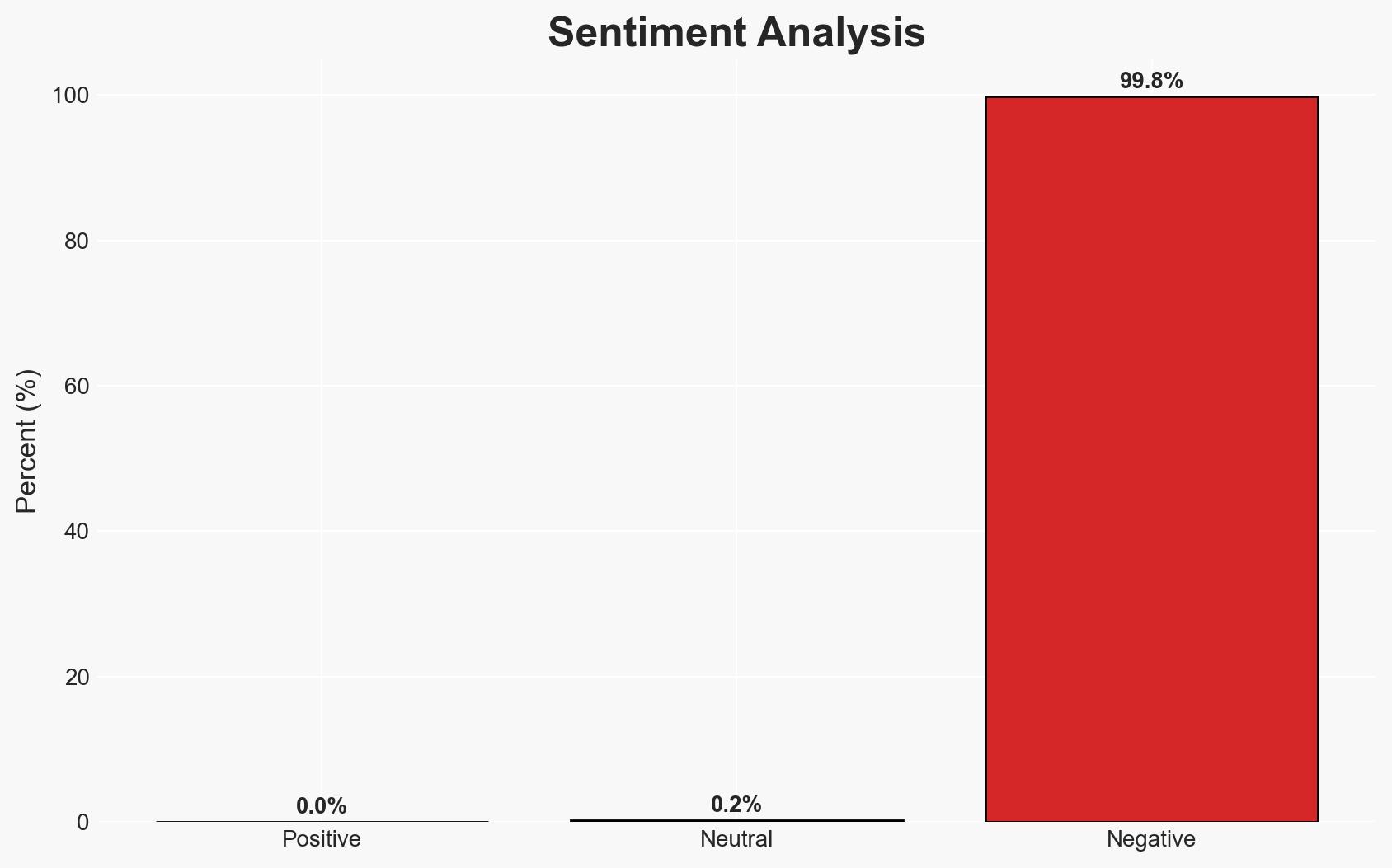
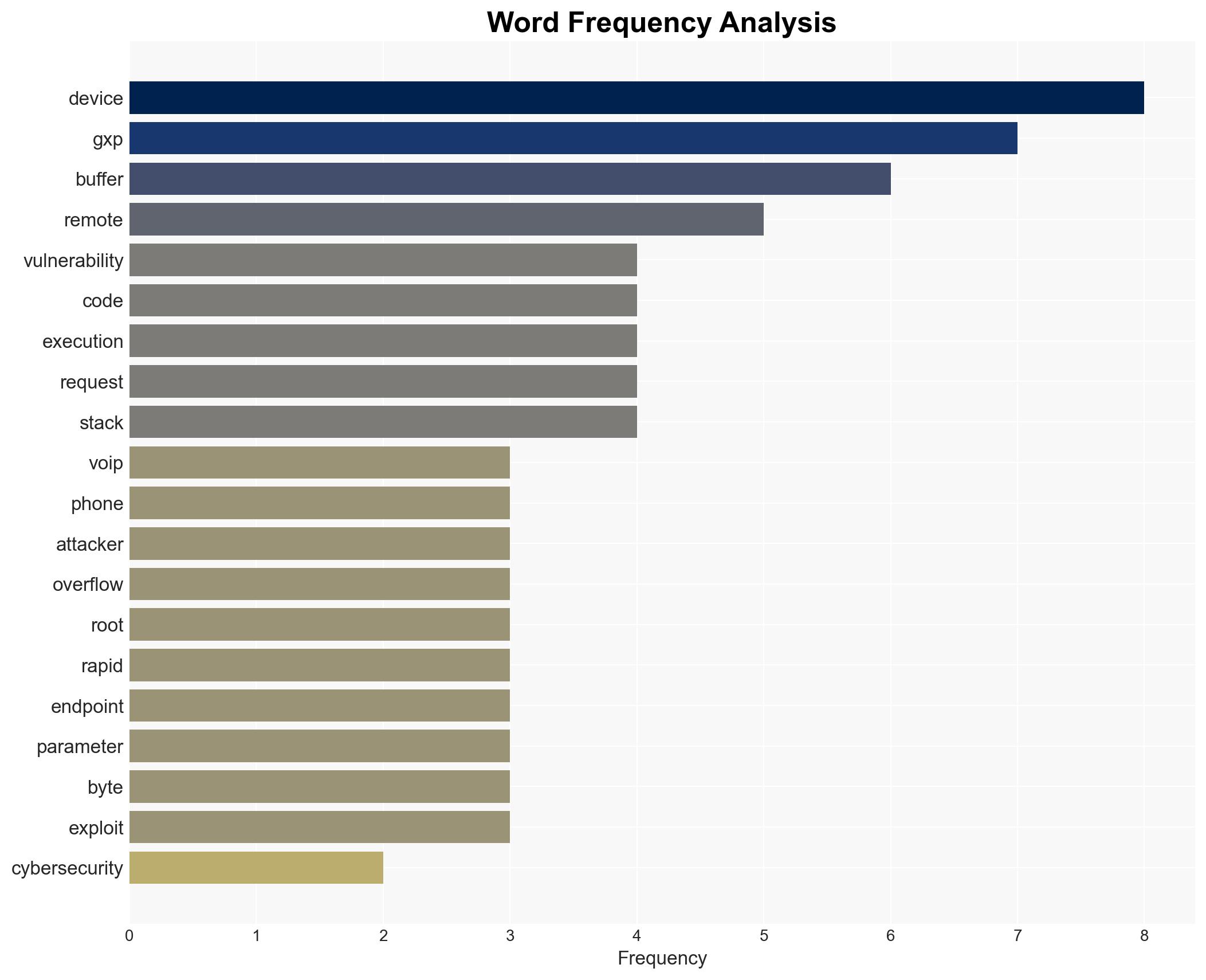
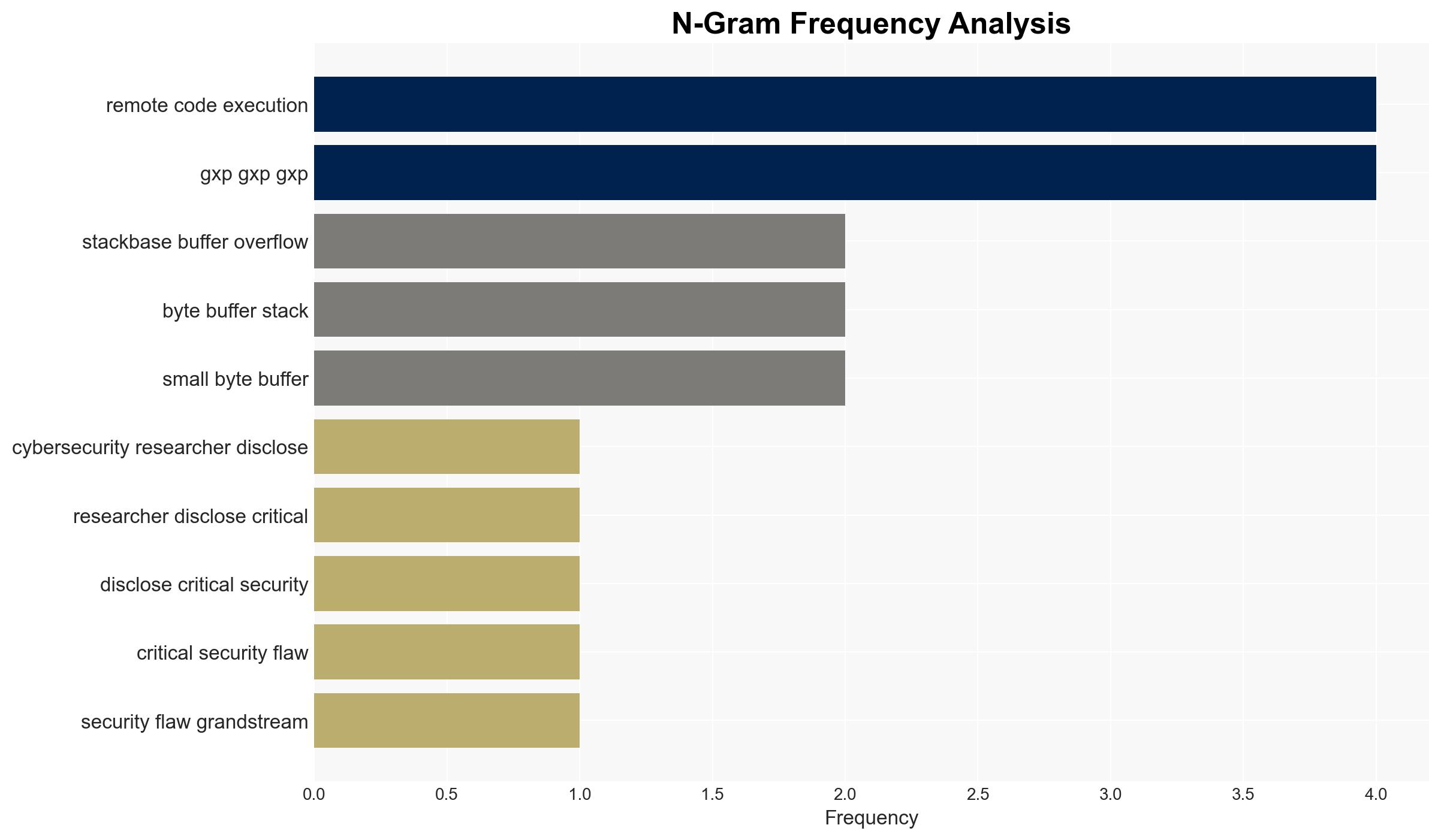
The Grandstream GXP1600 series VoIP phones are vulnerable to a critical security flaw (CVE-2026-2329) that allows unauthenticated remote code execution. This vulnerability, if exploited, could enable attackers to intercept communications and extract sensitive data. The primary affected entities are users and organizations deploying these devices. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the available information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will be actively exploited by cybercriminals to intercept communications and extract data from compromised devices. Supporting evidence includes the high CVSS score and the potential for remote code execution with root privileges. Key uncertainties include the extent of current exploitation and the speed of patch adoption.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability will be mitigated effectively through timely patching and will not lead to significant exploitation. This is supported by the release of a firmware update and awareness efforts by cybersecurity entities. Contradicting evidence includes the historical lag in patch adoption in similar scenarios.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the critical nature of the vulnerability and the potential for significant impact if exploited. Indicators such as increased reports of exploitation or slow patch adoption could further support this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The firmware update is effective in mitigating the vulnerability; organizations will prioritize patching; attackers have the capability to exploit the vulnerability.
- Information Gaps: Current exploitation levels, patch adoption rates, and the presence of additional vulnerabilities in the affected devices.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms aiming to highlight their role in discovering vulnerabilities; lack of independent verification of exploitation claims.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to significant operational and reputational damage for affected organizations, with broader implications for cybersecurity practices in VoIP deployments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are implicated in exploitation efforts.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of compromised communications in sensitive sectors, potentially affecting national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on VoIP security and potential for increased cyber espionage activities.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses from data breaches and potential loss of trust in VoIP technology.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urge organizations to apply the firmware update immediately, monitor for signs of exploitation, and review VoIP security policies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing and enhance VoIP security training for IT staff.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch adoption prevents significant exploitation.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to major data breaches.
- Most Likely: Mixed patch adoption results in isolated but impactful exploitation incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Stephen Fewer, Rapid7 researcher
- Douglas McKee, Rapid7 representative
- Grandstream Networks, Manufacturer
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, remote code execution, VoIP security, vulnerability management, data interception, patch management, cyber-espionage
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us