Cyber Fraud Surpasses Ransomware as Primary Concern for Business Leaders, WEF Report Reveals
Published on: 2026-01-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: World Economic Forum Cyber-fraud overtakes ransomware as business leaders’ top cyber-security concern
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
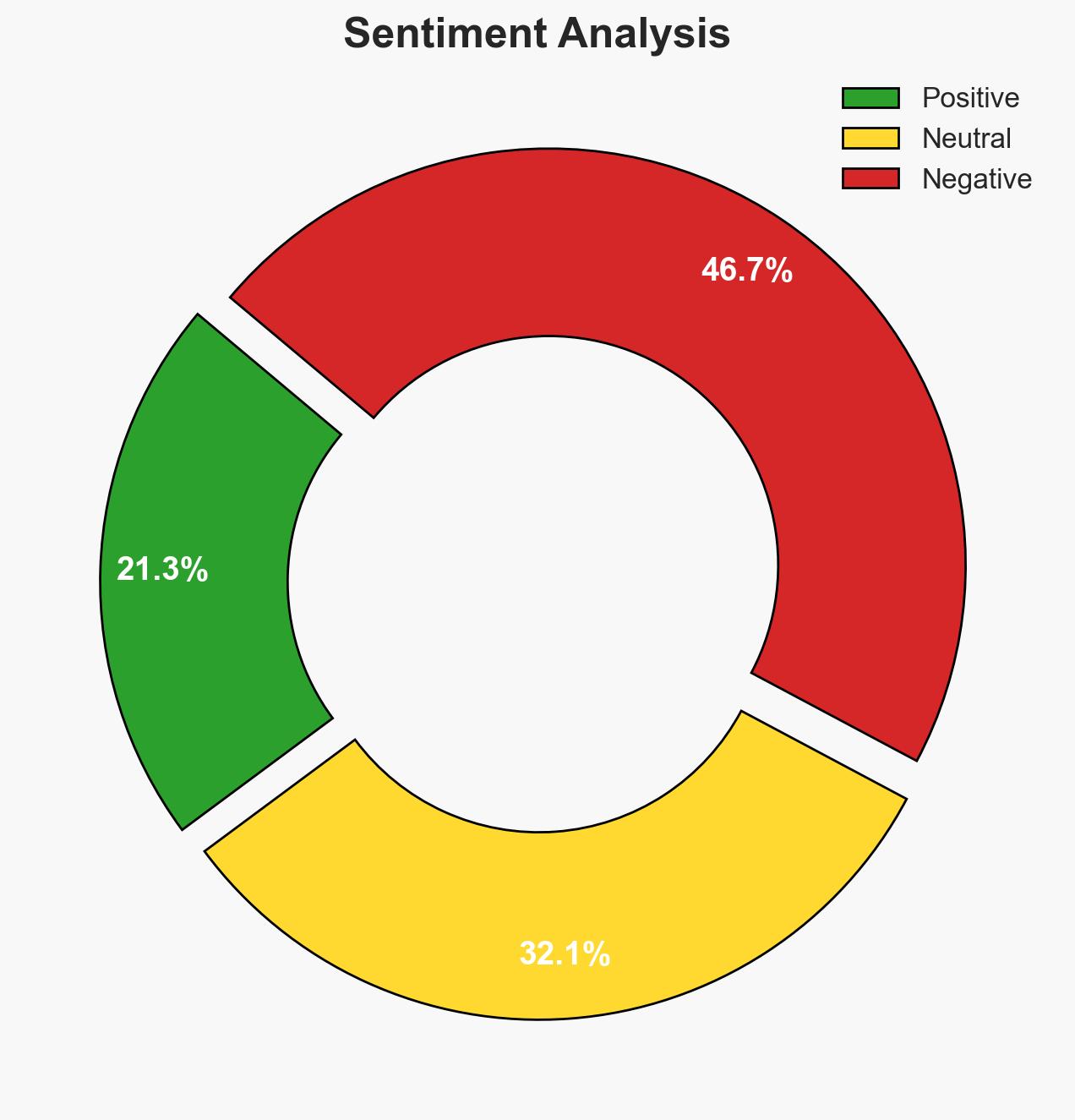
The World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook for 2026 identifies cyber fraud, particularly phishing, as the top cybersecurity concern for business leaders, surpassing ransomware. This shift indicates a significant threat to financial stability and trust in digital systems. The report highlights the interconnected nature of cyber risks, exacerbated by AI advancements. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the assessment due to the comprehensive survey data but acknowledges potential information gaps.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cyber fraud has overtaken ransomware as the primary concern due to its pervasive nature and the increasing sophistication of phishing attacks. Evidence includes the high percentage of business leaders reporting increased incidents and financial losses. However, the extent to which AI contributes to this trend remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The perceived increase in cyber fraud concerns is a temporary shift driven by recent high-profile incidents and media coverage, rather than a fundamental change in threat landscape. This hypothesis is less supported due to consistent reporting of increased fraud incidents across diverse sectors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the widespread acknowledgment of cyber fraud’s impact across industries and the detailed survey data. Future shifts in threat perception could be influenced by emerging AI-related vulnerabilities or significant ransomware events.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Business leaders’ responses accurately reflect the broader threat landscape; AI will continue to amplify cyber risks; organizations have comparable exposure to cyber fraud.
- Information Gaps: Detailed breakdown of industry-specific impacts; comprehensive data on AI’s role in cyber fraud; longitudinal data on fraud trends.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in survey responses due to recent incidents; media influence on threat perception; possible underreporting of ransomware incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of cyber fraud as a primary concern could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures. The integration of AI in cyber threats may accelerate these dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international cooperation on cybersecurity standards; increased diplomatic tensions over cybercrime attribution.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened focus on cyber defense capabilities; possible shifts in resource allocation from traditional security to cyber domains.
- Cyber / Information Space: Expansion of cyber fraud tactics leveraging AI; increased emphasis on cyber hygiene and resilience.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic destabilization due to financial losses; erosion of trust in digital transactions and communications.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing and fraud activities; initiate awareness campaigns on cyber hygiene; collaborate with industry partners for intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-driven detection and response capabilities; strengthen public-private partnerships; invest in cybersecurity training and education.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective collaboration reduces fraud incidents; AI tools improve defense mechanisms.
- Worst: Cyber fraud incidents continue to rise, causing significant economic damage and loss of trust.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in defenses with ongoing challenges from evolving AI threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jeremy Jurgens, Managing Director, World Economic Forum
- Accenture (collaborator on the report)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber fraud, phishing, AI threats, economic impact, digital trust, public-private partnership
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us