Cyber Threats Remain Top Global Risk in Allianz Barometer, AI Rises to Second Place in 2026 Rankings
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
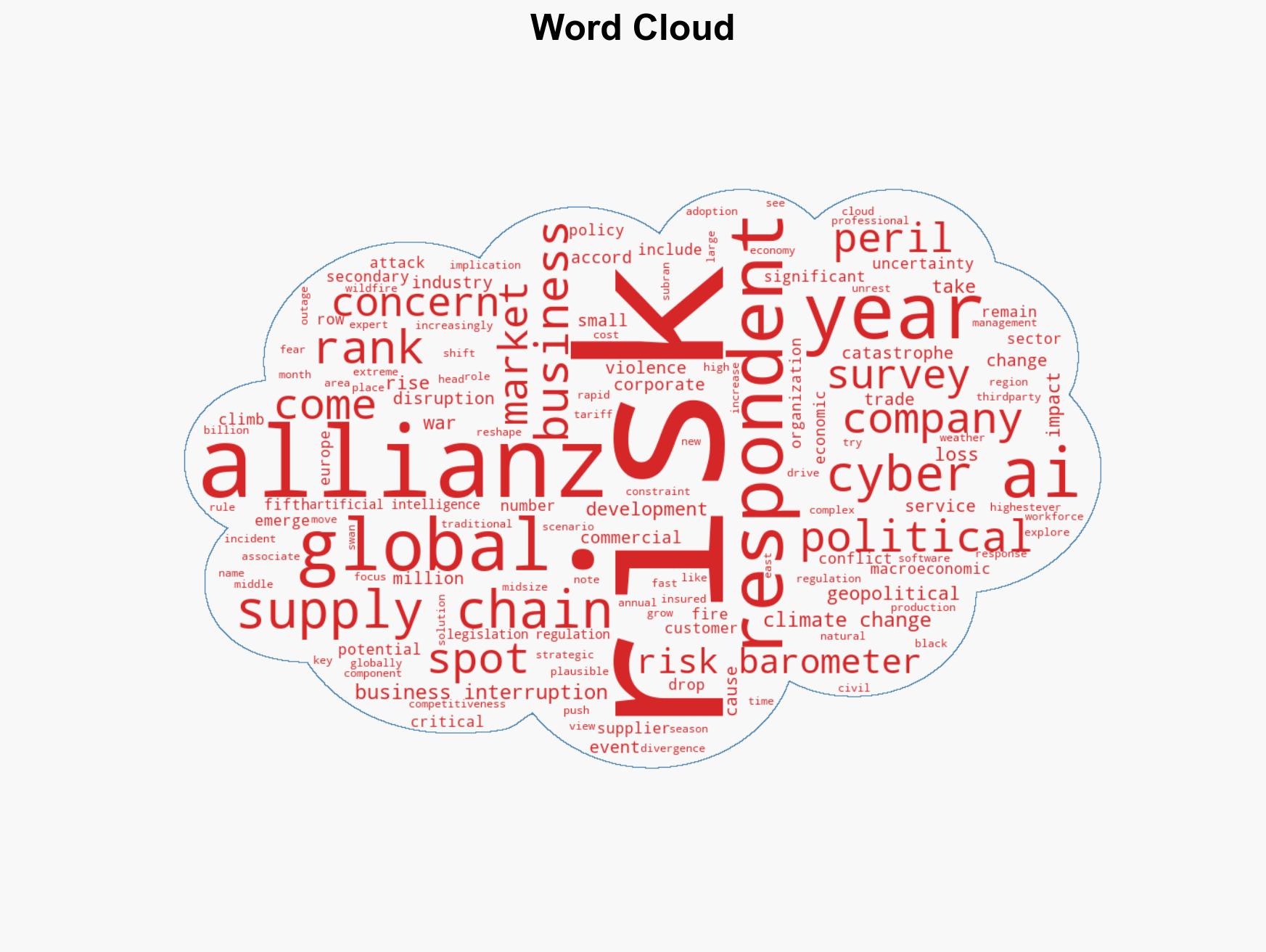
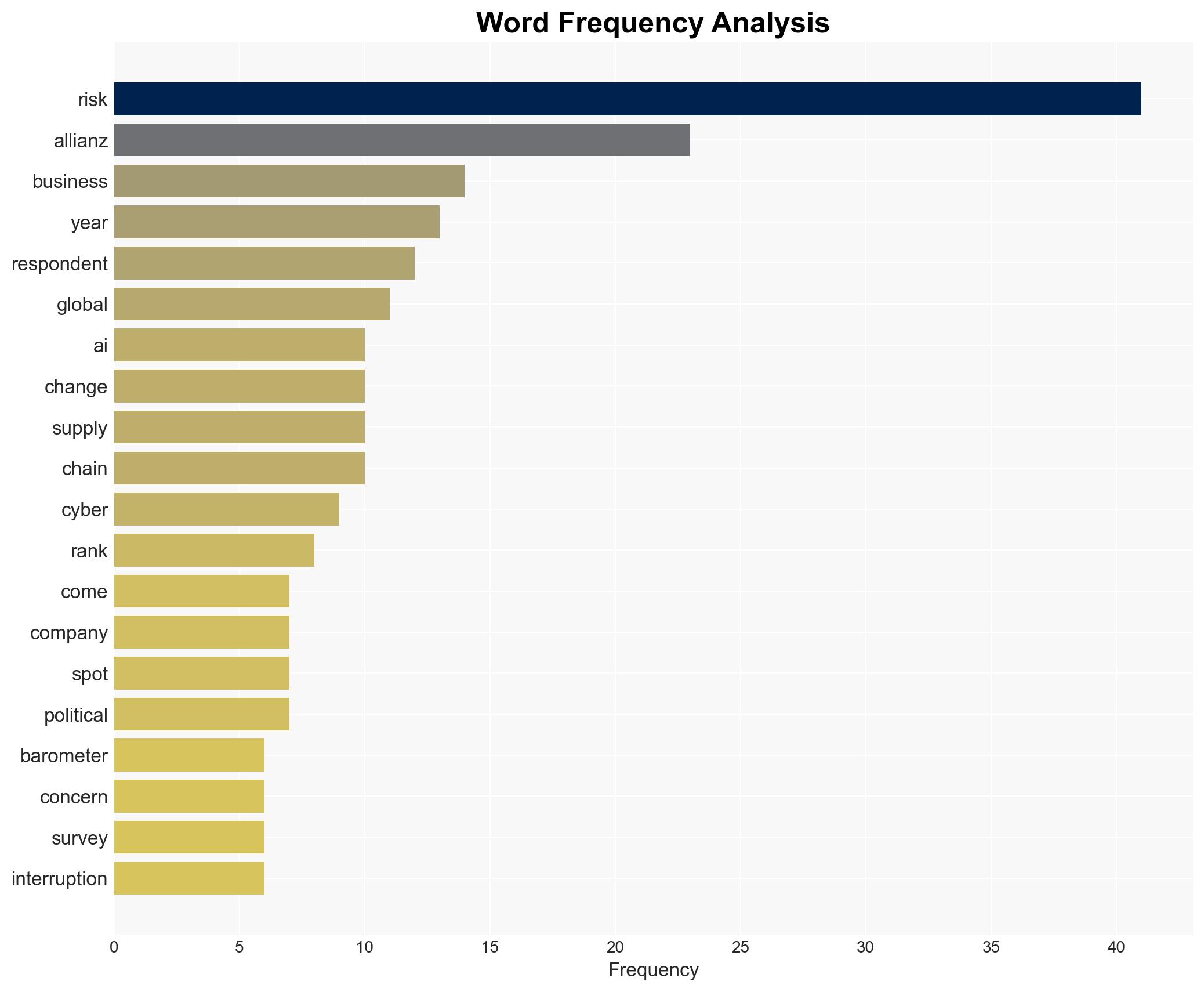
Intelligence Report: AI Is the Biggest Mover on Allianz Risk Barometer Cyber Takes Top Spot for Fifth Year
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The Allianz Risk Barometer for 2026 identifies cyber incidents as the top global risk, with artificial intelligence (AI) rapidly rising to the second position. This trend highlights increasing vulnerabilities in digital infrastructure and the strategic importance of AI. The assessment is made with moderate confidence, affecting businesses of all sizes across multiple sectors globally.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cyber incidents and AI are perceived as top risks due to recent high-profile cyber attacks and rapid AI integration, which have exposed vulnerabilities and operational challenges. Supporting evidence includes the consistent ranking of cyber risks and the sharp rise of AI in the risk barometer. Key uncertainties involve the evolving nature of these technologies and their threat vectors.
- Hypothesis B: The ranking reflects a temporary overestimation of risks due to media amplification and recent incidents, rather than a sustained increase in actual risk levels. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of long-term data showing increased frequency or severity of incidents directly attributable to AI.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of expert assessments and the consistent high ranking of cyber risks over multiple years. Indicators that could shift this judgment include significant advancements in cybersecurity measures or a decrease in AI-related incidents.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cyber and AI risks will continue to grow as digital integration deepens; businesses will remain reliant on a limited number of third-party suppliers; AI will increasingly influence regulatory and operational landscapes.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the frequency and impact of AI-related incidents; comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of current cybersecurity measures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on survey data, which may reflect perception rather than reality; risk of media-driven amplification affecting stakeholder perceptions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The prioritization of cyber and AI risks suggests a need for enhanced resilience strategies. This development may drive regulatory changes and increased investment in cybersecurity and AI governance.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased focus on international cooperation for cyber norms and AI regulation; potential for geopolitical tensions over technology control.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as adversaries exploit cyber vulnerabilities and AI capabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater emphasis on securing digital infrastructure; potential for increased cyber espionage and misinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Economic impacts from business disruptions; societal concerns over AI ethics and job displacement.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cyber threats and AI developments; engage with industry stakeholders to share best practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for cyber resilience; invest in AI governance frameworks and workforce training.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Strengthened cyber defenses and AI regulations reduce risks. Worst: Major cyber attack or AI failure causes significant disruption. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security and governance with ongoing challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Rishi Baviskar, Global Head of Cyber Risk Consulting at Allianz Commercial
- Allianz Risk Barometer respondents (corporate risk survey participants)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, risk management, digital infrastructure, business continuity, regulatory compliance, geopolitical risks
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us