Cyber Threats to Automotive Sector: Risks of Infrastructure Attacks and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities by 2026
Published on: 2026-02-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyberattacks on automobile manufacturers taxi fleets and logistics providers The risks to automotive infrastructure in 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Cyberattacks targeting the automotive industry are expected to increase in 2026, with financially motivated actors focusing on infrastructure vulnerabilities. The potential impacts include production shutdowns, data breaches, and operational disruptions. The most likely hypothesis is that these attacks will continue to exploit supply chain weaknesses, affecting manufacturers, fleet operators, and logistics providers. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
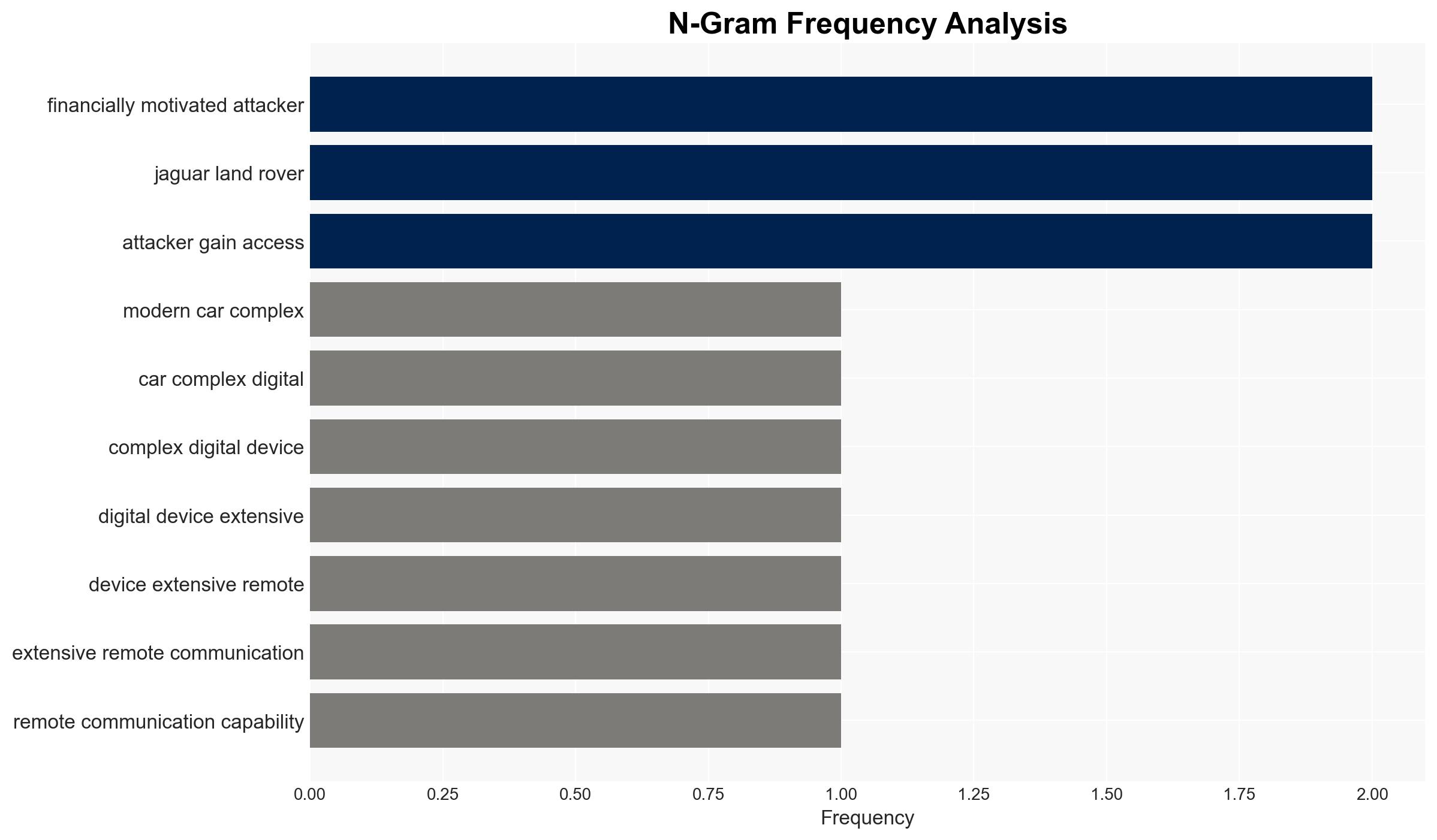
- Hypothesis A: Financially motivated cyberattacks on the automotive industry will primarily target supply chain vulnerabilities, leading to significant operational disruptions and financial losses. This is supported by past incidents, such as the Jaguar Land Rover attack, and the trend of supply chain attacks.
- Hypothesis B: Cyberattacks will focus more on direct vehicle manipulation and user data theft, causing immediate operational impacts and privacy concerns. While possible, there is less evidence of this being the primary focus compared to supply chain attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the historical precedence of supply chain attacks and the broader impact on operations and financial stability. Indicators such as increased targeting of third-party providers could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Attackers will continue to be financially motivated; supply chain vulnerabilities will remain exploitable; automotive digital infrastructure will not significantly improve in resilience by 2026.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the cybersecurity measures currently in place across the industry; intelligence on emerging attacker tactics and tools.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on cybersecurity firm reports; risk of underestimating state-sponsored or politically motivated cyber threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of cyber threats in the automotive sector could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures. The interconnected nature of automotive systems means that disruptions can have cascading effects across multiple sectors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated in attacks.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber-enabled sabotage or terrorism targeting critical transportation infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber capabilities and tactics used by attackers, potentially leading to more sophisticated and widespread attacks.
- Economic / Social: Economic losses from production disruptions and increased costs for cybersecurity investments; potential public backlash over privacy breaches.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct comprehensive security audits of automotive supply chains; enhance monitoring of third-party provider networks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop industry-wide cybersecurity standards; foster public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Industry-wide adoption of robust cybersecurity measures mitigates threat impact.
- Worst: Major cyberattack causes prolonged industry-wide disruptions and economic losses.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with moderate disruptions, prompting gradual improvements in cybersecurity.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jaguar Land Rover
- Stellantis
- Kaspersky
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, automotive industry, supply chain, ransomware, data breach, operational disruption, financial impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us