Cybersecurity Experts Charged for Involvement in Ransomware Attacks and Extortion Scheme
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cybersecurity pros admit to moonlighting as ransomware scum
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
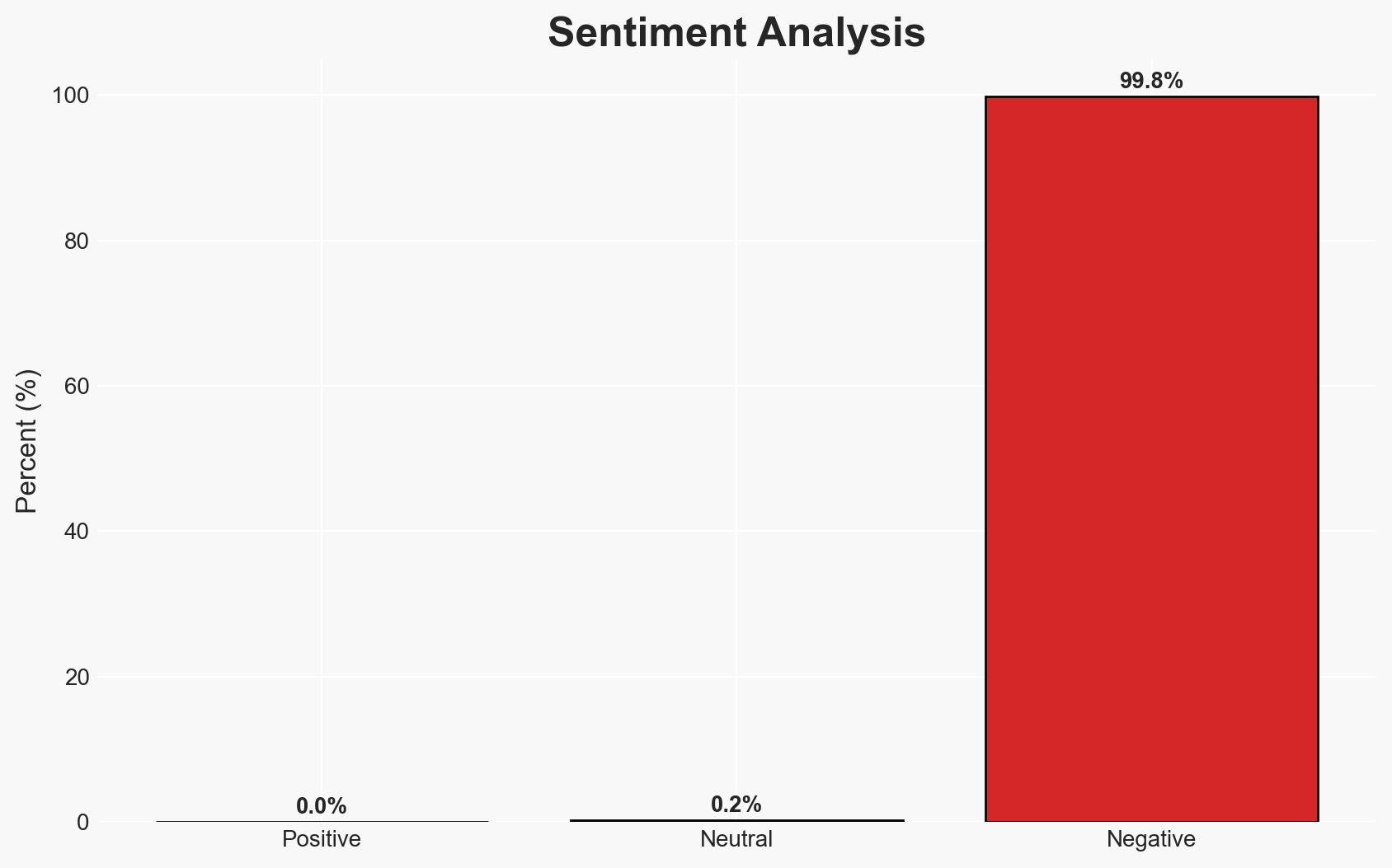
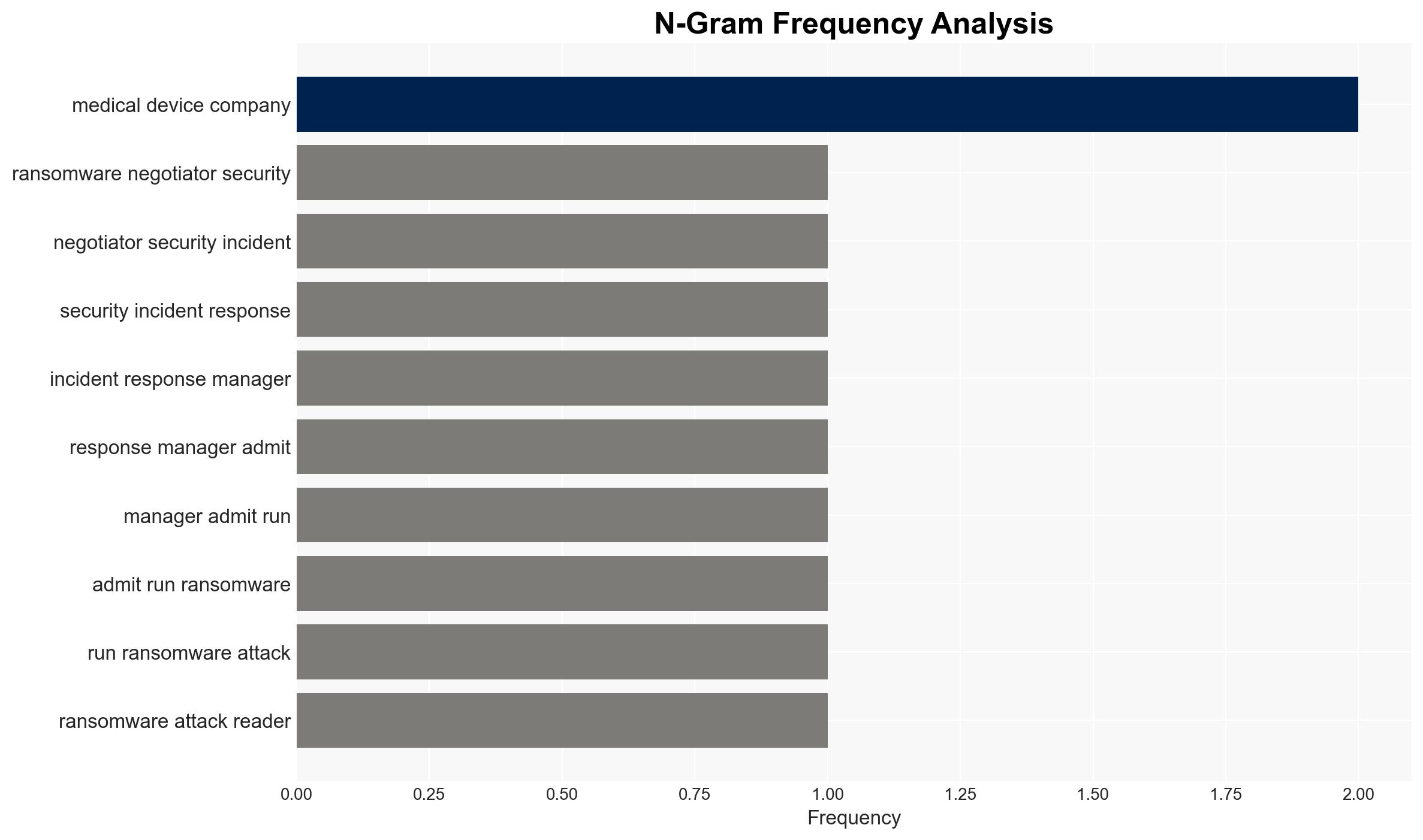
Cybersecurity professionals have been implicated in conducting ransomware attacks, leveraging their expertise to exploit vulnerabilities rather than protect against them. This development underscores a potential insider threat within the cybersecurity industry. The most likely hypothesis is that these individuals acted opportunistically for financial gain, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to limited information on broader motivations or affiliations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The individuals acted independently for personal financial gain. This is supported by their direct involvement in the attacks and the financial transactions. However, the extent of their connections to larger criminal networks remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The individuals were part of a larger organized crime network or were coerced into participating. This is contradicted by the lack of evidence indicating coercion or direct ties to broader networks, but the use of ALPHV BlackCat ransomware suggests some level of organized crime interaction.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct financial motive and lack of evidence for broader network involvement. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of coercion or organized crime ties.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The individuals had full autonomy in their actions; the financial motive was primary; ALPHV BlackCat’s involvement was transactional rather than organizational.
- Information Gaps: Details on the unnamed co-conspirator, full extent of ALPHV BlackCat’s involvement, and potential other victims or undisclosed attacks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting the defendants’ motivations solely as financial; risk of deception in the defendants’ statements to authorities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident may lead to increased scrutiny of cybersecurity professionals and highlight the insider threat risk within the sector. It could also influence policy and regulatory frameworks governing cybersecurity practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory measures and international cooperation against cybercrime.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness of insider threats within critical infrastructure sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible shifts in cybersecurity hiring practices and trust dynamics within the industry.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for companies to safeguard against insider threats and potential reputational damage to the cybersecurity industry.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cybersecurity personnel, review access controls, and increase awareness training on insider threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with law enforcement for rapid response to insider threats, and invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened cybersecurity protocols and reduced insider threat incidents.
- Worst: Increased insider attacks leading to significant economic and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvements in insider threat detection and mitigation, with sporadic incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
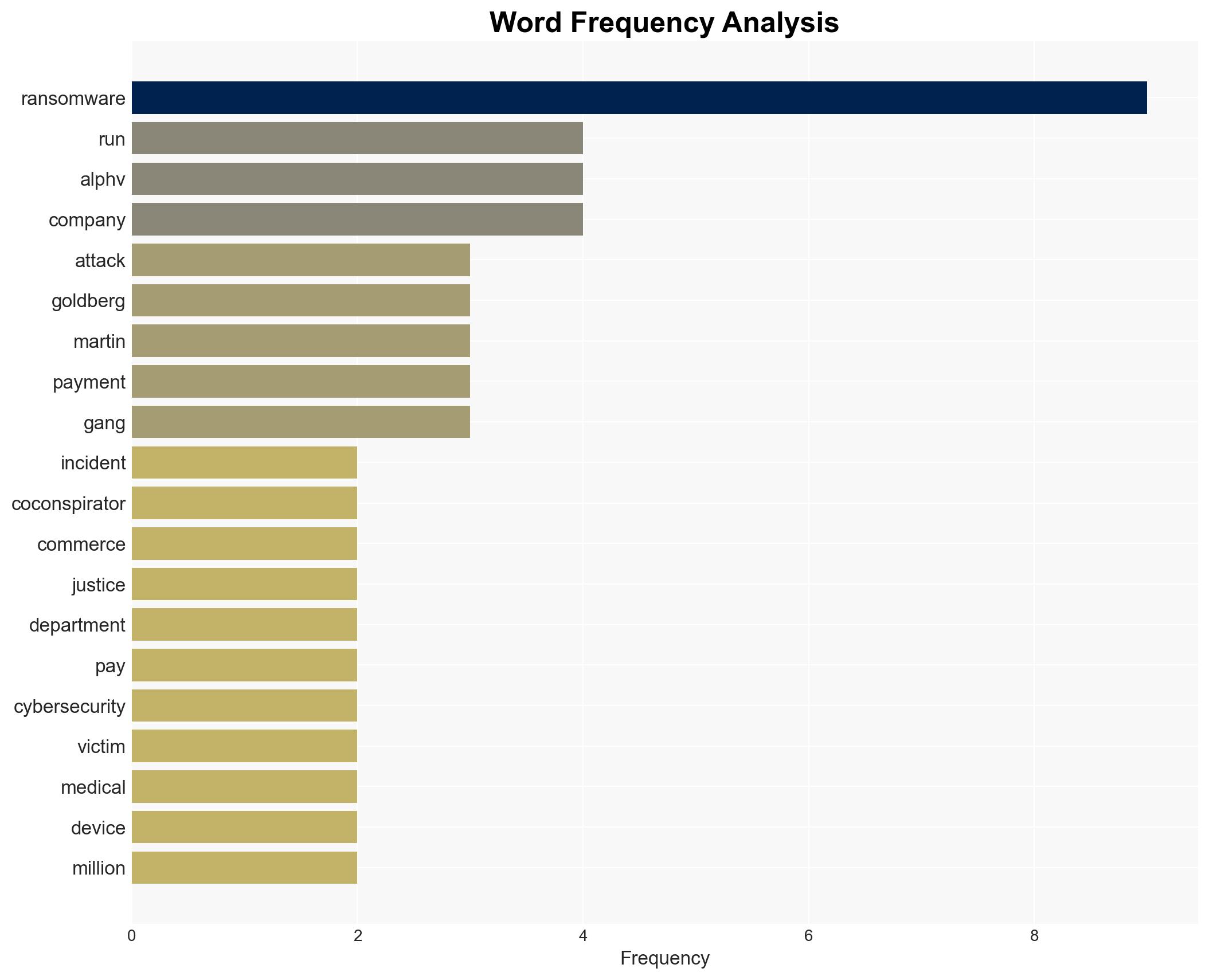
- Ryan Clifford Goldberg
- Kevin Tyler Martin
- Unnamed third co-conspirator
- ALPHV BlackCat ransomware group
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, insider threat, ransomware, organized crime, financial crime, cyber policy, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us