Cybersecurity signals Connecting controls and incident outcomes – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-09-01
Intelligence Report: Cybersecurity signals Connecting controls and incident outcomes – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
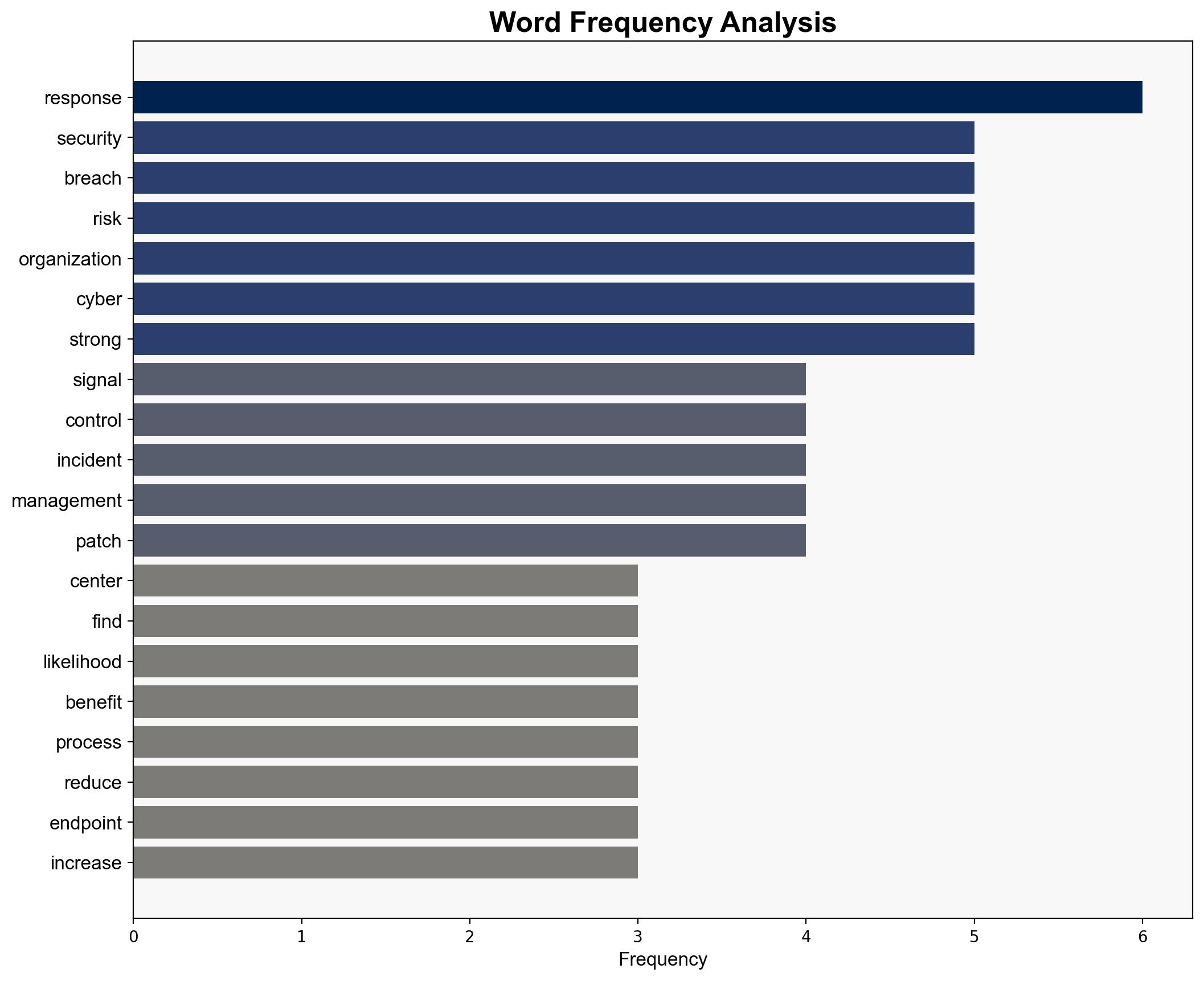
The analysis suggests that comprehensive cybersecurity controls, including incident response planning and endpoint detection, significantly reduce breach likelihood. The most supported hypothesis is that organizations with robust, well-implemented security protocols experience fewer breaches. Confidence level: High. Recommended action: Prioritize investment in comprehensive cybersecurity measures, including advanced endpoint detection and multi-factor authentication.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Organizations that implement comprehensive cybersecurity controls, including incident response planning and endpoint detection, experience a reduced likelihood of breaches. This hypothesis is supported by evidence linking specific security measures to lower breach incidents.
Hypothesis 2: The reduction in breach likelihood is primarily due to external factors such as decreased targeting by threat actors or inherent industry characteristics, rather than the implementation of specific controls. This hypothesis considers the possibility that some organizations might naturally face fewer cyber threats.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions for Hypothesis 1 include the effectiveness of the controls and the accurate reporting of breach incidents. A red flag is the potential bias in self-reported data, which may overstate the effectiveness of implemented controls. For Hypothesis 2, an assumption is that external factors significantly influence breach likelihood, which may not be consistently measurable. A blind spot is the lack of data on threat actor motivations and targeting strategies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
If Hypothesis 1 holds, organizations that fail to implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures risk increased breach incidents, leading to financial loss and reputational damage. If Hypothesis 2 is accurate, reliance on controls without understanding external threat dynamics might lead to a false sense of security. Strategic risks include potential escalation of cyber threats targeting unprepared sectors, and the economic impact of breaches on vulnerable organizations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Invest in comprehensive cybersecurity measures, emphasizing endpoint detection and multi-factor authentication.
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises and red team tests to enhance incident response capabilities.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best: Organizations achieve high resilience with minimal breach incidents.
- Worst: Failure to adapt controls leads to significant breaches and economic losses.
- Most likely: Mixed results with some organizations achieving resilience while others remain vulnerable.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Tom Reagan, Marsh McLennan Cyber Risk Intelligence Center (CRIC).
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus