Cybersecurity Takes Center Stage at Davos as Global Leaders Address Rising Threats and Strategic Challenges
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: At Davos Cybersecurity Is a Leadership Imperative
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
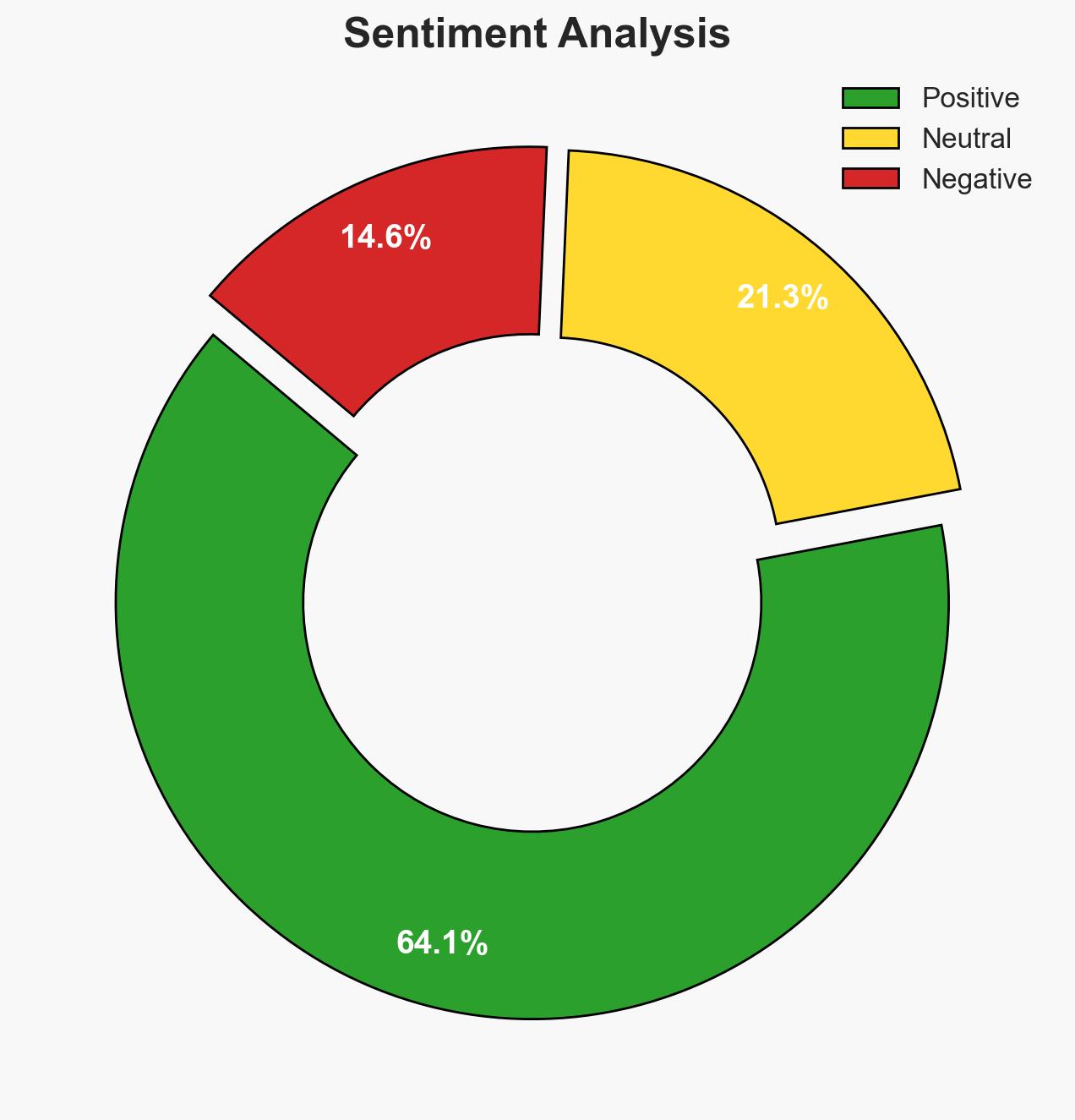
Cybersecurity has become a critical leadership issue, transitioning from a technical concern to a strategic imperative. This shift is driven by geopolitical tensions, rapid AI adoption, and increased cybercrime. The need for leadership engagement and cross-sector collaboration is paramount. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cybersecurity is now a strategic leadership issue due to the convergence of geopolitical tensions, AI adoption, and cybercrime. This hypothesis is supported by the increased focus on cybersecurity at leadership forums like Davos and the recognition of cyber risks as systemic challenges. However, the extent to which leaders are prepared to address these challenges remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Cybersecurity remains primarily a technical issue, with leadership engagement being more rhetorical than practical. This hypothesis is contradicted by the reported shift in discussions at Davos and the emphasis on leadership accountability and cross-sector collaboration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit recognition of cybersecurity as a strategic issue at Davos and the evolving role of leadership in addressing cyber risks. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of sustained leadership disengagement or failure to integrate cybersecurity into broader strategic frameworks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cyber threats will continue to grow in complexity and scale; leadership engagement is critical for effective cybersecurity; cross-sector collaboration is achievable and beneficial.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on how leadership plans to integrate cybersecurity into strategic decision-making processes; metrics for measuring leadership effectiveness in cybersecurity.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from cybersecurity firms promoting their services; risk of overestimating leadership engagement based on forum discussions rather than concrete actions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The elevation of cybersecurity to a leadership issue could lead to more robust governance frameworks and improved resilience. However, failure to act could exacerbate vulnerabilities and lead to significant economic and societal harm.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased focus on cybersecurity could lead to international cooperation or, conversely, exacerbate tensions if perceived as a competitive advantage.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced leadership engagement may improve defenses against state-aligned cyber activities and cyber-enabled terrorism.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater leadership focus could drive innovation in cybersecurity practices and technologies, but also increase the complexity of threat landscapes.
- Economic / Social: Improved cybersecurity could enhance economic resilience and public trust, while failure to adapt may lead to economic disruptions and societal unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor leadership statements and commitments from Davos; engage in dialogues to foster cross-sector collaboration.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop frameworks for integrating cybersecurity into strategic planning; enhance public-private partnerships for information sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Leadership effectively integrates cybersecurity, enhancing resilience. Worst: Leadership fails to act, leading to increased vulnerabilities. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements with ongoing challenges in coordination and implementation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
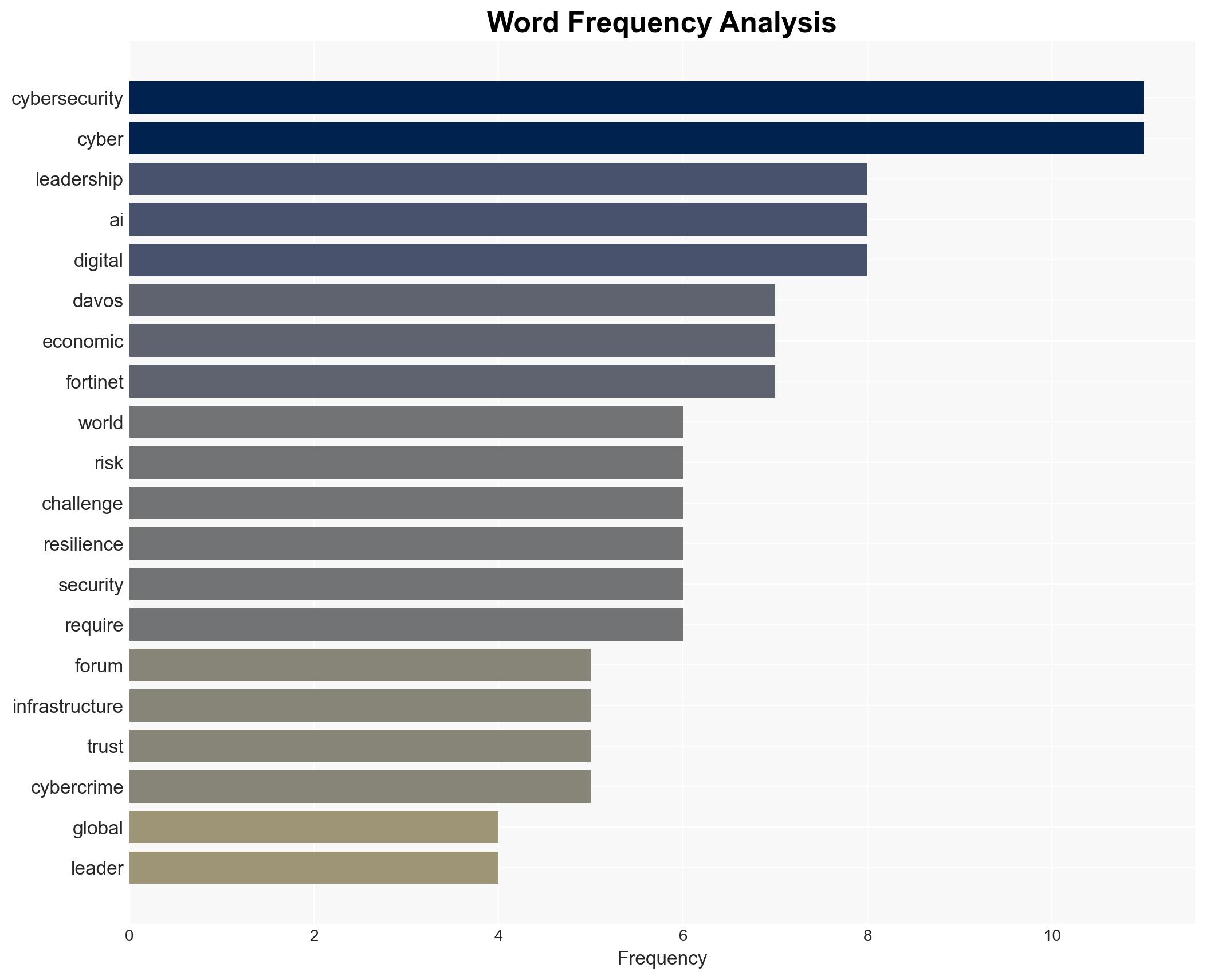
cybersecurity, leadership, geopolitical tensions, AI adoption, cybercrime, strategic risk
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us