Danish PM warns US takeover of Greenland could jeopardize NATO alliance stability
Published on: 2026-01-06
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
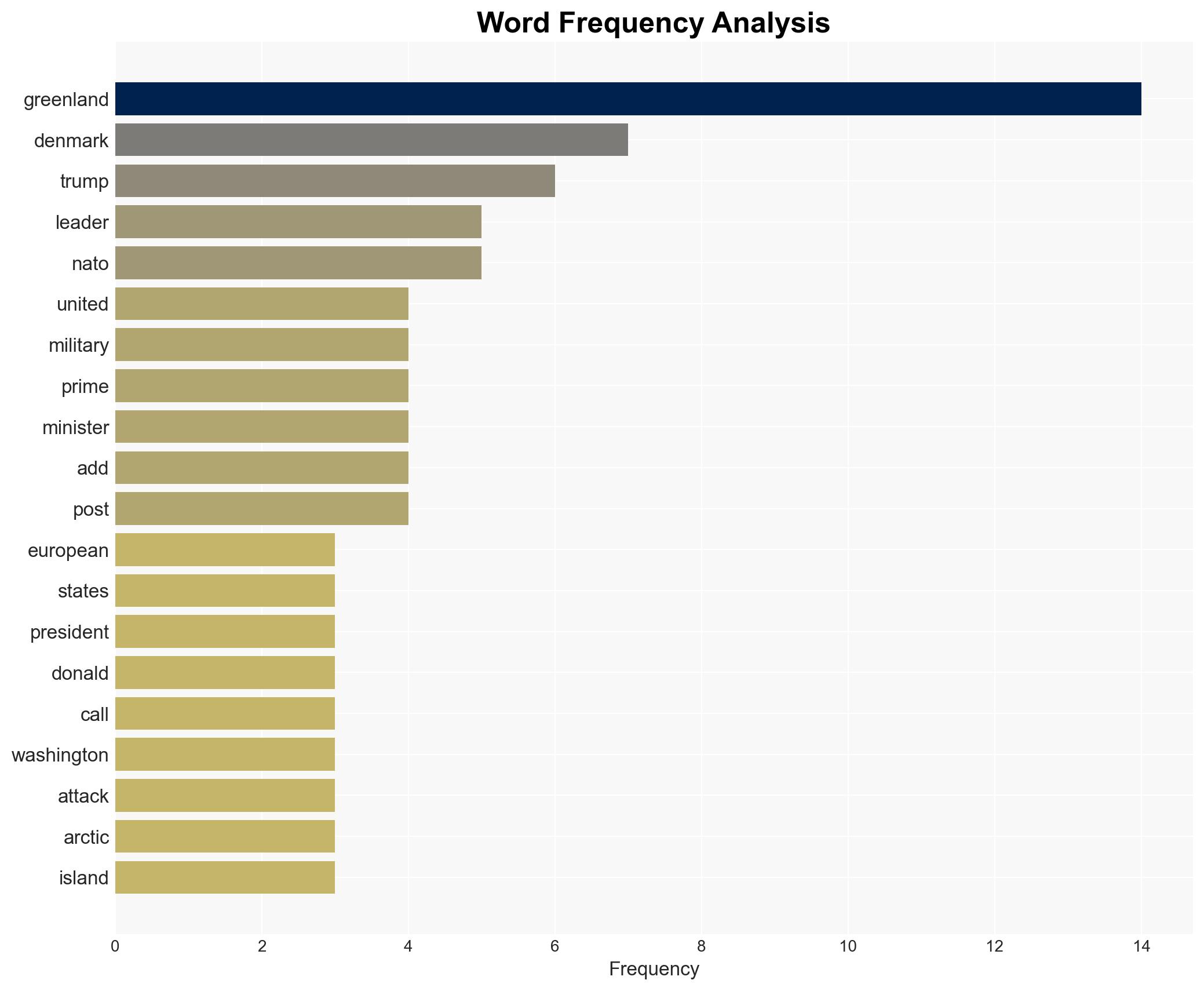
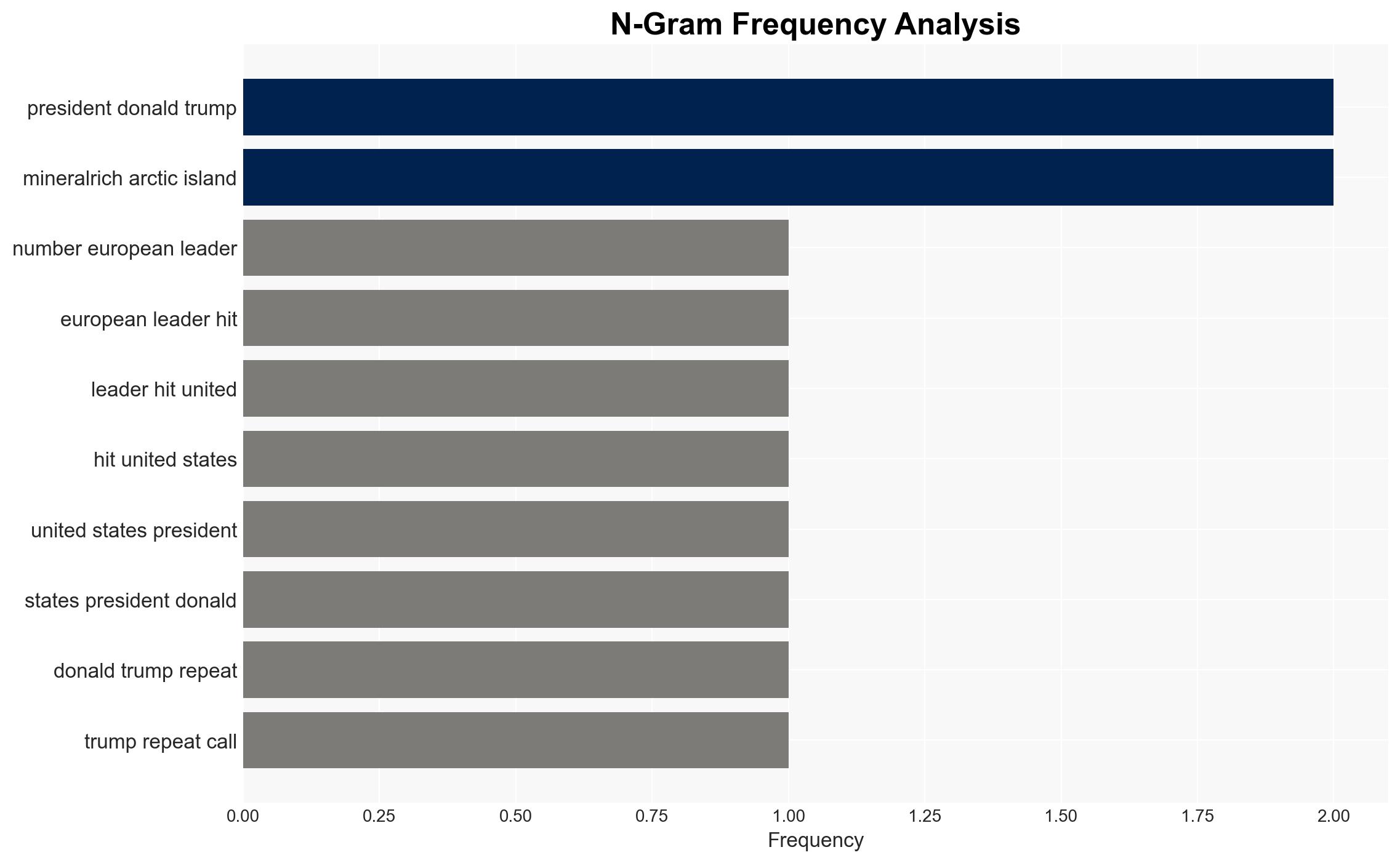
Intelligence Report: Danish PM says US attack on Greenland would be the end of NATO
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
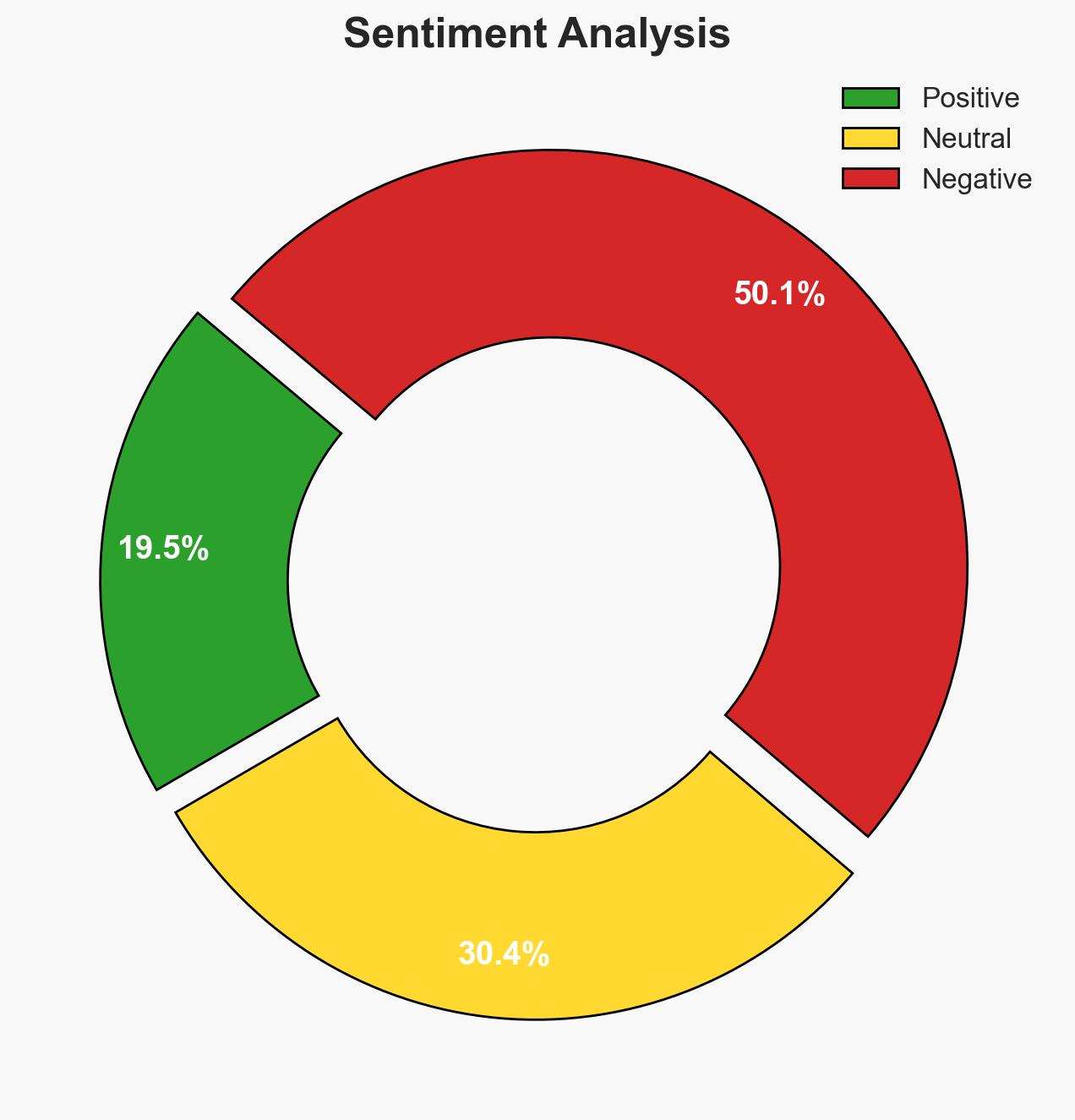
The Danish Prime Minister’s statement highlights potential severe geopolitical consequences if the US attempts to assert control over Greenland, potentially leading to the dissolution of NATO. The most likely hypothesis is that the US will continue to exert pressure on Greenland diplomatically rather than militarily, given the international backlash and strategic risks. This situation affects NATO member states, particularly Denmark and Greenland. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US will pursue diplomatic and economic means to gain influence over Greenland, avoiding military confrontation. Supporting evidence includes the international backlash from European leaders and the strategic risks of military action. However, the appointment of a special envoy suggests ongoing interest.
- Hypothesis B: The US will escalate to military action to secure Greenland. This is supported by President Trump’s rhetoric and recent military actions in Venezuela. Contradicting evidence includes the potential for severe geopolitical fallout and NATO dissolution.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the significant geopolitical risks and international opposition associated with military action. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in US diplomatic engagement or increased military presence in the Arctic.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US values NATO’s stability; Denmark and Greenland will resist US pressure; European leaders will maintain a unified stance against US actions; US military actions in Venezuela are not directly linked to Greenland strategy.
- Information Gaps: Detailed US strategic plans for Greenland; internal Danish and Greenlandic political dynamics; potential Russian and Chinese responses.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive bias in underestimating US willingness to use force; source bias from European leaders’ statements; possible US strategic deception regarding intentions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions within NATO and strain US-European relations. The situation may evolve into a broader geopolitical conflict involving Arctic sovereignty and resource competition.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential fracturing of NATO; increased European alignment against US unilateral actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened military readiness in the Arctic; potential for new security alliances.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased information warfare and propaganda efforts by involved states.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of Arctic resource development; potential economic sanctions or trade disruptions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor US diplomatic engagements and military movements; engage in diplomatic dialogue with NATO allies; prepare contingency plans for NATO response.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen NATO cohesion; explore alternative security arrangements; enhance Arctic surveillance capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: US pursues diplomatic resolution; Worst: US military action leads to NATO dissolution; Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic tension with strategic posturing.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Donald Trump, Mette Frederiksen, Jens-Frederik Nielsen, Emmanuel Macron, Friedrich Merz, Keir Starmer, Jeff Landry, Katie Miller
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitics, NATO, Arctic strategy, US foreign policy, European security, international law, resource competition
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us