Data breach at Red Hat’s GitLab compromises information of 21,000 Nissan customers
Published on: 2025-12-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Red Hat GitLab breach exposes data of 21000 Nissan customers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The breach of Red Hat’s GitLab instance, resulting in the exposure of data from 21,000 Nissan customers, highlights significant vulnerabilities in self-managed software environments. The incident, linked to the Crimson Collective, suggests potential risks to other major organizations referenced in the stolen data. Overall, the most likely hypothesis is that the breach was primarily opportunistic, targeting Red Hat’s repositories for valuable data. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete information on the threat actors’ motivations and capabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was an opportunistic attack by the Crimson Collective, primarily aimed at extracting valuable data from Red Hat’s repositories. Supporting evidence includes the broad scope of stolen data and the lack of specific targeting of Nissan. However, the absence of confirmation from Red Hat about the Crimson Collective’s involvement introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was a targeted operation against Nissan, using Red Hat’s GitLab as an entry point. This hypothesis is less supported due to the broader scope of data theft affecting multiple organizations and the lack of specific targeting indicators towards Nissan alone.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the wide array of data stolen and the public claims made by the Crimson Collective. Indicators that could shift this judgment include further evidence of specific targeting or confirmation of the threat actors’ identity and intent.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Crimson Collective is responsible for the breach; the breach was not specifically targeting Nissan; Red Hat’s other services remain secure; the exposed data does not include financial information.
- Information Gaps: The exact method of breach entry, full scope of data accessed, and the motivations of the Crimson Collective.
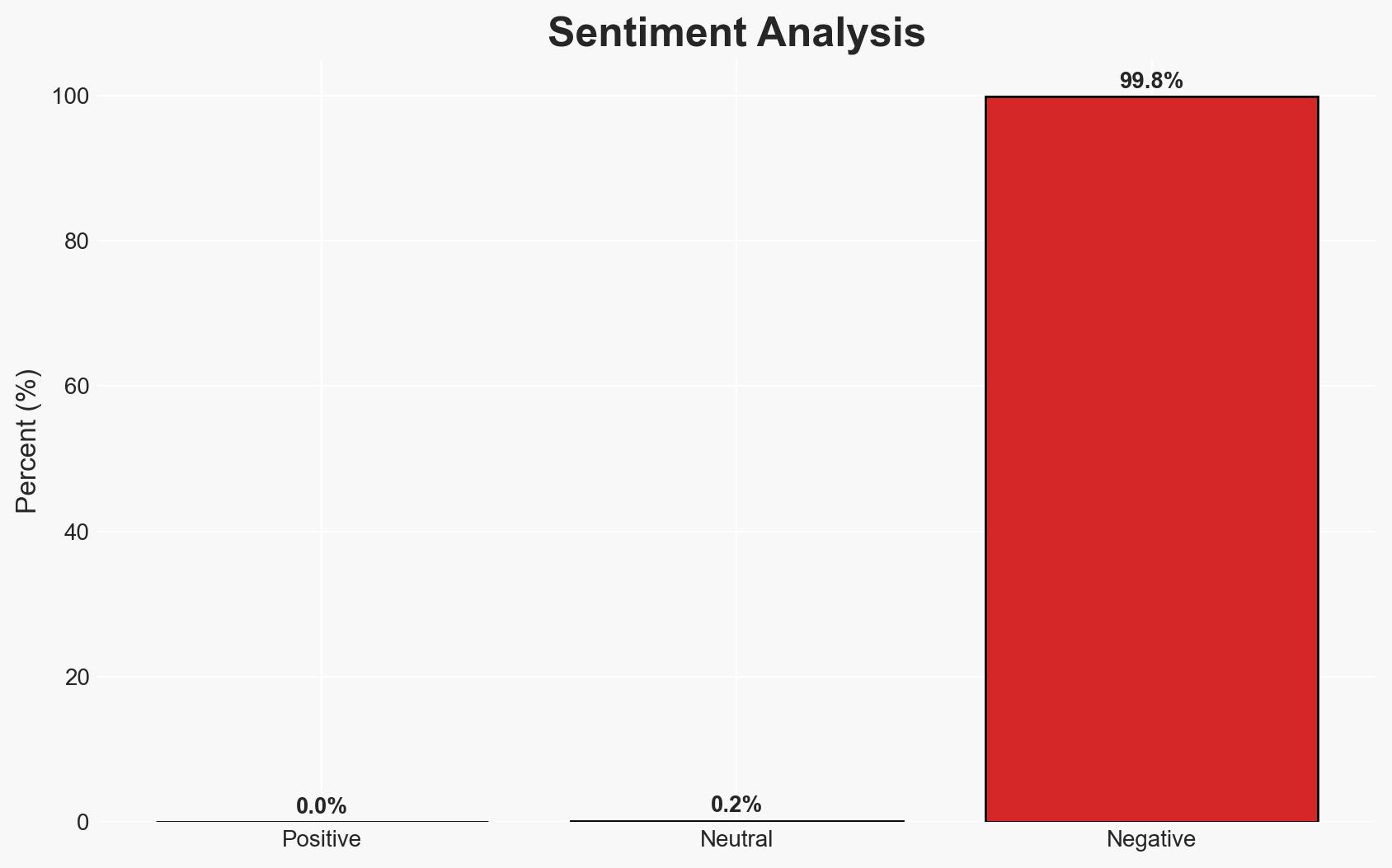
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in threat actor claims on Telegram; Red Hat’s public statements may downplay the breach’s impact to protect reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach could lead to increased scrutiny of self-managed software environments and prompt organizations to reassess their cybersecurity postures. The incident may also embolden similar threat actors to exploit other vulnerable systems.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if state actors are suspected or if affected entities are critical infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of follow-on attacks using the stolen data, particularly against critical sectors like finance and telecommunications.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness of vulnerabilities in GitLab and similar platforms; potential for misinformation if threat actors manipulate stolen data.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected companies; erosion of customer trust in data security practices.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough forensic investigation of the breach; enhance monitoring of affected systems; notify all potentially impacted entities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen cybersecurity protocols for self-managed environments; develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Breach contained with minimal impact. Worst: Data exploited for further attacks. Most-Likely: Increased cybersecurity measures and awareness prevent similar breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Red Hat Consulting
- Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.
- Crimson Collective
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
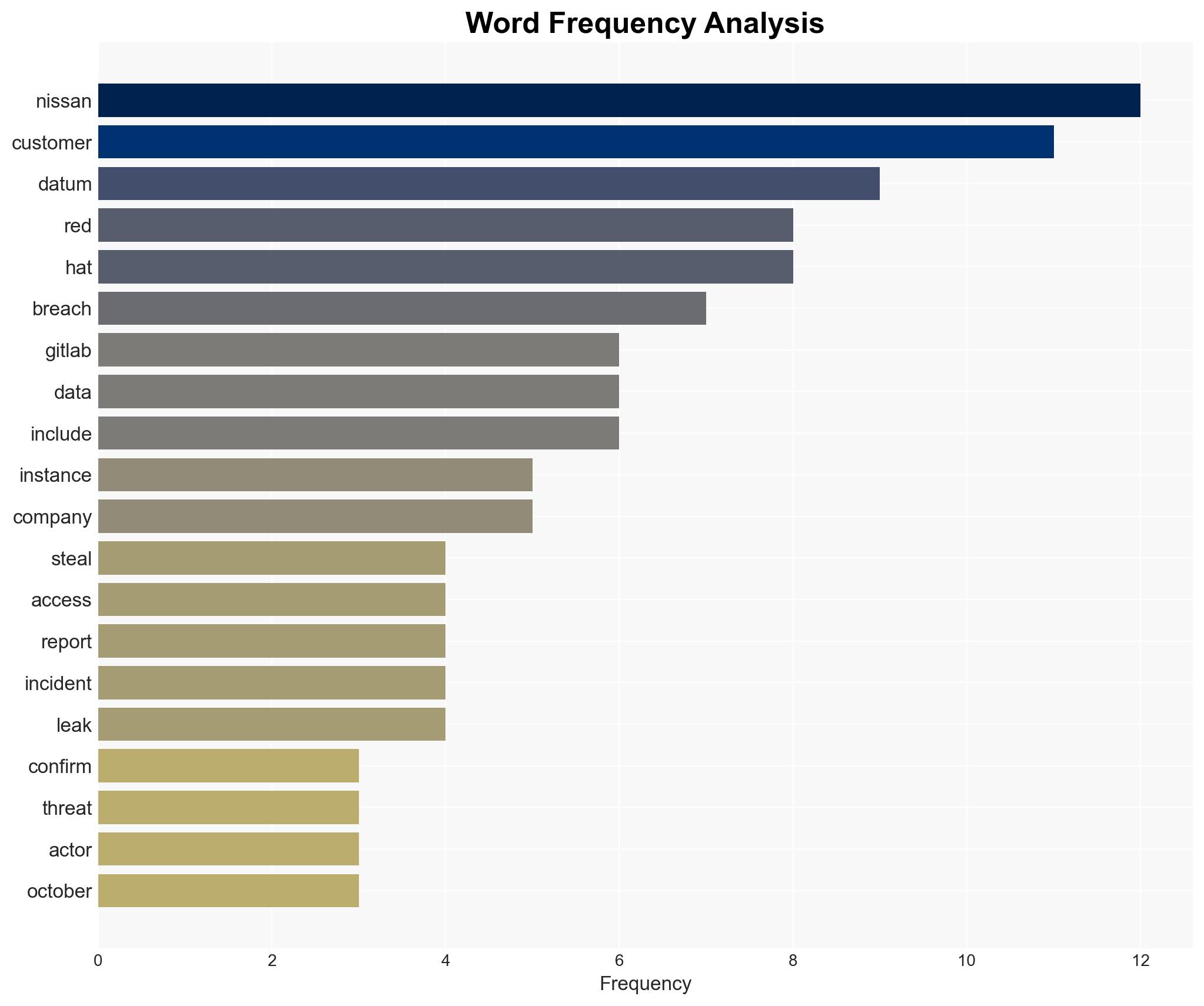
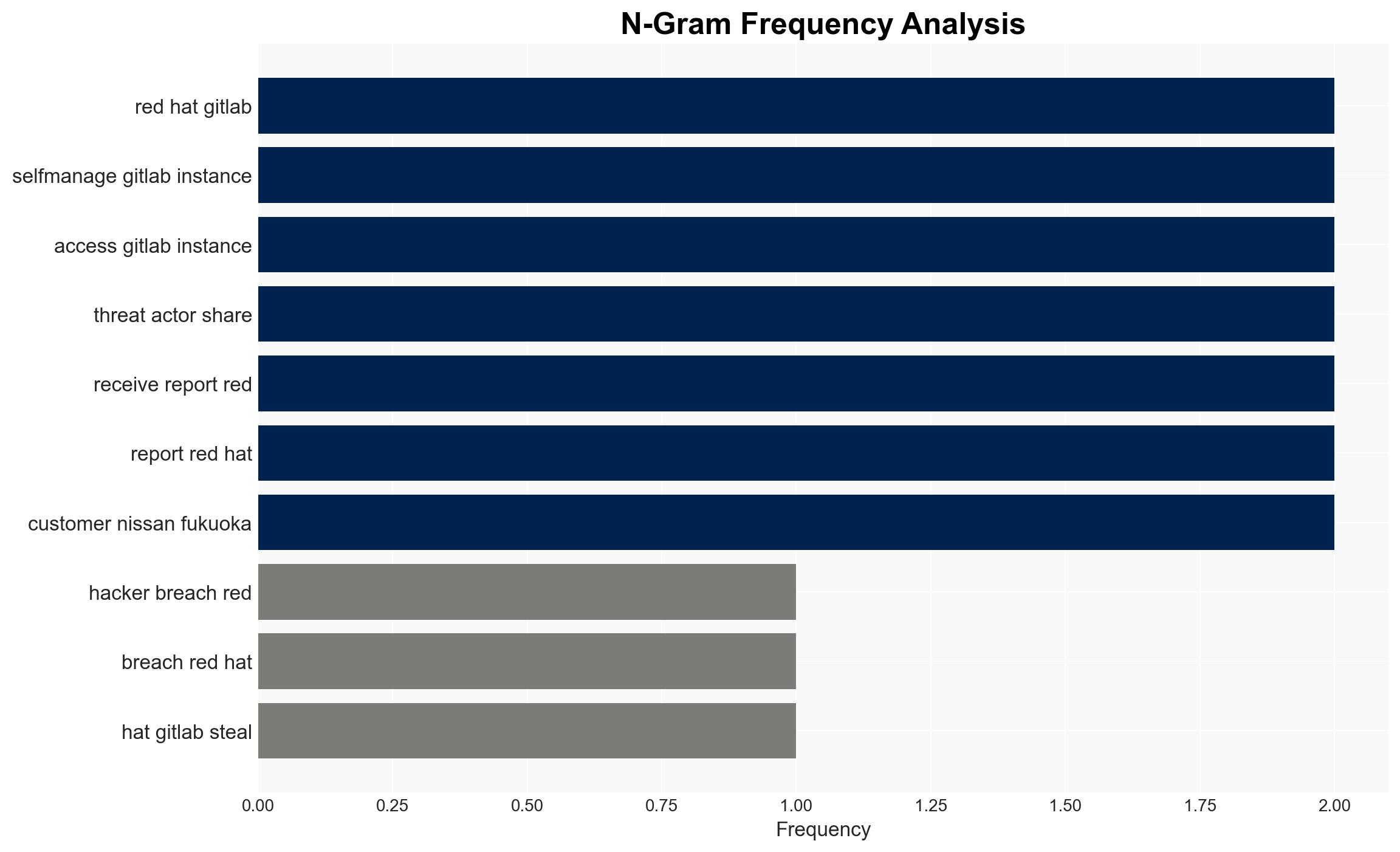
cybersecurity, data breach, Red Hat, Nissan, GitLab, threat actors, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us