Data breach compromises personal information of over 10.5 million Americans in significant healthcare incident
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Massive data breach exposes 105 million Americans info
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
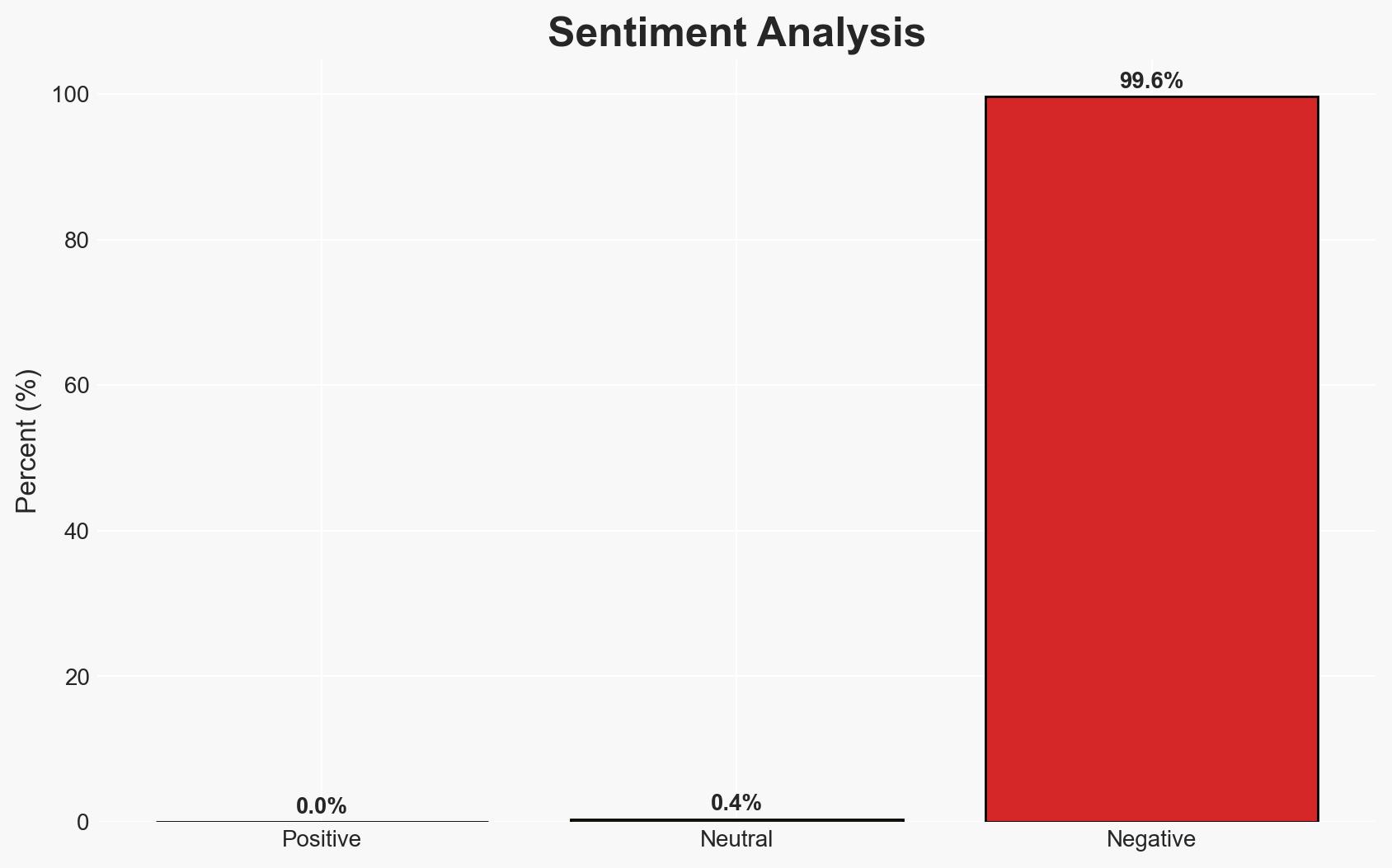
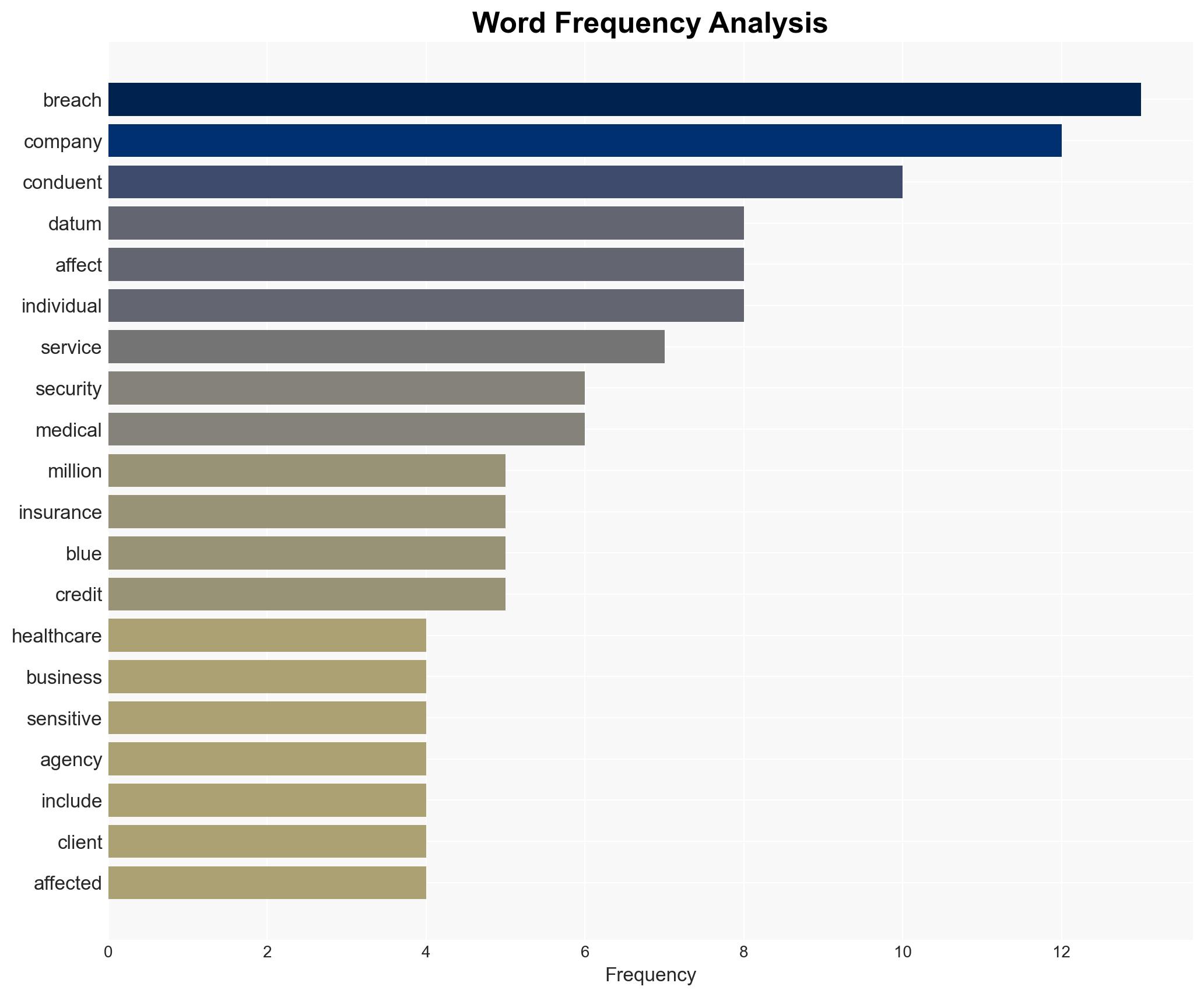
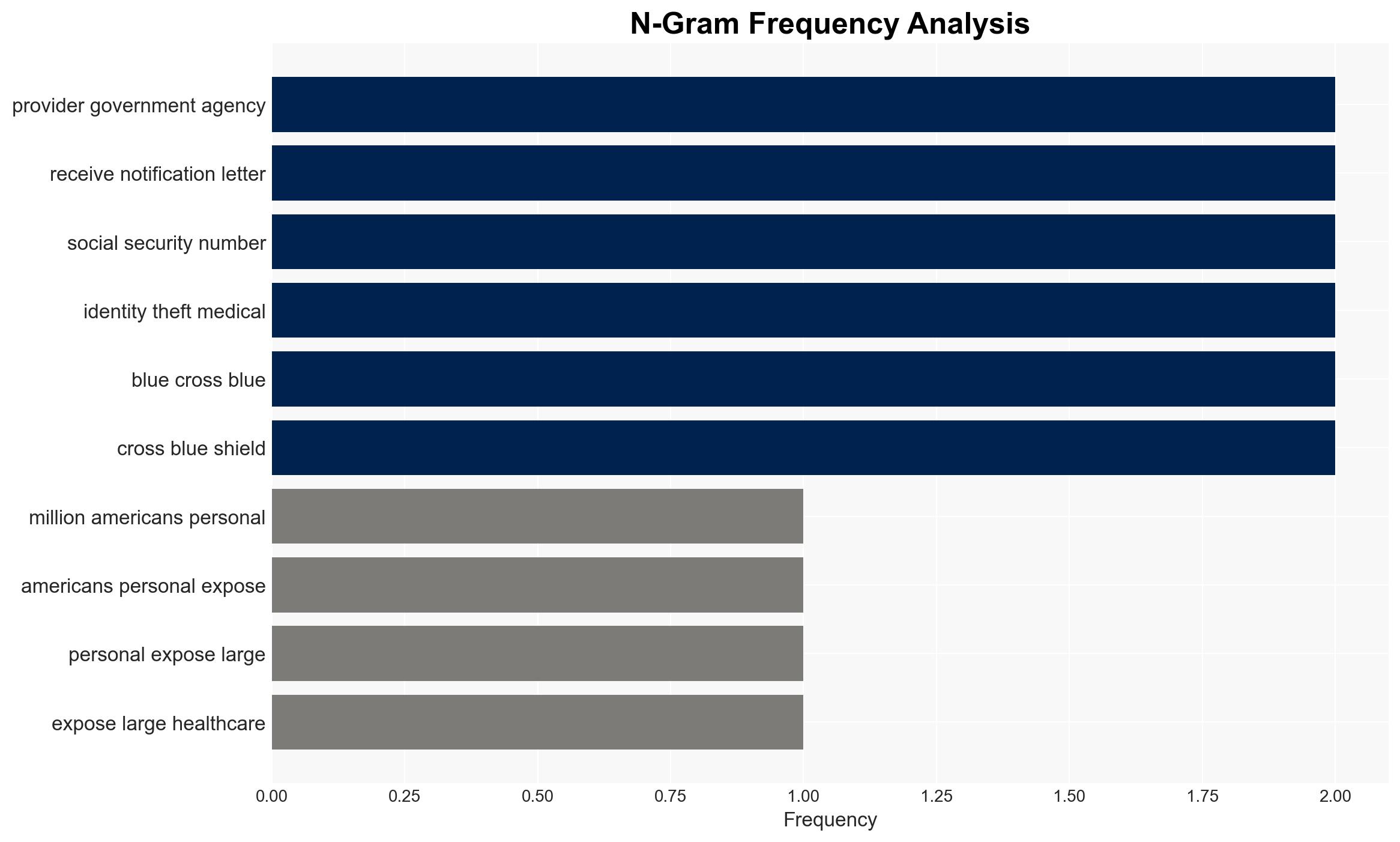
A significant data breach at Conduent has exposed sensitive personal information of over 10.5 million Americans, with potential for identity theft and fraud. The breach remained undetected for nearly three months, affecting multiple healthcare providers and government agencies. The most supported hypothesis is that the breach resulted from inadequate cybersecurity measures. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily due to inadequate cybersecurity measures at Conduent. Supporting evidence includes the long duration of undetected access and the subsequent lawsuits alleging insufficient safeguards. Key uncertainties include the specifics of the security failures and whether internal negligence played a role.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was a targeted attack by a sophisticated threat actor exploiting unknown vulnerabilities. While the prolonged access period could suggest a targeted operation, there is limited direct evidence of advanced persistent threat (APT) involvement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate response actions and legal claims focusing on security inadequacies. Indicators such as discovery of specific vulnerabilities or attribution to known threat actors could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Conduent’s cybersecurity measures were below industry standards; the breach was not detected due to insufficient monitoring; the attackers’ primary motive was data theft for financial gain.
- Information Gaps: Detailed forensic analysis of the breach; identification of the threat actors; specifics of the exploited vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the breach solely to internal failures without considering external threat actor capabilities; risk of underestimating the sophistication of the attack.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach could lead to increased scrutiny on cybersecurity practices within the healthcare sector and influence regulatory changes. It may also embolden cybercriminals to target similar vulnerabilities in other organizations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for legislative action to enhance data protection laws and cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of identity theft and fraud, potentially funding further criminal activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlighting the need for improved cybersecurity infrastructure and threat detection capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for affected individuals and reputational damage to involved organizations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive cybersecurity audit of Conduent and similar entities; enhance monitoring and detection capabilities; provide support to affected individuals.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop public-private partnerships to improve cybersecurity resilience; invest in advanced threat detection technologies; implement stricter data protection regulations.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid containment and mitigation with minimal long-term impact.
- Worst: Continued exploitation of stolen data leading to widespread identity theft and financial loss.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity practices with ongoing legal and regulatory repercussions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Conduent Business Services
- Blue Cross Blue Shield of Montana
- Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas
- Humana
- Premera Blue Cross
- Wisconsin Department of Children and Families
- Oklahoma Human Services
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, healthcare, identity theft, regulatory compliance, cyber resilience, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us